
Overwhelming listerial fetal infection-granulomatosis infantiseptica-is characterized by miliary microabscesses and granulomas, most often in the skin, liver, and spleen. Diagnosis Timely diagnosis requires that the illness be considered in groups at risk: pregnant women, elderly pts, neonates, immunocompromised pts. Of live-born treated neonates in one series, 60% recovered fully, 24% died, and 13% were left with sequelae or complications. Prevention Pregnant women and other persons at risk for listeriosis should avoid soft cheeses and should avoid or thoroughly reheat ready-to-eat and delicatessen foods. Meningitis is associated with high morbidity; 6% of pts have sensorineural hearing loss; one-fourth have some significant sequelae; mortality is ~5%. Epiglottitis, which occurs in older children and occasionally in adults, involves cellulitis of the epiglottis and supraglottic tissues that begins with a sore throat and progresses rapidly to dysphagia, drooling, and airway obstruction. Miscellaneous: childhood otitis media, puerperal sepsis, neonatal bacteremia, sinusitis, and-less commonly-invasive infections. Many agents are useful: amoxicillin/ clavulanate, extended-spectrum cephalosporins, newer macrolides (azithromycin or clarithromycin), and fluoroquinolones (in nonpregnant adults). Prevention Hib vaccine is recommended for all children; the immunization series should be started at ~2 months of age. All children and adults (except pregnant women) in households with a case of Hib disease and at least one incompletely immunized contact <4 years of age should receive prophylaxis with oral rifampin. In households, attack rates are 80% among unimmunized contacts and 20% among immunized contacts. Pertussis remains an important cause of infant morbidity and death in developing countries. In the United States, the incidence has increased slowly since 1976, particularly among adolescents and adults. Respiratory infections should be treated with a 5-day course and sinusitis for longer durations. Several Haemophilus species, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, and Kingella kingae make up this group. It is associated with severe destructive periodontal disease, which also is frequently evident in pts with endocarditis. The organism is usually pan-sensitive, but high-level penicillin resistance has been reported. The organism is typically resistant to clindamycin, metronidazole, and aminoglycosides. Haemophilus species, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Cardiobacterium hominis 512 Eikenella corrodens Kingella kingae aSusceptibility bFluoroquinolones Ceftriaxone (2 g/d) or fluoroquinolonesb Fluoroquinolonesb testing should be performed in all cases to guide therapy. Escherichia coli and, to a lesser degree, Klebsiella and Proteus account for most infections. Combination empirical antimicrobial therapy may be appropriate pending susceptibility results. Currently, cephalosporins (particularly second-, third-, and fourth-generation agents), monobactams, piperacillin-tazobactam, carbapenems, and aminoglycosides retain good activity. However, testing for Shiga toxins or toxin genes is more sensitive, specific, and rapid.

Physical examination reveals erythematous plaques with adherent silvery scales that induce punctate bleeding points when removed. Biopsy of lesional skin would most likely show an accumulation of which of the following cells in the epidermis Skin biopsy discloses separation of the basal layer of the epidermis from its basement membrane and is devoid of inflammatory cells. Histologically, the lesions show separation of the stratum spinosum from the basal layer. Which of the following proteins is targeted by IgG autoantibody in the skin of this patient The patient is observed to have a flat, pigmented lesion on the atrophic, sun-damaged skin (shown in the image). A biopsy of one of the nodules (shown in the image) reveals buds of atypical, deeply-basophilic keratinocytes extending from the overlying epidermis into the papillary dermis. She said the lesions first appeared as red swollen plaques on her abdomen and flexor aspect of her forearms. Physical examination reveals urticarial plaques, as well as large bullae on her abdomen and thighs (shown in the image). A skin biopsy shows a positive direct immunofluorescence test for IgG antibasement membrane antibody. Histologic examination of a lesion reveals squamous epithelial-lined fronds with fibrovascular cores (shown in the image). Which of the following viruses is most likely responsible for the development of these skin lesions Physical examination reveals numerous wheal-like lesions with small vesicles over her elbows and knees. A skin biopsy demonstrates inflammation in the tips of the dermal papillae and subepidermal vesicles. Which of the following histopathologic findings would provide the best evidence to support a diagnosis of dermatitis herpetiformis in this patient Over the past 3 months, she has experienced malaise, joint pain, weight loss, and sporadic fever. Other physical findings include malar rash, erythematous-pink plaques with telangiectatic vessels, oral ulcers, and nonblanching purpuric papules on her legs. Biopsy of sun-damaged lesional skin would most likely show which of the following histopathologic findings in this patient She recently had a urinary tract infection for which she was treated with trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim). Biopsy discloses focal hemorrhage, neutrophilic infiltrates in the subcutaneous fibrous tissue septa, and giant cells at the interface between the septa and the adipose fat tissue. Which of the following bacteria is associated with the development of these lesions A 30-year-old man presents with flat-topped papules that have appeared gradually on the flexor surfaces of his wrists. Histologically, the lesions showed hyperkeratosis, thickening of the stratum granulosum, and a bandlike infiltrate of lymphocytes and macrophages in the upper dermis, disrupting the basal layer of the epidermis. Physical examination reveals plaques with telangiectases, atrophy, and pigmentation. Biopsy of lesional skin shows that the epidermis and papillary dermis are expanded by an extensive infiltrate of atypical lymphocytes. These infiltrating lymphocytes most likely express which of the following "cluster of differentiation" cell surface markers Physical examination reveals multiple, purpuric, 2- to 4-mm papules on the skin (shown in the image). Which of the following represents the most important step in the pathogenesis of the sensitization phase of injury in this patient Which of the following terms best describes the morphologic appearance of her freckles
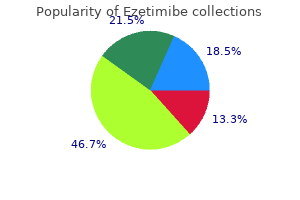
| Comparative prices of Ezetimibe | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | ShopRite | 194 |
| 2 | Bed Bath & Beyond | 500 |
| 3 | IKEA North America | 998 |
| 4 | Winn-Dixie Stores | 258 |
| 5 | Limited Brands | 591 |
These malignant cells are highly sensitive to chemotherapy, and the cure rates are now over 90%. The pathologic findings in this case show undifferentiated neoplastic cells, forming sheets and chords, surrounded by dilated vascular channels filled with red blood cells. Lymphoma (choice C) is more common in older men and does not have the morphology shown. She complains of having had dull pelvic pain for 9 months, which is accentuated during menstruation. Laparoscopy reveals multiple, small hemorrhagic lesions over the surface of both ovaries and fallopian tubes and abundant pelvic scarring. Physical examination reveals a 3-cm firm mass in the anterior wall of the upper vagina. Biopsy of the vaginal mass will most likely show which of the following pathologic findings Physical examination reveals an exophytic, ulcerated 1-cm polypoid mass near the external end of the urethra. A multilocular tumor filled with thick, viscous fluid is removed (shown in the image). Tumor spaces are lined by mucinous, columnar epithelial cells, showing no evidence of atypia. Pelvic examination is exquisitely painful and reveals an ill-defined thickening in the right and left adnexae. If untreated, which of the following would be the most likely complication in this patient Physical examination reveals vulval white plaques, atrophic skin, and a parchment-like appearance. Biopsy of the lesion (shown in the image) demonstrates hyperkeratosis, loss of rete ridges, and a homogeneous, acellular zone in the upper dermis. Pelvic examination shows a markedly enlarged vulva, inguinal lymph node enlargement, and rectal stricture. Biopsy of an inguinal lymph node reveals necrotizing granulomas, neutrophilic infiltrates, and inclusion bodies within macrophages. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of infertility in this patient Physical examination reveals vesiculopustular lesions on the labium major and cervix. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this constellation of signs and symptoms Colposcopy shows white epithelium, punctation, and a mosaic pattern in the transformation zone (shown in the image). The pelvic lymph nodes are slightly enlarged, raising the possibility of nodal involvement by the tumor. Which of the following is the best prognostic indicator of survival in this patient A cervical biopsy shows atypical squamous cells throughout the entire thickness of the epithelium, with no evidence of epithelial maturation (shown in the image). If untreated, which of the following will be the most likely cause of death in the patient described in Question 15 During the last two menstrual cycles, she noticed spotting throughout the entire cycle. An ultrasound examination reveals a thickened endometrial stripe with a polypoid mass in the uterine fundus. A 35-year-old woman presents with a 6-week history of vaginal discharge, which is occasionally blood tinged. Pelvic examination reveals a 2-cm pedunculated, lobulated, and smooth cervical growth; it is excised. Histologic examination of the specimen would most likely reveal which of the following Bimanual pelvic examination reveals an enlarged uterus with multiple, irregular masses. A hysterectomy is performed, and a sharply circumscribed fleshy tumor is found within the uterine wall (shown in the image). Which of the following is the most likely cause of vaginal bleeding and anemia in this patient
Variations in temperature were recorded every 5 seconds, and the amount of implant substance removed (reduction in weight of the implant) was evaluated. Under proper cooling conditions, implantoplasty does not generate excess temperature increases that can damage soft tissue or bone surrounding the treated implant. This in vitro study was designed to evaluate the effect of implantoplasty on implant strength. The specimens were then loaded 30 degrees off-axis in a universal testing machine until fracture failure occurred. Bending and fracture strength values were recorded and analyzed statistically (=. The mean bending strength of narrow implants was statistically significantly reduced by implantoplasty (511. Implantoplasty did not affect the strength of wide implants; fracture failures occurred at the abutment screw. The fracture mode was ductile and the crack growth was oblique in direction, indicating complex stress distribution and concentration under loading. Therefore, this procedure should be performed with caution on narrower, freestanding implants that are subject to greater occlusal force (eg, posterior regions). Analysis of Implant Strength after implantoplasty in Three Implant-Abutment Connection Designs: An In Vitro Study. Three groups (n = 20) were established based on the following implant connections: external hexagon (group 1), internal hexagon (group 2), and Morse taper (group 3). The implants of each group were submitted to a compressive load before (n = 10) and after the implantoplasty (n = 10). The wear was performed in a mechanical lathe machine using a carbide bur, and the final dimensions of each sample were measured. All groups were subjected to quasi-static loading at a 30-degree angle to the implant axis in a universal testing machine and 5 mm out of the implant support. The mean fracture strengths for the groups before and after the implantoplasty were, respectively, 773. Peri-implantitis is an irreversible inflammatory reaction in the soft and hard tissues around a functional implant. One of the treatment approaches of this disease include smoothing and polishing the rough surface and removing threads on the implants using rotary instruments, which is called implantoplasy. Clinicians should perform implantoplasty with caution because it may raise the temperature of the implant body as well as the surrounding bone. This study aimed to compare micromorphology and thermal changes obtained with different rotary instruments and piezoelectric device after implantoplasty. The roughness of treated surfaces was evaluated with a profilometer for Ra1, Rz1 (single polish procedures), Ra2, and Rz2 (sequence polish procedures) parameters. Also, surfaces were observed using a field emission scanning electron after each step of implantoplasty. No statistically significant differences were observed between the carbide and diamond burs regarding the temperature changes and the temperature decreased from the start point in both groups. Besides, this measure in the carbide group was significantly lower than that of the diamond group (p< 0. Rz1 value was significantly greater in diamond and carbide groups compared to piezoelectric group. The results revealed significant differences among the three groups concerning Rz2. The minimum Rz2 value was seen in piezoelectic group, while the diamond group showed the highest Rz2 parameter. The piezoelectric device produced smoother surfaces in single or sequence procedures compared to the burs and can be useful for implantoplasy. The antimicrobial activity was tested against Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, Actinomyces meyeri, Parvimonas micra, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Prevotella nigrescens according to the agar diffusion method. With regard to the cell viability, this solution showed results similar to those with 5.
Almost all patients will have microscopic hematuria and proteinuria; nephrotic syndrome and kidney impairment are common. However, if the histologic lesions are mainly chronic (see Rationale) there may be less overt clinical activity, other than progressive kidney failure. Nonetheless, the overall goals of treatment are similar between trials, and definitions of response based on published trials are provided as a guide to the success of therapy (Table 27). Thorough review with the nephropathologist is required to ensure accurate classification prior to starting therapy. The objective is to rapidly decrease kidney inflammation by initial intensive treatment, and then consolidate treatment over a longer time. The initial phase is often called induction, which implies remission is achieved at its completion. This, however, is often not the case, and remissions continue to occur well into the maintenance phase. Untested in blacks, Hispanics, Chinese Effective in whites, blacks, Chinese; easy to administer and lower cost than i. Cyclophosphamide was used in a different regimen than in most published trials: eight i. There were no differences in responses or remissions at 9 or 18 months, or relapse rate after 40 months of follow-up. A criticism of these studies is the small number of patients, especially during long-term follow-up. In this initial trial, patients were exposed to large cumulative amounts of cyclophosphamide; oral cyclophosphamide was used at doses up to 4 mg/kg/d for a median of 4 years, far greater than now recommended, and i. Given the potential for developing hematologic malignancies later in life, these large cumulative doses of cyclophosphamide should be avoided. We suggest a lifetime maximum of 36 g cyclophosphamide in patients with systemic lupus. There are other important considerations, when using cyclophosphamide, to reduce its toxicity. When using oral cyclophosphamide, white blood cell counts should be monitored weekly and cyclophosphamide dose should be adjusted to keep leucocytes X3000/ml. Leukopenia requires careful evaluation, since systemic lupus, as well as cyclophosphamide, can cause suppression of bone marrow. To minimize bladder toxicity with oral cyclophosphamide, we suggest instructing patients to take cyclophosphamide in the morning, and to drink extra fluid at each meal and at bed time. The use of sodium-2-mercaptoethane (mesna) will also minimize the risk of hemorrhagic cystitis when cyclophosphamide is given as i. To protect fertility, women should be offered prophylaxis with leuprolide and men testosterone while cyclophosphamide is being given. The efficacy of testosterone 224 in preserving fertility in males is poorly established, so sperm banking should be offered. Given the toxicity of cyclophosphamide, studies were undertaken to determine if the dosing regimen could be modified. In this trial, the majority of patients were white, and most patients did not have clinically severe disease. These combined clinical findings have been associated, in other studies, with deterioration of kidney function over time.
Syndromes
Diagnosis: 1-Antitrypsin deficiency, emphysema 28 the answer is E: Smooth muscle hyperplasia and basement membrane thickening. When severe acute asthma is unresponsive to therapy, it is referred to as status asthmaticus. Histological examination of lung from a patient who died in status asthmaticus often shows a bronchus containing a luminal mucous plug, submucosal gland hyperplasia, smooth muscle hyperplasia, basement membrane thickening, and increased numbers of eosinophils. All of the other choices concern alveolar damage, whereas the photograph demonstrates a section of bronchus. Silicosis is caused by inhalation of small crystals of quartz (silicon dioxide), which are generated by stone cutting, sandblasting, and mining. The condition is marked by the insidious development of fibrotic pulmonary nodules containing quartz crystals. The disease may be asymptomatic for prolonged periods of time or may cause only mild to moderate dyspnea. Continued exposure may lead to progressive fibrosis and severe respiratory embarrassment. Anthracosis (choice A) by itself does not cause restrictive lung disease, whereas asbestosis (choice B) is characterized by interstitial fibrosis. The nodules of sarcoidosis (choice C) and Wegener granulomatosis (choice E) are not fibrotic. Amorphous carbon by itself is not fibrogenic owing to its inability to kill alveolar macrophages. By contrast, silica is highly fibrogenic, and the inhalation of rock particles may therefore lead to the lesions of anthracosilicosis. Asbestosis refers to the diffuse interstitial fibrosis that results from the inhalation of asbestos fibers. The disease occurs as a result of the processing and handling of asbestos, rather than mining, which is a surface operation. Asbestosis is characterized by bilateral, diffuse interstitial fibrosis and asbestos bodies in the lung. These ferruginous bodies are golden brown and beaded, with a central colorless core fiber. In this patient, the dome of the diaphragm is covered by a smooth, pearly white, nodular fibrotic lesion (pleural plaque), a common feature of asbestos exposure. A clear-cut relationship between occupational asbestos exposure and malignant mesothelioma is established. The dominant hypothesis concerning the pathogenesis of emphysema is the proteolysis-antiproteolysis theory. In most patients with emphysema, it is thought that tobacco smoke induces an inflammatory reaction. Serine elastase in neutrophils is a particularly potent elastolytic agent, which injures the elastic tissue of the lung. Over time, an imbalance in elastin generation and catabolism in the lung leads to emphysema. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a nonspecific term that describes patients with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both who evidence obstruction to air flow in the lungs. It is often difficult to separate the relative contribution of each disease to the clinical presentation. Chronic bronchitis is defined clinically as the presence of a chronic productive cough without a discernible cause for more than half the time over a period of 2 years. It is primarily a disease of cigarette smoking, with 90% of all cases occurring in smokers. The frequency and severity of acute respiratory tract infections is increased in patients with chronic bronchitis. The combination of cyanosis and edema secondary to cor pulmonale has led to the label "blue bloater" for such patients. In contrast to patients with predominantly chronic bronchitis, those with emphysema are at lower risk of recurrent pulmonary infections and are not so prone to the development of cor pulmonale. The clinical course of emphysema is marked by an inexorable decline in respiratory function and progressive dyspnea, for which no treatment is adequate. Diagnosis: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis, emphysema the answer is B: Asthma.
Cells are spheroidal, ellipsoidal, or cylindrical, and reproduce by multilateral budding; pseudomycelium may be formed. The medium contains sterile serum and nutrient broth (3:1 by volume) and glucose (ca. In use, no part of the loop handle should enter the culture vessel; loops with longer wires may be used. The louping-ill virus can also cause a fatal infection in Red grouse (Lagopus lagopus scoticus). The chamber is evacuated and formaldehyde is admitted; this step is carried out three times. Subsequently, formaldehyde, and then steam, are admitted to the chamber, and a temperature of ca. The chamber is then evacuated, steam is admitted, and the chamber is again evacuated; this last evacuation removes traces of formaldehyde and steam and gives rise to a dry, odourless load. The fungus can grow saprotrophically on dead lupin plant material and on mature living plants. Luteoviruses can infect various monocotyledonous and/or dicotyledonous plants, and many can cause important economic losses in crop plants; transmission occurs persistently (circulatively) via aphids, and weeds may provide important reservoirs of infection. Symptoms of infection typically include severe stunting with yellowing or reddening of the leaves (which may also become brittle); the severity of the symptoms depends on the virus, species and cultivar of host plant, and environmental conditions. Probable members: milk-vetch dwarf virus, subterranean clover stunt virus, and tomato yellow top virus. When the basidiocarp is mature, the exoperidium (the outer layer(s) of the peridium) ruptures and peels back to form a stellate fringe; in Geastrum, an apical pore develops in the remaining peridium (endoperidium) to permit spore release. Failure of chemotherapy may be due to inaccessibility to antibiotics of intracellular spirochaetes [see. Small, benign, whitish, tumour-like nodules or clusters of nodules develop on skin and fins; the nodules contain greatly hypertrophied cells (to 1 mm diam. Transmission occurs chiefly via the egg, although horizontal transmission can occur. Lysis inhibition results in the formation of plaques which each have a turbid halo. In a phage-infected cell, a holin must be active only after normal phage assembly has been completed; if lysis occurred too early then fewer (or no) mature phages would be released Lyssavirus when the cell burst. Such early lysis was reported with a strain of phage l containing a mutant S gene [Mol. In some holin-encoding genes there are two start codons (separated by one or two codons), i. The shorter product is the holin, while the longer polypeptide seems to be an inhibitor of holin activity; this arrangement may be a mechanism for controlling the timing of cell lysis [Mol.
Good-quality final effluent depends on efficient flocculation (= aggregation) of the organisms, this facilitating clarification of the effluent by sedimentation. It consists of a submerged bed of fine granular material coated with biofilm; the sewage passes downwards through the bed while air is pumped in at the base of the bed. Because the granules are small, the system can function as a mechanical filter (for fine particulate matter) as well as allowing mineralization of dissolved organic matter. This reduces the bulk of sludge, giving a less offensive material which can be de-watered in sludge-drying beds; much of the carbon is eliminated as methane (which can supply most or all of the energy needs of the plant). The Immedium filter is a sand filter in which the grain size increases progressively from top to bottom; effluent flows upwards through the filter. Other forms of filter, and grassland irrigation, are also used for tertiary treatment. Phosphorus has been removed 701 by using a cycle of alternating anaerobic and aerobic treatments. An individual colony in the lower (anaerobic) part of the agar can be removed for subculture. Adult sheep typically develop vesicular, scabforming lesions on the skin; there is no systemic involvement and mortality rates are generally low, but in ewes the disease may predispose towards mastitis if the udder is affected. Aquatic bivalve molluscs (clams, cockles, mussels, oysters etc) obtain their food by filtering microscopic organisms from the ambient water. Any human pathogens present in the water can thus be concentrated in the bodies of the shellfish and can cause disease when these are eaten by humans. The shiga holotoxin consists of an A subunit associated with a pentameric ring of B subunits. All members of the shiga toxin family appear to share a common membrane receptor site and apparently have the same mode of action. However, it has been suggested that they may act as vasculotoxins whose primary target is the vascular endothelium. Most strains ferment mannitol but not sucrose or lactose; serotype 6 includes the Newcastle strain (mannitol not fermented, gas produced from glucose), the Manchester strain (acid and gas from glucose and mannitol), and the Boyd 88 strain (acid, no gas, from glucose and mannitol). Mannitol is fermented; fermentation of lactose and sucrose is detectable after 24 hours. Hardwood logs are inoculated via drill-holes; fruiting, which occurs in spring and autumn, begins after ca. Shwartzman reaction the local Shwartzman reaction involves localized skin necrosis which occurs when an intravenous injection of. Cells: cocci or coccoid forms which occur singly or in clusters within a common capsule. The two main structural classes of siderophores are catecholamides and hydroxamates; a given organism may produce siderophores of one or both classes. One example is enterobactin (= enterochelin): a cyclic trimer of 2,3-dihydroxy-N -benzoyl-Lserine produced. There are many examples of the way in which the timing of gene expression is controlled by the activity of particular sigma factor(s). In vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis the major sigma factor is s43 (formerly called s55; encoded by gene rpoD); this sigma factor shows some homology with the E. A sigma factor may be present at low levels during normal growth but up-regulated under appropriate conditions.
Up to 30% of psychiatric admissions are prompted by attempted suicide via overdosage. Acetaminophen toxicity is the most common pharmaceutical agent causing fatalities. Other drug-related fatalities are commonly due to analgesics, antidepressants, sedative-hypnotics, neuroleptics, stimulants and street drugs, cardiovascular drugs, anticonvulsants, antihistamines, and asthma therapies. Nonpharmaceutical agents implicated in fatal poisoning include alcohols and glycols, gases and fumes, chemicals, cleaning substances, pesticides, and automotive products. The Physicians Desk Reference, regional poison control centers, and local/hospital pharmacies may be useful for identification of ingredients and potential effects of toxins. The diagnosis of poisoning in cases of unknown etiology primarily relies on pattern recognition. The first step is a physical exam with initial focus on the pulse, blood pressure, respiratory rate, temperature, and neurologic status and then characterization of the overall physiologic state as stimulated, depressed, discordant, or normal (Table 31-1). Examination of the eyes (for nystagmus, pupil size, and reactivity), abdomen (for bowel activity and bladder size), and skin (for burns, bullae, color, warmth, moisture, pressure sores, and puncture marks) may narrow the diagnosis to a particular disorder. When the history is unclear, all orifices should be examined for the presence of chemical burns and drug packets. Hypoglycemia may be due to poisoning with -adrenergic blockers, ethanol, insulin, oral hypoglycemic agents, quinine, and salicylates, whereas hyperglycemia can occur in poisoning with acetone, -adrenergic agonists, calcium channel blockers, iron, theophylline, or Vacor. Toxicologic analysis of urine and blood (and occasionally of gastric contents and chemical samples) may be useful to confirm or rule out suspected poisoning. Quantitative analysis is useful for poisoning with acetaminophen, acetone, alcohol (including ethylene glycol), antiarrhythmics, anticonvulsants, barbiturates, digoxin, heavy metals, lithium, salicylate, and theophylline, as well as for carboxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin. Resolution of altered mental status and abnormal vital signs within minutes of intravenous administration of dextrose, naloxone, or flumazenil is virtually diagnostic of hypoglycemia, narcotic poisoning, and benzodiazepine intoxication, respectively. Poisoning and Drug Overdose Goals of therapy include support of vital signs, prevention of further absorption, enhancement of elimination, administration of specific antidotes, and prevention of reexposure. Drug-induced pulmonary edema is usually secondary to hypoxia, but myocardial depression may contribute. Seizures are best treated with -aminobutyric acid agonists such as benzodiazepines or barbiturates. The efficacy of activated charcoal and gastric lavage decreases with time, and there are insufficient data to support or exclude a beneficial effect when they are used >1 h after ingestion. Activated charcoal is prepared as a suspension in water, either alone or with a cathartic. It is given orally via a nippled bottle (for infants), or via a cup, straw, or small-bore nasogastric tube. Charcoal may inhibit absorption of other orally administered agents and is contraindicated in pts with corrosive ingestion. Place pt in Trendelenburg and left lateral decubitus position to minimize aspiration (occurs in 10% of pts). Lavage is contraindicated with corrosives and petroleum distillate hydrocarbons because of risk of aspiration-induced pneumonia and gastroesophageal perforation. Whole-bowel irrigation may be useful with ingestions of foreign bodies, drug packets, and slow-release medications. Dilution of corrosive acids and alkali is accomplished by having pt drink 5 mL water/kg. Endoscopy or surgical intervention may be required in large foreign-body ingestion, heavy metal ingestion, and when ingested drug packets leak or rupture. Syrup of ipecac, once the most commonly used decontamination procedure, has no role in the hospital setting. Some argue it can still be considered for the home management of patients with accidental ingestions, reliable histories, and mild predicted toxicity when transport to a hospital site is prolonged. It is administered orally in doses of 30 mL for adults, 15 mL for children, and 10 mL for infants. Phentolamine, a nonselective 1adrenergic receptor antagonist, for severe hypertension due to 1adrenergic agonists; propranolol, a nonselective blocker, for hypotension and tachycardia due to 2 agonists; labetalol, a blocker with -blocking activity, or phentolamine with esmolol, metoprolol, or other cardioselective blocker for hypertension with tachycardia due to nonselective agents (blockers, if used alone, can exacerbate hypertension and vasospasm due to unopposed a stimulation); benzodiazepines; propofol. Physiologic stimulation (Table e35-2); pronounced gastrointestinal symptoms and agonist effects (see above).

Overall, the risk of leukemia is increased 60-fold in workers exposed to the highest atmospheric concentrations of benzene. Diagnosis: Acute myelogenous leukemia the answer is A: Chronic myelogenous leukemia. The evidence that whole-body radiation can lead to cancer is incontrovertible and comes from animal experiments and studies of the effects of occupational exposure, radiation therapy for nonneoplastic conditions, the diagnostic use of certain radioisotopes, and the atom bomb explosions. Some survivors of the atom bomb explosions and patients subjected to spinal radiation later developed chronic myelogenous leukemia. Although the other choices may lead to hepatosplenomegaly, they are not linked to acute radiation exposure. Vitamin K deficiency is common in severe fat malabsorption, as seen in celiac sprue and biliary tract obstruction. The destruction of intestinal flora by antibiotics may also result in vitamin K deficiency. Deficiency of vitamin K can be serious because it can lead to catastrophic bleeding. A laceration is a linear tear of the skin produced by a force that causes unidirectional displacement. Physical examination shows generalized lymphadenopathy, most prominent in the cervical lymph nodes, and mild hepatosplenomegaly. Pelvic examination is exquisitely painful and reveals an illdefined thickening in both adnexae. Physical examination shows an extensive, desquamative maculopapular rash of the palms and soles (shown in the image). Which of the following lesions is also expected in this patient at this stage of his disease Physical examination shows an elevated cutaneous papule with bloody purulent exudate. The rash disappears, but 1 year later, the patient develops arthralgias and right facial nerve palsy. Postmortem examination demonstrates bilateral adrenal hemorrhages (shown on right). Her urine appears dark on visual inspection, and a urine dipstick is positive for hemoglobin. An X-ray film of the chest shows multiple areas of consolidation, with a large cavity in the right upper lobe. Examination of the lungs at autopsy discloses multiple, sharply delineated, gray foci with hemorrhagic borders. Which of the following mechanisms of disease best accounts for these pathologic findings Physical examination shows marked pallor, respiratory distress, nasal flaring, and intercostal retractions. There are enlarged cells with prominent, dark-blue nuclear inclusions (shown in the image). His past medical history is significant for a splenectomy following a motor vehicle accident 3 years ago. Physical examination shows puffiness around the eyes and pitting edema of the lower extremities. Blood analysis discloses reduced serum levels of C3 and an elevated titer of antistreptolysin O antibodies. A 6-month-old female infant is brought to the physician with a 2-day history of severe cough, wheezing, and respiratory distress. An autopsy shows necrotizing bronchitis and diffuse, hemorrhagic necrotizing pneumonia. Her parents report that her rash began in the form of pink papules behind the ears and spread around her body. Sputum cultures are negative, and the patient does not respond to antibiotic therapy. Histologic examination of the lungs at autopsy shows giant cells with up to 100 nuclei (shown in the image). The patient reports that a number of similar cases have occurred recently in the building where he works. An X-ray film of the chest shows an ill-defined area of consolidation at the periphery of the right middle lobe and mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
References: