
Indications the main indication is reversion to sinus rhythm of atrioventricular junctional tachycardia. In the non-emergency setting it should only be initiated under specialist supervision. Unlike many other antiarrhythmic drugs, amiodarone causes little or no myocardial depression. Oral Oral administration is 200 mg three times daily for 1 week reduced to 200 mg twice daily for a further week; the maintenance dose is usually 200 mg daily or the minimum required to control the arrhythmia. Intravenous Intravenous administration is via central line catheter (in an emergency. As soon as an adequate response has been obtained, oral therapy should be initiated and the i. Side effects Amiodarone therapy can be proarrhythmogenic in patients with significant structural heart disease. Thyroid function tests including T3 should be measured before treatment and then every 6 months of treatment. Liver toxicity can also occur, so liver biochemistry should be measured before and then every 6 months of treatment. Other side effects are reversible corneal microdeposits (drivers may be dazzled by headlights at night), phototoxic skin reactions (advise use of sunblock creams), slate-grey skin pigmentation, pneumonitis and peripheral neuropathy. Cautions/contraindications It is contraindicated in sinus bradycardia or sinoatrial heart block, unless pacemaker fitted, iodine sensitivity and thyroid dysfunction. Many drugs interact with amiodarone, including warfarin and digoxin (check British National Formulary for full list). It has a very long half-life (extending to several weeks) and many months may be required to achieve steady-state concentrations; this is also important when drug interactions are considered. It is a membrane-depressant drug that reduces the rate of entry of sodium into the cell (sodium channel blocker). This may slow conduction, delay recovery or reduce the spontaneous discharge rate of myocardial cells. Occasionally it is used in ventricular tachyarrhythmias resistant to other treatments. Interactions with other drugs, including -blockers and calcium-channel blockers, can occur (check British National Formulary for full list). It is also used for rate control in sedentary patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter. Check renal function and electrolytes before starting therapy; reduce dose in the elderly and in renal impairment. Intravenous infusion Intravenous infusion for emergency loading dose for atrial fibrillation or flutter 0. Side effects Side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, conduction disturbances, blurred or yellow vision and ventricular arrhythmias. Side effects are common because of the narrow therapeutic index (the margin between effectiveness and toxicity). In suspected toxicity, measure plasma potassium concentration first and correct if hypokalaemia is evident. Plasma digoxin concentrations should be measured if toxicity is suspected; concentrations of > 2 mmol/L usually suggest toxicity. Contraindications Digoxin is contraindicated in arrhythmias associated with accessory conduction pathways. Blocking the normal pathway can increase the speed of conduction in the abnormal pathway and lead to ventricular arrhythmias. Diltiazem, verapamil, spironolactone and amiodarone inhibit renal excretion of digoxin; avoid with amiodarone and measure plasma levels with other drugs (see British National Formulary for full interaction list). Tetracycline, erythromycin and possibly other macrolides enhance the effect of digoxin. These effects reduce myocardial oxygen demand and give more time for coronary perfusion. Preparations and dose Most -blockers are equally effective, but there are differences between them which may affect the choice in particular diseases or individual patients.
A 70-year-old female is brought to the emergency room by her granddaughter because she has developed ecchymosis covering many areas of her body. Her granddaughter states that her grandmother lives alone at home and has not been eating well. Her diet has consisted of mainly tea and toast, as she does not drink milk or eat fruits or vegetables. Your physical examination reveals small hemorrhages around hair follicles, some of these follicles having an unusual "corkscrew" appearance. The signs and symptoms in this individual are most likely caused by a deficiency of a. Epidermal edema Intraepidermal vesicles Full-thickness epithelial necrosis Partial dermal necrosis Necrosis of adnexal structures 127. Lead poisoning Carcinoma of the pancreas Chronic pyelonephritis Vitamin C intoxication Ulcerative colitis 128. A comatose 27-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by paramedics, and the strong odor of bitter almonds is present. Ethylene glycol Carbon monoxide Carbon tetrachloride Cyanide Arsenic 76 Pathology 130. Which one of the following sets of serum levels is most likely to be seen in a young female as a result of self-induced starvation (anorexia nervosa) Abnormal limbs and phocomelia Arachnodactyly and dissecting aortic aneurysm Congenital goiter and hypothyroidism Congenital pigment abnormalities and deafness Synpolydactyly and brachydactyly 132. An 8-year-old boy is found to have progressive corneal vascularization, deafness, notched incisors, and a flattened nose. Artificial surfactant is most likely to be used in the treatment of an infant with a. Hemolytic disease of the newborn Hyaline membrane disease Physiologic jaundice of the newborn Retrolental fibroplasia Transposition of the great vessels 135. Because of extensive medical intervention, this premature infant survives, but unfortunately he is found to be blind resulting from the use of oxygen. Accumulation of abnormal material in the ganglion cells of the retina Fibrous obliteration of the canal of Schlemm Formation of a fibrovascular mass behind the lens Lipid accumulation at the periphery of the cornea Severe degeneration of the macula 78 Pathology 136. A 3-month-old female dies during sleep and the cause of death is unknown after autopsy c. A 4-week-old female dies from respiratory complications after being born 10 weeks prematurely d. A 9-month-old male dies and an autopsy finds evidence of repeated bone fractures and bilateral retinal hemorrhages. A male is stillborn at 29 weeks of gestation to a mother with obstetrical complications 137. A histologic section from the mass reveals a tumor composed of small, primitive-appearing cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and little to no cytoplasm. Occasional focal groups of tumor cells are arranged in a ring around a central space. Adrenal cortical carcinoma Ganglioneuroma Nephroblastoma Neuroblastoma Pheochromocytoma General Pathology 79 138. Aspartate aminotransferase Creatine phosphokinase Lactic dehydrogenase Alkaline phosphatase 59-nucleotidase 139. True negatives/(true negatives + false negatives) True negatives/(true negatives + false positives) True positives/(true positives + false negatives) True positives/(true positives + false positives) (True positives + false negatives)/(true negatives + false positives) General Pathology Answers 1. Abnormalities involving any of these normal metabolic pathways may lead to the accumulation of triglycerides within the hepatocytes. Examples of abnormalities that produce hepatic steatosis include diseases that cause excess delivery of free fatty acids to the liver or diseases that cause impaired lipoprotein synthesis.
Syndromes
Dra v a r i o u s t y p e s o f s k u l l d e f e c t s i n w h i c h me n i n g e s (meB)i n g o c e l e; n or me n i n g e s w i t h n e u r a l t i s s u e (me n i n g o e n c e p h a;l o c e l e, C and me n i n g o h y d r o e n c e p h a l o cD)l e, r o t r u d e t h r o u g h a b o n y d e f e c t. T h e e p d e f e c t s u s u a l l y o c c u r i n the o c c i p i t a l r e g i o n, b u t ma y i n v o l v e o the r a r e a s o f the s k u l l, s u c h a s the f r o n t o n a s a l r e g i o n. S o me 6 i n f a n t s w i t h s ma l l e r d e f e c t s c a n s u r v i v e w i t h s u r g e r y a n d the i r d e g r e e o f n e u r o l o g i c a l d e f i c i t s d e p e n d s o n the a mo u n t o f n e u r a l t i s s u e t h a t i s a b n o r ma l o r l o s t. F e t u s w i t h a n e n c e p h a l y (a b s e n t b r a i n) d u e t o a l a c k o f 7 closure of the cranial neural folds. Once the folds fail to close, neural tissue i s d i s o r g a n i ze d a n d i s e xp o s e d t o a mn i o t i c f l u i d, w h i c h c a u s e s n e c r o s i s a n d l o s s o f t i s s u. T h i s d e f e c t i s a l w a y s f a t a l a n d mo s t p r e g n a n c i e s w i t h s u c h c a s e s a r e t e r mi n a t B d. F The neural tube has failed to close in cranial and upper spinal cord regions r e s u l t i n g i n ma s s i v e n e c r o s i s o f n e u r a l t i s s u. H y d r o c e p h a l ui s c h a r a c t e r i ze d b y a n a b n o r ma l a c c u mu l a t i o n o f c e r e b r o s p i n a l f l u i d w i t h i n the v e n t r i c u l a r s y s t e m. In mo s t c a s e s, h y d r o c e p h a l u s i n the n e w b o r n i s d u e t o a n o b s t r u c t i o n oa qtu e d u c t o f S y l v i u s (a q u e d u c t a l s t e n o s i s). As a r e s u l t, f l u i d a c c u mu l a t e s i n the l a t e r a l ventricles and presses on the brain and bones of the skull. Since the cranial s u t u r e s h a v e n o t y e t f u s e d, s p a c e s b e t w e e n the m w i d e n a s the h e a d e xp a n d s. In e xt r e me c a s e s, b r a i n t i s s u e a n d b o n e s b e c o me t h i n a n d the h e a d ma y b e v e r y l a r g e (s eF i g. T h e A r n o l d - C h i a r i m a l f o r m a t soc a u d a l d i s p l a c e me n t a n d h e r n i a t i o n o f ii n c e r e b e l l a r s t r u c t u r e s t h r o u g h the f o r a me n ma g n u m. Ar n o l d - C h i a r i ma l f o r ma t i o n o c c u r s i n v i r t u a l l y e v e r y c a s e o f s p i n a b i f i d a c y s t i c a a n d i s u s u a l l y a c c o mp a n i e d by hydrocephalus. M i c r o c e p h a l d e s c r i b e s a c r a n i a l v a u l t t h a t i s s ma l l e r t h a n n o ri ma l (s e e y F g. S i n c e the s i ze o f the c r a n i u m d e p e n d s o n g r o w t h o f the b r a i n, u n d e r l y i n g) d e f e c t i s i n b r a i n d e v e l o p me n t. C a u s a t i o n o f the a b n o r ma l i t y i s v a r i e d; i t ma y b e g e n e t i c (a u t o s o ma l r e c e s s i v e) o r d u e t o p r e n a t a l i n s u l t s s u c h a s i n f e c t i o n o r e xp o s u r e t o d r u g s o r o the r t e r a t o g e n s. Imp a i r e d me n t a l d e v e l o p me n t o c c u r s i n mo r e t h a n h a l f o f c a s e s. F e t a l i n f e c t i o n b y t o xo p l a s mo s i s ma y r e s u l t i n c e r e b r a l c a l c i f i c a t i o n, me n t a l r e t a r d a t i o n, h y d r o c e p h a l u s, o r mi c r o c e p h a l y. H y p e r the r mi a p r o d u c e d b y ma t e r n a l i n f e c t i o n o r b y s a u n a b a t h s ma y c a u s e s p i n a b i f i d a a n d e xe n c e p h a l y. S i n c e the c r a n i a l s u t u r e s 8 h a d n o t c l o s e d, p r e s s u r e f r o m the a c c u mu l a t e d c e r e b r o s p i n a l f l u i d e n l a r g e d the h e a d, t h i n n i n g the b o n e s o f the s k u l l a n d c e r e b r a l c o r t e x. T h e a f o r e me n t i o n e d a b n o r ma l i t i e s a r e the mo s t s e r i o u s o n e s, a n d the y ma y b e i n c o mp a t i b l e w i t h l i f. A g r e a t ma n y o the r d e f e c t s o f the C N S ma y o c c u r w i t h o u t mu c h e xt e r n a l ma n i f e s t a t i o n. F o r e xa mp oe,p tu s c a l l o s uma y b e c l r he m p a r t i a l l y o r c o mp l e t e l y a b s e n t w i t h o u t mu c h f u n c t i o n a l d i s t u r b a n c. L i k e w i s e, p a r t i a l o r c o mp l e t e a b s e n c e o f the c e r e b e l l u m ma y r e s u l t i n o n l y a s l i g h t d i s t u r b a n c e o f c o o r d i n a t i o n. O n the o the r h a n d, c a s e s o fn sa lv e r e me t e r e t a r d a t i o n y n o t b e a s s o c i a t e d w i t h mo r p h o l o g i c a l l y d e t e c t a b l e b r a i n ma a b n o r ma l i t i e s.

T lymphocytes also release cytokines that activate cell-mediated immunity pathways. The response of rod cells to light causes hyperpolarization, whereas olfactory stimuli result in depolarization. The olfactory epithelium and rod cells are two examples of signal transduction that bypass a protein kinase system. In the case of the olfactory epithelium, an odorant molecule binds to an odor-specific transmembrane receptor found on the modified cilia at the apical surface. The resulting membrane depolarization is transmitted from the modified cilia to the olfactory vesicle through the neuron to the basal axon. Axonal processes traverse the lamina propria as the olfactory nerve and pass through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid to terminate in the olfactory bulb. This Respiratory System Answers 299 barrier consists of type I pneumocytes, endothelial cells, and their fused basal laminae. Pulmonary capillaries are sometimes in direct contact with the alveolar wall, whereas in other locations, the alveolar wall and capillaries are separated by cells and extracellular fibers. The areas of direct contact are the location of gas exchange, whereas the other areas represent sites of fluid exchange between the interstitium and air spaces. The pores of Kohn are connections from one alveolus to another, and macrophages travel through these passageways. The pores normally equalize air pressure between alveoli and can, in the disease state, provide collateral circulation of air in the event that a bronchiole is blocked. In that pathway, fixation of C1 to antibody combined with antigen leads to activation of C3b, which binds to bacterial cell walls and enhances opsonization. Mucociliary action is a critical component of the immune function of the respiratory system, but clearance occurs in the bronchioles bronchi trachea as part of the mucociliary apparatus. Microorganisms are entrapped in mucus and then cilia propel them toward the oropharynx. Microorganisms phagocytosed in the alveoli need to be transported to the bronchioles in order to ride on the mucociliary escalator (answer c). IgA functions to prevent attachment of microorganisms to the epithelium, particularly in the upper respiratory tract (answer d). Overall defense mechanisms of the respiratory system include nasal clearance of material, which occurs through sneezing, whereas other material may be swept into the nasopharynx and subsequently swallowed. The mucociliary action within the trachea and bronchi is often called the mucociliary, or tracheobronchial, escalator. At the distal end of the system, the alveolar macrophages phagocytose foreign material and secrete and respond to an array of cytokines. Neutrophils are attracted by chemokines and factors derived from macrophages and other cells and phagocytose bacteria. The B cells are precursors of plasma cells and synthesize immunoglobulins such as IgA associated with the bronchial secretion. Recruitment and proliferation of periendothelial cells (answer e), smooth muscle cells, pericytes, and fibroblasts are required for development and maturation of new blood vessels. The angiopoietins (Ang) 1 and 2 bind their receptor, Tie2, a receptor tyrosine kinase which regulates endothelial cell proliterative status. Ang 1 binds Tie2 leading to periendothelial cell recruitment and therefore vascular maturation. A 43-year-old woman presents with a cyst on her labia majora with foul-smelling drainage. She says the drainage occurs spontaneously and recently the cyst has enlarged and has become painful. The cyst is associated with the structure in the photomicrograph delineated by the arrow. The mechanism of secretion normally used by this structure is which of the following
M a t e r n a l h y p e r t e n s i o n a n d d i a b e t e s a s w e l l a s abruptio placenta are risk factors. Maternal infections, including bacterial vaginosis, are also associated with an increased risk. G r o w t h i n l e n g t h i s p a r t i c u l a r l y s t r i k i n g d u r i n g the t h i r d, f o u r t h, a n d f i f t h mo n t h s (a p p r o xi ma t e l y 5 c m p e r mo n t h), w h i l e i n c r e a s e i n w e i g h t i s mo s t s t r i k i n g d u r i n g t h l a s t 2 mo n t h s o f g e s t a t i o n (a p p r o xi ma t e l y 7 0 0 g p e r b l e n7. A s t r i k i n g c h a n g e i s the r e l a t i v e s l o w d o w n i n the g r o w t h o f the h e a d. B y the f i f t h mo n t h, the s i ze o f the h e a d i s a b o u t o n e t h i r d o f C H L, a n d a t b i r t h i t i s o n e f o u r t hF og. D u r i n g the f i f t h mo n t h, f e t a l mo v e me n t s a r e c l e a r l y r e c o g n i ze d b y the mo the r, a n d the f e t u s i s c o v e r e d w i t h f i n e, s ma l l h a i r. A f e t u s b o r n d u r i n g the s i xt h o r the b e g i n n i n g o f the s e v e n t h mo n t h h a s d i f f i c u l t y s u r v i v i n g, ma i n l y b e c a u s e the r e s p i r a t o r y a n d c e n t r a l n e r v o u s s y s t e ms h a v e n o t d i f f e r e n t i a t e d s u f f i c i e n t l y. In g e n e r a l, t he n g t h o f p r e g n a nfc y a f u l l - t e r m f e t u s i s c o n s i d e r e2 8t0 b e le or d o d a y s, o r 4 0 w e e k s a f t e r o n s e t o f the l a s t m e n,s or u aoiro n a c c u r a t e l y, t r,m t e 2 6 6 d a y s o r 3 8 w e e k s a f t e r f e r t i l. T h e f e t a l c i r c u l a t i o n i s a t a l l t i me s s e p a r a t e d f r o m the ma t e r n a l c i r c u l a t)i o n sb y c y t i a l me mb r a n e (a a a yn (c h o r i o n d e r i v a t i v e) a n de (d o the l i a l c e l l s f r o m f e t a l c a p i l l a r i e s. H e n c e, the b) n h u ma n p l a c e n t a i s o f ht e m o c h o r i at ly p. T h e v i l l o u s a r e a v a r i e s f r o m 4 t o 12, m c i l i t a t i n g e xc h a n g e b e t w e e n mo the r a n d c h i l d. T ha) fau is o (b s j o l t s, (l l o w s f o r f e t a l e lbd r b) a mo v e me n t s, a nc) (p r e v e n t s a d h e r e n c e o f the e mb r y o t o s u r r o u n d i n g t i s s u e s. T h e d f e t u s s w a l l o w s a mn i o t i c f l u i d, w h i c h i s a b s o r b e d t h r o u g h i t s g u t a n d c l e a r e d b y the p l a c e n t a. T h e f e t u s a d d s u r i n e t o the a mn i o t i c f l u i d, b u t t h i s i s mo s t l y w a t e r. An e xc e s s i v e a mo u n t o f a mn i o t i c(h ly dd a m n i o s) a s s o c i a t e d w i t h a n e n c e p h a l y f ui r is a n d e s o p h a g e a l a t r e s i a, w h e r e a s a n i n s u f f i c i e n t la mo h n td r a m n i ois) (o igo uy s related to renal agenesis. T h e u m b i l i c a l c o,r d u r r o u n d e d b y the a mn i o n, c o na)a it n s (u mb i l i c a l a r t e r i e s, s t wo (b) o n e u mb i l i c a l v e i n, a) d (h a r t o n j e l l y, w h i c h s e r v e s a s a p r o t e c t i v e c u s h i o n cn W f o r the v e s s e l s. F e t a l me mb r a n e s i n t w i n s v a r y a c c o r d i n g t o the i r o r i g i n a n d t i me o f o r ma t i o n. T w o t h i r d s o f t w i n si z y g o t i,co r f r a t e r n a l the y h a v e t w o a mn i o n s, d are; t w o c h o r i o n s, a n d t w o p l a c e n t a s, w h i c h s o me t i me s Mro n fo zsy g o t i c t w i n s a e u ed. S i g n a l s i n i t i a t iP a r t u r i t i o nb i r t h) a r e n o t c l e a r, b u t p r e p a r a t i o n f o r l a b o r u s u a l l y ng (begins P. L a b o r i t s e l f c o n s i s t s o f t h r e e s t a g e s: (1) e f f a c e me n t a n d d i l a t a t i o n o f the c e r v i x, (2) d e l i v e r y o f the f e t u s, a n d (3) d e l i v e r y o f the p l a c e n t a a n d f e t a l me mb r a n e s. L a t e r i n h e r p r e g n a n c y, a w o m a n r e a l i z e s t h a t s h e w a s p r o b a b l y e xp o s e d to toluene in the workplace during the third week of gestation but tells a fellow worker that she is not concerned about her baby because the p l a c e n t a p r o t e c t s h e r i n f a n t f r o m t o xi c f a c t o r s b y a c t i n g a s a b a r r i e r. The r ms u s e d t o d e s c r i b e the s t u d y o f the s e d i s o r d e r s a rt e r a t o l o g yG r. D y s mo r p h o l o g i s t s a r e u s u a l l y w i t h i n a d e p a r t me n t o f c l i n i c a l g e n e t i c s. M a j o r s t r u c t u r a l a n o ma l i e s o c c u r i n 2 % t o 3 % o f l i v e b o r n i n f a n t s, a n d a n a d d i t i o n a l 2 % t o 3 % a r e r e c o g n i ze d i n c h i l d r e n b y a g e 5 y e a r s, f o r a t o t a l o f 4 % t o 6 %. B i r t h d e f e c t s a r e the l e a d i n g c a u s e o f i n f a n t mo r t a l i t y, a c c o u n t i n g f o r a p p r o xi ma t e l y 2 1 % o f infant deaths. T hey are the fifth leading cause of years of potential life lost prior t a g e 6 5 a n d a ma j o r c o n t r i b u t o r t o d i s a b i l i t i e s. T h e y a r e a l s o n o n d i s c r i mi n a t o r y; mo r t a l i t y r a t e s p r o d u c e d b y b i r t h d e f e c t s a r e the s a me f o r As i a n s, Af r i c a n Ame r i c a n s, L a t i n Ame r i c a n s, w h i t e s, a n d N a t i v e Ame r i c a n s. In 4 0 % t o 6 0 % o f p e r s o n s w i t h b i r t h d e f e c t s, the c a u s e i s u n k n o w n. G e n e t i c f a c t o r s, s u c h a s c h r o mo s o me a b n o r ma l i t i e s a n d mu t a n t g e n e s, a c c o u n t f o r a p p r o xi ma t e l y 1 5 %; e n v i r o n me n t a l f a c t o r s p r o d u c e a p p r o xi ma t e l y 1 0 %; a c o mb i n a t i o n o f g e n e t i c a n d e n v i r o n me n t a l i n f l u e n c e s (mu l t i f a c t o r i a l i n h e r i t a n c e) produces 20% to 25%; and twinning causes 0. M i n o r a n o m a l i e s c u r i n a p p r o xi ma t e l y 1 5 % o f n e w b o r n s. T h e s e s t r u c t u r a l oc a b n o r ma l i t i e s, s u c h a s mi c r o t i a (s ma l l e a r s), p i g me n t e d s p o t s, a n d s h o r t p a l p e b r a l f i s s u r e s, a r e n o t the ms e l v e s d e t r i me n t a l t o h e a l t h b u t, i n s o me c a s e s, a r e a s s o c i a t e d w i t h ma j o r d e f e c t s.
Function of the Placenta M a i n f u n c t i o n s o f the p l a c e n t a) a rx c(h a n g e o f m e t a b o l i c a n d g a s e o u s a ee p r o d u c t s e t w e e n ma t e r n a l a n d f e t a l b l o o d s t r e a mspa o d u c t i o n o f b b) r n (h o r m o n. P o r t i o n s o f the w a l l o f the u t e r u s 2 a n d the a mn i o n h a v e b e e n r e mo v e d t o s h o w the f e t u s. In the b a c k g r o u n d a r e p l a c e n t a l v e s s e l s c o n v e r g i n g t o w a r d the u mb i l i c a l c o r d. T h e u mb i l i c a l c o r d i s t i g h t l y w o u n d a r o u n d the a b d o me n, p o s s i b l y c a u s i n g a b n o r ma l f e t a l p o s i t i o n i n the uterus (breech position). T h e c o t y l e d o n s a r e 3 p a r t i a l l y s e p a r a t e d b y the d e c i d u a l (ma t e r n a l) s e p t a. M o s t o f the i n t e r v i l l o u s b l o o d r e t u r n s t o the ma t e r n a l c i r c u l a t i o n b y w a y o f the e n d o me t r i a l v e i n s. T h e ma t e r n a l s i d e o f the p l a c e n t a i s a l w a y s c a r e f u l l y i n s p e c t e d a t b i r t h, a n d f r e q u e n t l y o n e o r mo r e c o t y l e d o n s w i t h a w h i t i s h a p p e a r a n c e a r e p r e s e n t b e c a u s e o f e xc e s s i v e f i b r i n o i d f o r ma t i o n a n d i n f a r c t i o n o f a g r o u p o f i n t e r v i l l o u s l a k e s. Ex change of Gase s E xc h a n g e o f g a s e s - s u c h a s o xy g e n, c a r b o n d i o xi d e, a n d c a r b o n mo n o xi d e - i s a c c o mp l i s h e d b y s i mp l e d i f f u s i o n. At t e r m, the f e t u s e xt r a c t s 2 0 t o 3 0 mL o f o xy g e n p e r mi n u t e f r o m the ma t e r n a l c i r c u l a t i o n, a n d e v e n a s h o r t - t e r m i n t e r r u p t i o n o f the o xy g e n s u p p l y i s f a t a l t o the f e t u s. P l a c e n t a l b l o o d f l o w i s c r i t i c a l t o o xy g e n s u p p l y s i n c e the a mo u n t o f o xy g e n r e a c h i n g the f e t u s p r i ma r i l y d e p e n d s o n d e l i v e r y, n o t diffusion. Ex change of Nutrie nts and Ele ctroly the s E xc h a n g e o f n u t r i e n t s a n d e l e c t r o l y t e s, s u c h a s a mi n o a c i d s, f r e e f a t t y a c i d s, c a r b o h y d r a t e s, a n d v i t a mi n s, i s r a p i d a n d i n c r e a s e s a s p r e g n a n c y a d v a n c e s. Tr a n s m i s s i o n o f M a t e r n a l A n t i b o d i e s Immu n o l o g i c a l c o mp e t e n c e b e g i n s t o d e v e l o p l a t e i n the f i r s t t r i me s t e r, b y w h i c h t i me the f e t u s ma k e s a l l o f the c o mp o n e n t s lo f m e n tImmu n o g l o b u l i n s com p. In t h i s ma n n e r, the f e t u s g a i n s p a s s i v e i mmu n i t y a g a i n s t v a r i o u s i n f e c t i o u s d i s e a s e s. N e w b o r n s b e g i n t o p r o d u c e the i r o w n Ig G, b u t a d u l t l e v e l s a r e n o t a t t a i n e d u n t i l the a g e o f 3 y e a r s. Clinical Corre late s Ery throblastosis Fe talis and Fe tal Hy drops O v e r 4 0 0 r e d b l o o d c e l l a n t i g e n s h a v e b e e n i d e n t i f i e d, a n d a l t h o u g h mo s t d o n o t c a u s e p r o b l e ms d u r i n g p r e g n a n c y, s o me c a n s t i mu l a t e a ma t e r n a l a n t i b o d y r e s p o n s e a g a i n s t f e t a l b l o o d c e l l s. T h e R h oa n t i g e ns hD b D r i the mo s t d a n g e r o u s, s i n c e i mmu n i za t i o n c a n r e s u l t f r o m a s i n g l e e xp o s u r e a n d o c c u r s e a r l i e r a n d w i t h g r e a t e r s e v e r i t y w i the a c h s u c c e e d i n g p r e g n a n c y. T h e antibody response occurs in cases where the fetus is D(Rh) positive and the mo the r i s D (R h) n e g a t i v e a n d i s e l i c i t e d w h e n f e t a l r e d b l o o d c e l l s e n t e r the ma t e r n a l s y s t e m d u e t o s ma l l a r e a s o f b l e e d i n g a t the s u r f a c e o f p l a c e n t a l v i l l i o r a t b i r t h. An a l y s i s o f a mn i o t i c f l u i d f o r b i l i r u b i n, a b r e a k d o w n p r o d u c t o f h e mo g l o b i n, s e r v e s a s a me a s u r e o f the d e g r e e o f r e d c e l l h e mo l y s i s. T r e a t me n t f o r the a f f e c t e d f e t u s i n v o l v e s i n t r a u t e r i n e o r p o s t n a t a l t r a n s f u s i o n s. H o w e v e r, the d i s e a s e i s p r e v e n t e d b y i d e n t i f y i n g w o me n a t r i s k u s i n g a n a n t i b o d y s c r e e n a n d t r e a t i n g the m w i t h a n t i - D - i mmu n o g l o b u l i n. An t i g e n s f r o m t A e O b l o o d g r o u p n a l s o e l i c i t a n a n t i b o d y r e s p o n s e, b u t hB ca the P. Horm one Production B y the e n d o f the f o u r t h mo n t h, the p l a c e n t a p r o d u c e s r o nie s u f f i c i e n t ge ste n a mo u n t s t o ma i n t a i n p r e g n a n c y i f the c o r p u s l u t e u m i s r e mo v e d o r f a i l s t o f u n c t i o n p r o p e r l y. In a l l p r o b a b i l i t y, a l l h o r mo n e s a r e s y n the s i ze d i n the s y n c y t i a l t r o p h o b l a s t. In a d d i t i o n t o p r o g e s t e r o n e, the p l a c e n t a p r o d u c e s i n c r e a s i n g a mo u n t s o f e s t r o g e n i c h o r m o n e s e d o mi n a n the y t r i o, l u n t i l j u s t b e f o r e the e n d o f, pr ls p r e g n a n c y, w h e n a ma xi mu m l e v e l i s r e a c h e d. T h e s e h i g h l e v e l s o f e s t r o g e n s s t i mu l a t e u t e r i n e g r o w t h a n d d e v e l o p me n t o f the ma mma r y g l a n d s. D u r i n g the f i r s t t w o mo n t h s o f p r e g n a n c y, the s y n c y t i o t r o p h o b l a s t a l s o p r o d u c e s h u m a n c h o r i o n i c g o n a d o t r o p i n,(h C G)h ma i n t a i n s the c o r p u s l u t e u m. T h i s whic h o r mo n e i s e xc r e t e d b y the mo the r i n the u r i n e, a n d i n the e a r l y s t a g e s o f g e s t a t i o n, i t s p r e s e n c e i s u s e d a s a n i n d i c a t o r o f p r e g n a n c y. An o the r h o r mo n e p r o d u c e d b y the p l a c e n t a m a t o m a m m o t r o p(ifn r me r l p l a c e n t a l l a c t o g e n so is o y).
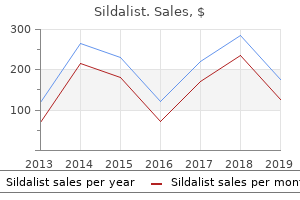
Canadian Hemlock (Pinus Bark). Sildalist.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96523
Patients are advised to wear a medical alert bracelet so they get proper pain management in case of an emergency. Or Clinically documented esophageal candidiasis, candidemia or wound infection due to candida. These requests will be approved when the following criteria are met: Xenical, Qsymia, Belviq, Alli, phentermine, diethylpropion, phendimetrazine, benzphetamine Initial Therapy Documentation of the following: 1. The member continues to practice lifestyle modifications including dietary changes and participates in a structured exercise program. Note: the Plan will not approve use of any of the above antiobesity medications for more than a total of 24 months. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the evidence report. Tetrabenazine as antichorea therapy in Huntington disease: A randomized controlled trial. Upon request, documentation of credentials supporting fellowship training in procedures of the hand must be made available. An inadequate response, contraindication, or intolerance to a trial (6 months or greater) of appropriate alternative treatments such as pentoxifylline or intralesional verapamil. Duration of therapy: Depends upon response to treatment and number of cords affected. Omalizumab provides long-term control in patients with moderate-to-severe allergic asthma. Omalizumab, anti-IgE recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of severe allergic asthma. The anti-IgE omalizumab reduces exacerbations and steroid requirement in allergic asthmatics. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, National Asthma Education and Prevention Program:Expert Panel Report 3. Patient is required to assemble and activate the device Patients with migraine who also have nausea, vomiting, or gastroparesis may not be able to take or absorb an oral triptan. Emtriva [emtricitabine] or Viread [tenofovir] to Truvada [emtricitabine/tenofovir] or vice versa) References Requests for continuing therapy that were approved by a previous Health Plan will be honored for at least 30 days upon receipt of documentation demonstrating that approval 1. Androgen deprivation treatment (hormonal therapy) for the management of prostate cancer [summary]. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists for prevention of chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage: Prospective randomized study. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and its analogues: A review of biological properties and clinical uses. Meeting highlights: International consensus panel on the treatment of primary breast cancer (commentary). Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist for chronic anovulatory uterine bleeding and severe anemia. Patients may require antiemetics, antidiarrheals and fluid and electrolyte replacement to prevent dehydration. Act is a three part program specifically designed to assist patients in obtaining Zolinza, help with insurance reimbursement issues, and provide support for those qualified individuals lacking insurance coverage for Zolinza.
Correction of Pectus Excavatum Definition the correction of a "funnel" chest deformity refers to the straightening of a deformity of the anterior chest wall in which there is a depression of the sternum and costal cartilages. A worsening of the appearance of the chest and the symptoms that occur happens during periods of rapid growth. The need for corrective surgery for pectus excavatum may be considered "cosmetic" until the asymptomatic child reaches late teens or adulthood. In reality, this procedure is performed to alleviate circulatory and/or respiratory symptoms. Variations of the procedure are performed according to the extent of the deformity. Many procedures have been devised to correct pectus excavatum, including reversal of a wedge osteotomy. The Nuss Procedure involves the insertion of a large curved bar that is removed after 2 to 3 years. In the Leonard Procedure, a wedge resection is taken from the lower sternum (wedge sternotomy) and the chest is repositioned. Wires through the sternum are fitted to a plastic external Jewitt brace to provide traction. The brace is worn for 6 weeks to secure the correct position during healing and removed after that time. The Lorenz procedure is a minimal access thoracoscopicallyassisted procedure in which a curved bar is inserted through a transverse substernal tunnel extending from the anterior axillary line to the opposite anterior axillary line. A modification of the Ravitch procedure obtains good long-term results, with less patient discomfort and a shorter hospital stay than previously performed procedures. The Lorenz procedure, employing a thoracoscopic-assisted technique, is less invasive and though patient discomfort is similar, avoids a large incision with less concomitant morbidity. The procedure is performed ideally with a combination of general anesthesia and thoracic epidural block. Approach is through a vertical presternal incision or through transverse submammary incisions. Small segments of rib cartilages (three to six) are separated from the sternum, medially and Chapter 20 Thoracic Surgery 469 laterally. An incision is made into the anterior mediastinum, and the pericardium is dissected from the sternum. A metal bar is positioned from behind (to correct the pectus excavatum) and is attached to a rib on each side. An incision (approximately 2 cm) is made on the mid-axillary line at the level of the deepest point of the depression on the right and left sides. On the right, 1 to 2 interspaces below the level of the incisions a thoracoscope is inserted thru a 5 mm port. The umbilical tapes are then used to guide the placement of the curved Lorenz bar through the previously created tunnel (under thoracoscopic visualization). Initially, the convex curve of the bar faces posteriorly and when in appropriate position, the bar is turned with a Lorenz bar rotational instrument so that the convexity faces anteriorly elevating the sternal depression. More than one attempt at positioning may be required with the bar rebent as needed; sometimes a second bar is required. The bar position is then maintained with suture loops about the adjacent ribs and chest wall musculature. Pulmonary function is assessed by the anesthesia provider including a chest x-ray which also notes the position of the bar. The bar usually remains in place for two years and is removed by a simple procedure. A pillow may be placed under the knees to avoid straining back muscles and for comfort. For submammary incisions, begin by preparing the area across the chest (at the nipple line), extending from the chin to below the umbilicus and down to the table at the sides. Circulator should check with the blood bank to determine that the correct number of units of blood is available and ready. He/she should bring a blood administration set, blood warmer, and blood pump into the room for use in case of inadvertent hemorrhage. Thoracotomy tray andVascular procedures tray should be available in the room (unopened) in case the pleural space is entered inadvertently or vascular injury results in hemorrhage. Discussion this surgery is performed in an attempt to alleviate myasthenia gravis or to remove benign or malignant tumors.
A 19-year-old female presents with sudden, severe right-sided chest pain that developed shortly after she had been placing heavy boxes on shelves in her garage. Breath sounds are markedly decreased on the right, and the right lung is hyperresonant to percussion. Pneumoconiosis Pneumocystis infection Bacterial pneumonia Viral pneumonia Pneumothorax 276 Pathology 259. A 57-year-old male presents with a lesion similar to that seen in this gross photograph of a sagittal section of the lung. Which one of the listed characteristics, if present in this lesion, would favor the diagnosis of mesothelioma Pulmonary edema can be classified based on the etiology into cardiogenic pulmonary edema and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema results from abnormalities of hemodynamic (Starling) forces, while noncardiogenic pulmonary edema results from cellular injury. Causes of cardiogenic pulmonary edema include increased hydrostatic forces, as seen with congestive heart failure (the most common cause of pulmonary edema); decreased oncotic pressure, such as resulting from decreased albumin levels; and lymphatic obstruction. Noncardiogenic edema may be the result of either endothelial injury (infections, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, or trauma) or alveolar injury (from inhaled toxins, aspiration, drowning, or near drowning). Microscopically, pulmonary edema reveals the alveoli to be filled with pale pink fluid. Cardiogenic edema may lead to alveolar hemorrhages and hemosiderin-laden macrophages (heart failure cells). Where cardiogenic edema is present, chest x-rays show an increase in the caliber of the blood vessels in the upper lobes, perivascular and peribronchial fluid ("cuffing"), and Kerley B lines (fluid in the interlobular septa). Absorptive (obstructive) atelectasis results from airway obstruction, such as occurs with mucus, tumors, or foreign bodies. The air within the lungs distal to the obstruction is absorbed, the lung collapses, and the mediastinum then shifts toward the collapsed lung. In contraction, atelectasis fibrosis causes collapse 277 278 Pathology of lung tissue. Patchy atelectasis may result from loss of pulmonary surfactant, which is seen in hyaline membrane disease of the newborn. In the acute edematous stage, the lungs are congested (pulmonary congestion) and show pulmonary edema with interstitial inflammation. In contrast, angioinvasive infiltrates of pleomorphic lymphoid cells are seen with lymphomatoid granulomatosis, a disease of middle-aged individuals that is characterized by an angiocentric and angioinvasive infiltrate of atypical lymphoid cells. Deposits of needle-like crystals from the membranes of eosinophils, called Charcot-Leyden crystals, can be seen in patients with asthma, while infiltrating groups of malignant cells having intercellular bridges characterize squamous cell carcinoma. Plexiform lesions within pulmonary arterioles are diagnostic of pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary emboli are common and are found in about 10 to 20% of hospital autopsies. Typical settings for the development of deep vein thrombosis include increased venous stasis and hypercoagulable states, such as after surgery. Pulmonary emboli may produce other clinical Respiratory System Answers 279 symptoms, such as anxiety, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, fever, cough, hemoptysis, or sudden death. Hypoxemia results from increased A-a gradients, the result of increased alveolar dead space. The majority of pulmonary thromboemboli do no harm and eventually organize or lyse; however, depending on the size of the embolus and the hemodynamic status of the patient, a pulmonary infarct may be produced. Pulmonary infarcts grossly have an apex pointing toward the occluded vessel and a pyramidal base extending toward the pleural surface. Elevation of the mean pulmonary arterial pressure is the result of endothelial dysfunction and vascular changes. The main arteries have atheromas that are similar to systemic atherosclerosis, but are not as severe.
Any circumferential splint padding must be placed judiciously to avoid contributing to a compartment syndrome with iatrogenic compression of the dressing/splint. Closed reduction with percutaneous pinning may be used when the articular surface is not involved and displacement is <2 mm. The mechanism of injury is a varus stress to the elbow with traction on the lateral condyle by the extensors of the forearm. These can be nondisplaced, and present only with mild swelling and/or point tenderness. The medial epicondyle is a traction apophysis to which the flexors of the forearm are attached. These may occur as a pure avulsion injury when falling on the arm with hyperextended wrist and fingers, in association with posterior elbow dislocation (about 50% of the time), and, rarely, from a direct blow. The epicondyle becomes entrapped in the joint after reduction of a posterior elbow dislocation 15 to 20% of the time. The medial epicondyle must always be identified when a spontaneously reduced elbow dislocation is suspected, or in post-reduction views to prevent this entrapment from going unnoticed. Inability to reduce an elbow dislocation may be due to an entrapped medial epicondyle, mandating open reduction. Acute and delayed ulnar nerve dysfunction may occur, especially in cases of ulnar nerve entrapment (50%). No growth aberrancies are associated with injuries to this (or any other) traction apophysis. Immobilization in a posterior long arm mold and prompt orthopedic referral is indicated. Young pitchers present with tenderness and swelling at the medial epicondyle with a mild loss of elbow extension. Patients are hospitalized and kept non-weight bearing until operative intervention occurs. There is an association with endocrine disturbances Pediatric Orthopedics Page 329 Notes (hypothyroidism) but the vast majority occurs in the absence of such. At birth, the superior acetabulum is poorly developed, and dislocation of the femoral head can occur. These do not typically "present"; they are found on neonatal and well-baby exams, most commonly via the Ortolani maneuver (abduction of the flexed hip results in a click). Parents may note difficulty in abducting the hip for diapering, or asymmetric thigh skin folds indicative of limb length discrepancy. Presentation varies from pain to frank limp, usually of Page 330 Notes less than 2 weeks duration. The child appears well and allows passive range of motion of the hip, with pain only at end range. The vast majority of septic arthritis cases are caused by strains of Staph, Strep and sometimes gram negatives. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head occurs due to repeated episodes of transient ischemia (of unknown etiology). Peak incidence is 6 years of age (3 to 10 years) with boys affected 4 times more than girls. Other contributing factors: trauma, alteration in coagulabilty of blood, endocrine and metabolic disorders. Patients present with hip pain or antalgic gait of insidious progression over weeks to months. X-ray may show flattening of the femoral head, subchondral lucency at the proximal epiphysis, and irregular calcification and fragmentation of the epiphysis. Multiple treatment approaches exist, all of which incorporate bracing to maintain abduction and flexion of the hip to contain the femoral head within the acetabulum. These are more common than other physeal injuries of the hip or about the knee, but less common than fractures of the ankles or upper extremities. Most commonly, these are Salter 2 injuries in the adolescent Pediatric Orthopedics Page 331 Notes 2. Repetitive microavulsion injuries occur with repeated traction of the patellar ligament during ossification of the tubercle.
References: