

Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is first-line therapy for more serious infections. The occurrence of more serious infections should prompt further workup to identify an associated underlying cause. Treatment modalities include corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, and more recently rituximab. Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune inflammatory myopathy usually treated with systemic corticosteroids and additional immunosuppressive therapeutic agents, such as azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil, as corticosteroid-sparing agents. Clinical improvement was seen in all, and the maintenance dose of the corticosteroid could be reduced in 6. Immunosuppressive agents and newer biologic therapies used more commonly in disorders associated with vasculitis and vasculitides are reviewed elsewhere. Treatment options for the different organ system manifestations of systemic sclerosis/scleroderma include immunosuppressive drugs and novel biologics, and were recently reviewed. However, improvements in the Rodnan skin score, a key outcome in clinical trials, was reported in patients who received additional doses. Henoch-Schnlein purpura is o a vasculitis occurring primarily in children, subsequent to a viral illness, that usually requires only symptomatic treatment. Corticosteroids may be used when symptoms are worsening, but there is debate over long-term benefit, and there can be worsening of gastrointestinal hemorrhage. The anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody group of disorders includes granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly, Wegener granulomatosis), microscopic polyangiitis, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly, Churg-Strauss syndrome), and renal-limited vasculitis. Graves ophthalmopathy is an autoimmune manifestation of hyperthyroidism that involves the orbital and periorbital tissues, secondarily resulting in proptosis and other ocular complications. Both treatment modalities were equally successful, but the adverse events were more frequent and severe in the corticosteroid-treated group. Additionally, Bcell depletion with rituximab is emerging as an alternative, especially in severe disease, because it efficiently decreases autoantibodies. Multispecialty management, including endocrinology and ophthalmology, is advisable due to other treatment modalities available, depending on severity, including radiation and surgical decompression. Autoimmune uveitis is a noninfectious inflammatory process of the vascular layer of the eye that without treatment can cause visual impairment and even blindness. Newer biologics are also being considered, depending on the type of autoimmune uveitis. Autoimmune hepatitis is typically treated with a corticosteroid and azathioprine or another immunosuppressive agent, such as rituximab, in refractory disease. Inflammatory bowel diseases are chronic inflammatory disorders involving the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract. Crohn disease may manifest from the oral cavity to the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis tends to be limited to the lower colon. For the most part, the efficacy of immunoglobulin therapy in patients with organ-specific autoimmune disease or various forms of autoimmune vasculitides is limited, and immunoglobulin therapy may be beneficial in only a subset of patients. Importantly, new biologic therapies have emerged recently as better alternatives or even as primary therapies for many of these autoimmune diseases. In susceptible individuals, chronic airway inflammation causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, chest tightness, coughing, and excessive mucus production. Immunoglobulin has been utilized as a corticosteroid-sparing agent in severe asthma due to its potent anti-inflammatory properties, but the results from clinical trials have been conflicting, and no recent trials have emerged. It will be essential, however, that subsequent studies employ randomized and controlled study designs. An autoimmune process is implicated in about one third of patients with chronic urticaria. Delayed-pressure urticaria is a variant of chronic urticaria that is also difficult to treat. In a retrospective review of data from 7 adult patients with chronic solar urticaria treated with 1. However, small numbers of patients have severe resistant disease despite receiving second-line therapies. Dosing in each patient varied from 300 mg/kg to 2 g/kg, and duration ranged from 6 to 39 months. Significant decreases in serum IgE and eosinophils were seen at the 3-month time point, and the decrease in serum IgE persisted after discontinuation. The severity of eczema was determined by an ordinal scale skin score ranging from 0 to 5.
Monitoring/Testing You may on a case-by-case basis obtain additional tests and/or consultation to adequately assess driver medical fitness for duty. To review the Valve Replacement Recommendation Table, see Appendix D of this handbook. Pulmonary Valve Stenosis Pulmonary valve stenosis is usually a well-tolerated cardiac lesion normally exhibiting a gradual progression. Pulmonary valve stenosis corrected by surgical valvotomy or balloon valvuloplasty. Pulmonary valve peak gradient greater than 50 mm Hg in the presence of a normal cardiac output. Main pulmonary artery diameter more than 5 cm noted by echocardiography or other imaging modality. Monitoring/Testing the driver should have annual cardiology evaluations by a cardiovascular specialist who is knowledgeable in adult congenital heart disease and who understands the functions and demands of commercial driving. To review the Congenital Heart Disease Recommendation Table, see Appendix D of this handbook. Respiratory (b)(5) the commercial driver spends more time driving than the average individual. Driving is a repetitive and monotonous activity that demands the driver be alert at all times. Symptoms of respiratory dysfunction or disease can be debilitating and can interfere with the ability to remain attentive to driving conditions and to perform heavy exertion. Even the slightest impairment in respiratory function under emergency conditions (when greater oxygen supply may be necessary for performance) can be detrimental to safe driving. As the medical examiner, your fundamental obligation during the respiratory assessment is to establish whether a driver has a respiratory disease or disorder that increases the risk for sudden death or incapacitation, thus endangering public safety. Key Points for Respiratory Examination During the physical examination, you should ask the same questions as you would for any individual who is being assessed for respiratory diseases or disorders. Additional questions about symptoms of respiratory disease should be asked to supplement information requested on the form. Findings that may require further testing such as pulmonary tests and/or X-ray of chest Advisory Criteria/Guidance Antihistamine Therapy Both prescription and over-the-counter antihistamines are used to treat respiratory tract congestion. First generation antihistamines have sedating side effects that may occur without the driver being aware. Second generation antihistamines have less incidence of sedating side effects and most do not interfere with driving. Page 120 of 260 Decision Recommend to certify if: As the medical examiner, you believe that the treatment does not endanger the health and safety of the driver and the public. Allergies and Asthma-related Diseases Allergic Rhinitis Allergic rhinitis, which involves inflammation of the nasal portion of the upper respiratory tract, should rarely render the driver medically unqualified for commercial driving. The symptoms should be treated with nonsedating antihistamines or with local steroid sprays that do not interfere with driving ability.
Diseases
Such a definition of kidney failure has obvious operational and administrative advantages. First, patients who have kidney failure may survive for variable periods of time without treatment by dialysis or transplantation. Second, some signs and symptoms of kidney failure appear at higher levels of kidney function that are compatible with long survival. Third, some have advocated ``early initiation of dialysis' or ``pre-emptive' kidney transplantation prior to the onset of kidney failure. Fourth, many patients living with dialysis or a kidney transplant find the phrase ``end-stage' threatening and misleading. Thus, it would be preferable to define kidney failure as a combination of signs and symptoms of uremia and a specific level of kidney function. One of the questions posed by the Work Group was: Is it possible to identify the level of kidney function corresponding to the stage of kidney failure One of the questions posed by the Work Group was: What is the prevalence of earlier stages of chronic kidney disease, based on the definitions and methods for measurement discussed above Prevalence of Kidney Damage Guidelines by the American Academy of Pediatricians recommend screening school-age children for proteinuria using the urine dipstick. Therefore, a large number of studies have been conducted to estimate the prevalence of proteinuria in children. One of the questions posed by the Work Group was: What is the prevalence of dipstick-positive proteinuria in children Another question asked by the Work Group was: What is the normal value for proteinuria in children Data from two community-based screening programs, the Framingham Study12 and the Okinawa Study,13 demonstrate an approximately 10% prevalence of dipstick-positive proteinuria in adults. The prevalence was higher in older than younger individuals and higher in women than men. First, the urine dipstick is not sensitive to small amounts of albumin, and thus these studies would not have detected most patients with microalbuminuria. Second, neither timed urine collections nor protein-to-creatinine ratios were measured, and thus the dipstick test result was affected by the state of diuresis in addition to the magnitude of proteinuria. Furthermore, at least some of the individuals in these studies with proteinuria also had reduced kidney function. Thus, they provide only a rough guide to the likely prevalence of individuals with kidney damage due to chronic kidney disease. Refinements in serologic tests and introduction of percutaneous biopsy technique have led to increasingly sophisticated classifications. Unfortunately, nomenclature has not been standardized, which hampers the development of strategies for prevention and treatment. One of the tasks of the Work Group was to recommend a classification of the types of kidney disease for application of these guidelines. Another task was to describe the actions necessary for evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease, irrespective of diagnosis. The Work Group recommended that these tasks be grouped as follows: treatment of comorbid conditions, prevention or slowing the loss of kidney function, prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease, prevention and treatment of complications of decreased kidney function, preparation for kidney failure, and replacement of kidney function (if necessary and desired) by dialysis and kidney transplantation. This suggests that demographic and clinical factors may be risk factors for the development or progression of chronic kidney disease. In addition, individuals with a family history of kidney disease appear to be at higher risk of developing kidney disease. Finally, patients who have recovered from an episode of acute kidney failure, whether due to acute tubular necrosis or other parenchymal diseases, may also be at risk of developing chronic kidney disease. Of course, kidney failure is the most visible outcome of chronic kidney disease, and loss of kidney function is associated with complications in virtually every organ system. Cardiovascular disease was considered separately because: (1) cardiovascular disease events are more common than kidney failure in patients with chronic kidney disease; (2) cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease is treatable and potentially preventable; and (3) chronic kidney disease appears to be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Loss of Kidney Function A number of studies have examined factors associated with more rapid loss of kidney function in chronic kidney disease. Some diseases are associated with a faster loss of kidney function than others, while some patient factors are known to predict a faster loss of function, irrespective of the underlying disease. Identification of risk factors for progression can provide insight into the mechanisms of progressive loss of kidney function as well as identification of patients at higher risk for adverse outcomes. One of the questions posed by the Work Group was: What are the risk factors associated with a more rapid loss of kidney function
Tacrolimus may need to be avoided in patients with obesity or who may be at risk for diabetes or already have signs of glucose intolerance such as acanthosis. Immunofluorescence microscopy is negative or shows low-intensity staining for C3 and/or IgM. Therefore, the benefits of corticosteroid treatment in children are likely to at least partially extend to adults. The Work Group also judged that the relatively low risk of harms of short-term corticosteroid treatment, including precipitation/worsening of diabetes, psychiatric conditions, or bone loss, would be an important consideration for many patients. Although the quality of the evidence supporting corticosteroid use is low, the long clinical experience with this regimen, the significant morbidity associated with untreated nephrosis, and the excess morbidity and mortality associated with progressive kidney function loss or kidney failure together with the low risk of harms all suggest a highly favorable risk-benefit ratio. Resources and other costs Corticosteroids are inexpensive and require little monitoring. In low-resource settings, this class of drugs is affordable and may be the only drug available. Only 50% of patients will respond after four weeks of corticosteroid, but an additional 10% to 25% may respond after a total of 16 weeks of treatment. Based on case series, steroids are usually tapered by 5 to 10 mg/week after remission has been achieved for a total period of corticosteroid exposure of approximately 24 weeks. These approaches were not found to be different in terms of eventual remission and subsequent relapse rates. These treatments are considered in patients who have relative contraindications (severe hyperglycemia, pre-existing osteoporosis or osteopenia, or steroidinduced psychosis) or are unwilling to take steroids. The frequency of serious adverse effects was also similar between the treatment arms. Most patients will relapse infrequently after remission, but a significant minority will relapse frequently or become corticosteroid-dependent. One regimen is to administer oral prednisone at a daily dose of 1 mg/kg (maximum dose of 80 mg/d) for four weeks or until remission is achieved, followed by 5 mg decrements every three to five days to discontinuation within one to two months. Infrequent relapses may be treated with corticosteroids without incurring major side effects if the duration of therapy is limited. The dose and duration of corticosteroid therapy in patients with infrequent relapses have not been fully investigated. Generally, these agents are started after inducing remission with corticosteroids. It may not be able to withdraw corticosteroids completely in patients who have been on maintenance corticosteroids in view of the possibility of adrenal suppression. Prolonged therapy (>12 weeks) and repeated courses of cyclophosphamide should be avoided in view of cumulative toxicities. However, experience with rituximab is limited, and the long-term efficacy/risks in this population are unknown. However, relapse rates are high and prolonged therapy may be necessary when patients relapse during dose reduction. Older studies used fixed weight-based doses whereas reports that are more recent used target drug levels. Values and preferences the Work Group judged that the potential benefit of reduced corticosteroid exposure is important to patients. However, each of the four alternative therapies is associated with potential tradeoffs. Although cyclophosphamide has a relatively low risk of side effects and is less expensive compared to the other three classes, patients of child-bearing age may prefer to avoid cyclophosphamide due to the risk of infertility. Rituximab may be preferred by patients as the medication is given as a single course for induction. Resources and other costs the medications discussed in this section, particularly rituximab, are more expensive than corticosteroids. Cyclophosphamide is less expensive than the other three classes, is widely available, and does not require any additional laboratory testing apart from monitoring of peripheral blood counts. Rituximab is the costliest among these drugs, but costs have declined with the advent of biosimilar agents.
Genetic counseling and cardiac evaluation are important for family members due to the risk of fatal cardiac arrhythmias even in asymptomatic individuals. Ghosh: drafting/revising the manuscript, study concept or design, analysis or interpretation of data, accepts responsibility for conduct of research and final approval, acquisition of data. Milone: drafting/ revising the manuscript, study concept or design, analysis or interpretation of data, accepts responsibility for conduct of research and final approval, acquisition of data, study supervision. Cardiac transplantation in twins with autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. He had pulmonary sarcoidosis at age 24 years, which remained in remission after treatment with corticotropin and prednisone. Clinical examination showed 4/5 strength of the iliopsoas and quadriceps muscles and slight weakness of the biceps brachii muscles. The results of gait examination, including stance, stride, posture and arm swing, were normal. The rest of the results of the neurologic examination, particularly the sensory examination, were normal. Hereditary spinal muscular atrophy is characterized by proximal muscle weakness but usually presents at an earlier age. Myopathies could be toxic, such as those associated with alcohol, steroid, or statins; metabolic, such as thyroid myopathy and Pompe disease; or inflammatory. In rare cases, genetically determined dystrophinopathies are the cause of limbgirdle weakness at this age. The prevalence of these disorders at older age and the presence of an associated autoimmune disorder should be considered. Needle electromyography of the left rectus femoris muscle showed no abnormalities. Biopsy of a symptomatic anterior tibial muscle showed nonspecific myopathic changes. What is the most likely diagnosis, and does the clinical course help you in the diagnostic process Steroid myopathy was also unlikely, because the prednisone was stopped several years previously. Over the following years, his muscle weakness progressed and spread to the distal legs and finger flexor of 2 digits of his right hand. He reported difficulties with swallowing solid foods but did not develop fasciculations, cramps, or pyramidal tract signs. Although the prevalence is low (5 to 10 patients per million inhabitants), it is considered one of the most frequently acquired myopathies in the elderly. Most patients present with weakness of quadriceps muscles or finger flexors or dysphagia. The onset is insidious, and the course is slowly progressive, painless, and mostly asymmetric. Some criteria also require positive amyloid staining or 16- to 20-nm tubulofilaments on electromicroscopy. Important clues for quadriceps weakness are difficulties when climbing stairs, repetitive falls on the knees, and difficulty with rising from a chair. There is asymmetric involvement of the adductor muscles, more pronounced on the right side. This case illustrates that the clinical picture was diagnostically more helpful than the histopathologic criteria. Verschuuren has received research support from Prosensa and the Princess Beatrix Foundation. Inclusion body myositis: clinical features and clinical course of the disease in 64 patients. Inclusion-body myositis: a myodegenerative conformational disorder associated with Abeta, protein misfolding, and proteasome inhibition.
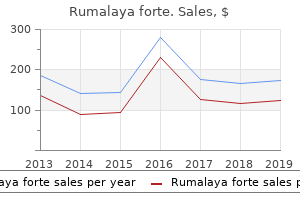
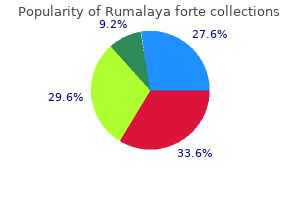
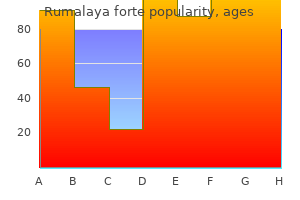
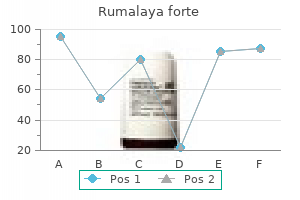
SP-303 (Sangre De Grado). Rumalaya forte.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96737
Your healthcare provider may also want to consider benzodiazepines (clonazepam), gabapentin or low-dose opiates. Discuss with your healthcare provider whether to reduce, rearrange or even eliminate daytime dopamine agonists. Examples of these behaviors may include obsession with shopping, sexual activity, eating and gambling, all of which can interfere with sleep. If you experience any of these behaviors, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider. Every attempt should be made to normalize the sleep-wake cycle and to improve sleep hygiene. Sleep hygiene can be further improved by the prudent use of physician-supervised sleeping medications such as quetiapine, clonazepam and others. Some antidepressant drugs, such as trazodone (Desyrel) or mirtazapine (Remeron), can also promote sleep due to their sedative properties. Most over-the-counter preparations are not suggested for use unless recommended by a physician, although the antihistamine diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may double as a sleeping pill and an antitremor drug because of its anticholinergic properties. If motor symptoms such as stiffness and tremor interrupt sleep because of the long gap between the last dose of antiparkinson medication in the evening and the first dose the following day, an extra dose of carbidopa/levodopa may be taken late in the evening or during the night on awakening. Stimulants such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) and mixed amphetamine salts (Adderall) can be tried. They should be given in low doses and taken in the morning initially, preferably before 8 a. Side effects include palpitations, high blood pressure, confusion, psychosis and insomnia (if the dose is too high or taken too late in the day). The non-stimulant modafinil (Provigil), approved only for treatment of narcolepsy, also is potentially useful. Its mode of action in the brain is unknown, but it has a good track record of reducing daytime sleepiness with fewer side effects because it is not a stimulant like methylphenidate and the amphetamines. In addition, the drugs commonly used to treat high blood pressure can make orthostasis worse. Any person who experiences orthostatic symptoms should inform all healthcare providers involved with their care. A good example of a frequent and straightforward parallel problem (or comorbidity) is back, neck and limb pain due almost always to degenerative arthritis of the spine. Orthostatic hypotension is usually the primary reason for the symptom, but general medical causes, especially involving the heart or lungs, must be explored. In addition, other medications prescribed by other physicians and healthcare providers, particularly medications for high blood pressure, should be thoroughly considered. Communication between all treating physicians and members of the healthcare team is mandatory in these matters. If the foregoing measures are not effective, then ask your physician or healthcare provider if medications to raise blood pressure would be appropriate in your case. Fludrocortisone (Florinef) will increase blood pressure by increasing retention of salt and blood volume. Leg edema (swelling) and high blood pressure when lying flat are potential adverse effects. Midodrine (Proamatine) increases blood pressure by stimulating the autonomic nervous system directly and is dosed three times per day. The development of high blood pressure when lying flat is greater with midodrine than fludrocortisone and should be carefully monitored. Pyridostigmine (Mestinon) can be used either as monotherapy or as an adjunctive drug to augment the blood pressure raising effect of flodrocortisone and midodrine. Ordinarily used to treat the neuromuscular disease myasthenia gravis, Mestinon has been evaluated in two single dose clinical trials (one open-label and one placebo-controlled), both of which showed a small but statistically significant elevating effect on diastolic blood pressure. Only one study, an open-label survey, has examined the long-term effect of using Mestinon for orthostatic hypotension. Therefore, the continued effectiveness of Northera should be assessed periodically by your doctor.
High cellular calcium levels cause muscle contraction with cramps or spasms as a common cause of pain. Boron, especially together with magnesium, can rapidly relax these muscles and take away the pain. However, with long-standing severe calcifications a large amount of calcium cannot be redistributed in a short time. This leads to increased calcium levels in the affected area, especially the hips and shoulders, and can cause problems for a considerable time, such as a tendency to severe cramping and pain, or problems with the blood circulation, or nerve transmission. Nerve-related effects in hands and feet may be numbness, or reduced sensitivity or feeling in the skin. Higher amounts of calcium and fluoride passing through the kidneys may cause temporary kidney pain. Such healing reactions cannot be avoided when aiming for a higher level of health. Whenever you experience an unpleasant effect reduce or temporarily stop borax intake until the problem subsides. Helpful additional measures are a greatly increased fluid intake, using more organic acids such as lemon juice, ascorbic acid or vinegar, and improving lymph flow as with rebounding, walking or inverted positions. Causes adverse reproductive effects in humans (fetotoxicity, abortion) by intraplacental route, may increase risk of Toxemia of Pregnancy in susceptible women. May cause adverse reproductive effects and birth defects in animals, particularly rats and mice - fetotoxicity, abortion, musculoskeletal abnormalities, and maternal effects (on ovaries, fallopian tubes). May affect behavior (muscle spasicity/contraction, somnolence), sense organs, metabolism, and cardiovascular system. Reproductive/developmental toxicity: Animal feeding studies in rat, mouse and dog, at high doses, have demonstrated effects on fertility and testes. Studies with boric acid in the rat, mouse and rabbit, at high doses, demonstrate developmental effects on the fetus, including fetal weight loss and minor skeletal variations. The doses administered were many times in excess of those to which humans would normally be exposed. No mutagenic activity was observed in a battery of short-term mutagenicity assays. Human epidemiological studies show no increase in pulmonary disease in occupational populations with chronic exposures to borate dust and no effect on fertility. It has been estimated that 5 to 10 grams can cause severe vomiting, diarrhoea, shock and even death, but it also says that lethal doses are not well documented in the literature. A review of 784 accidental human poisonings from 10 - 88 grams of boric acid reported no fatalities, with 88% of cases being asymptomatic, meaning they did not notice anything. However, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, hepatic, renal, and central nervous system effects, dermatitis, erythema, and death have been observed in some children and adults exposed to more than 84 mg boron/kg, corresponding to more than 40 grams of borax for 60 kg of body weight. Animal studies have identified reproductive toxicity as the most sensitive effects of boron ingestion. Exposure of rats, mice, and dogs for several weeks showed some damage to the testes and sperm at doses of more than 26 mg boron/kg which corresponds to 15 grams of borax/day for 60 kg body weight. Most at risk is the developing foetus, and in the studied animals rats were most affected. In one study slight reductions in the foetal body weight were already found at 13. However, a rat study lasting for 3 generations found no reproductive toxicity or effect on the parents or offspring at 30 mg boron/kg/day. Therefore we can assume that the safe reproductive dose is up to about 20 grams/60 kg/day. One study even reported elevated fertility rates in borax production workers as compared to the U. All this is important because possible reproductive toxicity is the official reason for the present assault on borax.

The drug is tested in a small group of 20-80 people while researchers observe side effects, judge the safety of the drug and determine safe dosage ranges. This is another way to prevent observer bias in evaluating the effect of the drug. Once approved, the medication can be prescribed by physicians and other licensed healthcare providers. The entire process of bringing a new medication to the pharmacy can take up to ten years from the time that it is tested in a laboratory to the time that the doctor prescribes the drug for a person with disease. While headlines may make it sound like new drugs are available, a closer look often reveals that the new drug is only in the early stages of research and years away from becoming an available treatment. Taking some time to evaluate the research behind the headlines can help determine the best way to use the new information. Has the information been published or presented at a reputable scientific meeting Check with a member of your healthcare team to determine if the source is reliable. The higher the number of participants, the more likely the results will achieve statistical significance. The gold standard for the most valid clinical trial is one that includes all of these elements. If we could diagnosis the disease earlier and slow its progression, people might never actually experience troublesome symptoms, effectively getting a "vaccination" effect. If we could make a treatment that would slow the disease progression, some of these brain cells could get better and start to work again, resulting in a moderate improvement in status. To date, there is not much evidence that this can be successful, with surgical approaches like transplants of brain cells failing to be effective in well-designed trials. However, there are scientists who are still working on studying therapies to replace lost cells in the brain, and there have been some promising developments. A better measure for progression would help with clinical trials of treatments to slow the disease. While treating the symptoms of the disease is not the same as slowing its progression, we are quite confident that exercising at least 2. Research is ongoing in many areas, including helping people who experience fluctuating medication effects. Scientists have some good leads that they are following with the hope of slowing the disease. All of us have to compensate for changes in our bodies and brains as we age, and so good therapy really does restore lost function. There appears to be an interplay between the actions of acetylcholine and dopamine. Symptoms vary widely, depending on which parts of the autonomic nervous system are affected. They may include dizziness and fainting upon standing (orthostatic hypotension); urinary problems including difficulty starting urination, overflow incontinence and inability to empty your bladder completely; sexual difficulties including erectile dysfunction or ejaculation problems in men, and vaginal dryness and difficulties with arousal and orgasm in women; difficulty digesting food (gastroparesis); and sweating abnormalities including decreased or excessive sweating. Initial symptoms may first appear on one side of the body, but eventually affect both sides. Other symptoms may include cognitive and visual-spatial impairments, loss of the ability to make familiar, purposeful movements, hesitant and halting speech, muscular jerks and difficulty swallowing.
The diagnosis of arterial disease should prompt you to evaluate for the presence of other cardiovascular diseases. An abnormal urinalysis indicates further testing to rule out underlying medical problems. Check for fixed deficits of the extremities caused by loss, impairment, or deformity of an arm, hand, finger, leg, foot, or toe. Does the driver have sufficient grasp and prehension in the upper limbs to maintain steering wheel grip Does the driver have sufficient mobility and strength in lower limbs to operate pedals properly Does the driver have signs of progressive musculoskeletal conditions, such as atrophy, weakness, or hypotonia Does the driver have clubbing or edema that may indicate the presence of an underlying heart, lung, or vascular condition Spine, Other Musculoskeletal You must check the entire musculoskeletal system for previous surgery, deformities, limitations of motion, and tenderness. Does the driver have a diagnosis or signs of a condition known to be associated with acute episodes of transient muscle weakness, poor muscular coordination, abnormal sensations, decreased muscular tone, and/or pain Neurological You must examine the driver for impaired equilibrium, coordination, and speech pattern. You should not make a certification decision until the etiology is confirmed, and treatment has been shown to be adequate/effective and safe. In some cases, you will also consider any reports and recommendations from the primary care provider and/or specialists treating the driver to supplement your examination and ensure adequate medical assessment. As a medical examiner, you are responsible for making the certification decision and signing the Medical Examination Report form. Your certification decision is limited to the certification and disqualification options printed on the Medical Examination Report form. When you determine that a driver has a health history or condition that does not meet physical qualification standards, you must not certify the driver. However, you should complete the examination to determine if the driver has more than one disqualifying condition. Some conditions are reversible, and the driver may take actions that will enable him/her to meet qualification requirements if treatment is successful. Discussion Regarding Certification Decision You must discuss your certification decision with the driver. If the examiner performs a complete physical examination, then the certification period is calculated from the date of this examination. You must retain a copy of the driver medical records, including the certificate, for a minimum of 3 years. Certify As a medical examiner, you determine when a driver meets physical qualification requirements. You also determine when the driver must repeat the physical examination for continuous certification. Although you cannot exceed the maximum certification period, you are never required to certify a driver for a certification interval longer than what you deem necessary to adequately monitor driver medical fitness for duty. Certify - Determine Certification Interval Overview Regulations - Maximum certification 2 years Qualify for 2-Year Certificate Page 44 of 260 Figure 12 - Medical Examination Report: 2 Year Certification When your examination finds that the driver meets all physical qualification standards, you can certify the driver for the maximum 2 years. Verify that the expiration date is 2 years from the date of the physical examination. Qualify - With Periodic Monitoring (less than 2 years) Figure 13 - Medical Examination Report: Certification with Periodic Monitoring You will certify for less than 2 years when a need exists to monitor the medical fitness for duty of the driver more frequently. You are never required to certify a driver for a certification interval longer than what you deem necessary to adequately monitor driver medical fitness for duty. Indicate the length of certification by checking 3 or 6 months, 1 year, or Other and write in the time frame.
The average blood pressure while sitting should not exceed 155 mm mercury systolic and 95 mm mercury diastolic maximum pressure for all classes. A medical assessment is specified for all applicants who need or use antihypertensive medication to control blood pressure. Examination Techniques In accordance with accepted clinical procedures, routine blood pressure should be taken with the applicant in the seated position. An applicant should not be denied or deferred first-, second-, or third-class certification unless subsequent recumbent blood pressure readings exceed those contained in this Guide. Any conditions that may adversely affect the validity of the blood pressure reading should be noted. An applicant whose pressure does not exceed 155 mm mercury systolic and 95 mm mercury diastolic maximum pressure, who has not used antihypertensive medication for 30 days, and who is otherwise qualified should be issued a medical certificate by the Examiner. Pulse (Resting) the medical standards do not specify pulse rates that, per se, are disqualifying for medical certification. These tests are used, however, to determine the status and responsiveness of the cardiovascular system. Abnormal pulse rates may be reason to conduct additional cardiovascular system evaluations. Examination Techniques the pulse rate is determined with the individual relaxed in a sitting position. Aerospace Medical Disposition If there is bradycardia, tachycardia, or arrhythmia, further evaluation is warranted and deferral may be indicated (see Item 36. If the Examiner believes this to be the case, the applicant should be given a few days to recover and then be retested. Examination Techniques Any standard laboratory procedures are acceptable for these tests. Aerospace Medical Disposition Glycosuria or proteinuria is cause for deferral of medical certificate issuance until additional studies determine the status of the endocrine and/or urinary systems. If the glycosuria has been determined not to be due to carbohydrate intolerance, the Examiner may issue the certificate. Trace or 1+ proteinuria in the absence of a history of renal disease is not cause for denial. The Examiner may request additional urinary tests when they are indicated by history or examination. If abnormalities are identified, additional work up or information may be requested. Regardless of who performs the tests, the Examiner is responsible for the accuracy of the findings, and this responsibility may not be delegated. If the form is complete and accurate, the Examiner should add final comments, make qualification decision statements, and certify the examination. If the applicant or holder fails to provide the requested medical information or history or to authorize the release so requested, the Administrator may suspend, modify, or revoke all medical certificates the airman holds or may, in the case of an applicant, deny the application for an airman medical certificate. Examination Techniques Additional medical information may be furnished through additional history taking, further clinical examination procedures, and supplemental laboratory procedures. When an Examiner determines that there is a need for additional medical information, based upon history and findings, the Examiner is authorized to request prior hospital and outpatient records and to request supplementary examinations including laboratory testing and examinations by appropriate medical specialists. The applicant should be advised of the types of additional examinations required and the type of medical specialist to be consulted. Responsibility for ensuring that these examinations are forwarded and that any charges or fees are paid will rest with the applicant. Comments on History and Findings Comments on all positive history or medical examination findings must be reported by Item Number. Item 60 provides the Examiner an opportunity to report observations and/or findings that are not asked for on the application form. The Examiner should record name, dosage, frequency, and purpose for all currently used medications.
References: