
Simulation: An activity that mimics the reality of a clinical environment and is designed to demonstrate procedures, decisionmaking, and critical thinking through techniques 38 such as roleplaying and the use of devices. Spiritual Care: "Interventions, individual or communal, that facilitate the ability to experience the integration of the body, mind, and spirit to achieve wholeness, health, and a sense of connection to self, others, and a higher power" (American Nurses Association and Health Ministries Association, 2005, p. It is that part of people that seeks healing and reconciliation with self or others (Puchalski, 2006). Clinical prevention and population health curriculum framework for health professions. Clinical prevention and population health curriculum framework: the nursing perspective. American Association of Colleges of Nursing (2002) Hallmarks of the professional nursing practice environment. The Future of the Nursing Workforce in the United States: Data, Trends and Implications. Prйcis of Chapters from Educating Nurses: Teaching and Learning for a Complex Practice of Care Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (n. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Merck Company Foundation (2007). Evaluating interprofessional education: Two systematic reviews for health and social care. Presented at the American Physical Therapy Meeting on February 7, 2008 in Nashville, Tenn. Health care at the crossroads, Strategies for addressing the evolving nursing crisis. Cultural humility versus cultural competence: A critical distinction in defining physician training outcomes in multicultural education. Plain language: A promising strategy for clearly communicating health information and improving health literacy. This task force was comprised of individuals representing an array of experts in baccalaureate nursing education, including deans and faculty representatives. Additionally, a chief nurse executive represented the practice setting on the committee (see Appendix A). The task force began their work by reviewing the literature and considering the changes occurring in health care, higher education, and health professions education. In February 2007, the task force convened a group of 20 stakeholders representing leaders from higher education, professional nursing, and interprofessional education in June 2007, three additional stakeholders met with the task force (see Appendix C). These leaders were asked to identify, from their own perspectives, the anticipated role of the professional nurse in the future healthcare system and the critical competencies needed to function in this role. The next phase consisted of a series of five regional meetings from September 2007 to April 2008. The purpose of these meetings was to gather feedback and to build consensus about the Essentials draft document. Participants, including nurse educators, clinicians, administrators, and researchers representing a range of nursing programs, specialties, and organizations, discussed, debated, and made recommendations regarding the draft document. Over 700 individuals, representing all 50 states and the District of Columbia, participated in the consensusbuilding process. In addition, 329 schools of nursing, 11 professional organizations, and 13 healthcare delivery systems were represented (see Appendices D, E, & F). To ensure a broad base of nursing input, the task force sought the participation of a wide range of nursing organizations and many of these organizations such as the American Academy of Nursing, Sigma Theta Tau, and American Organization of Nurse Executives sent written feedback to the task force. Nursing administrators and clinicians were specifically asked to participate to ensure that the recommendations for nursing education would address future healthcare practice. Participants in the regional meetings were asked to focus on the rationale supporting each Essential and a list of end of program outcomes. In addition, the participants provided input into the development of supporting documents including a list of integrative learning strategies, quality indicators, and clinical learning environments. One or more specific behaviors related to risky alcohol and drug use are targeted. It is comprehensive (comprised of screening, brief intervention/treatment, and referral to treatment). Primary care centers, hospital emergency rooms, trauma centers, and community health settings provide opportunities for early intervention with at-risk substance users before more severe consequences occur.
Knowing the prospective audience helps the writer decide what information to include in the research report. An article directed toward a narrow audience will have a different perspective than one submitted to a journal that is relevant to a broad range of disciplines. Regardless of the audience, findings and conclusions must be stated clearly with as few words as possible. Returning to the original reference is required as the author who first cites the article, i. A return to an original document ensures that both the original intent of a statement or finding and the details of the citation are accurate. Authors are required to adhere to the referencing guidelines of the publication to which they are submitting. Attendees received a list of resources to utilize as they develop their writing skills. Published reports particularly in peer-reviewed journals have undergone rigorous reviews so using them as a guide can be advantageous. Seuss, "So the writer who breeds more words than he needs is making a chore for the reader who reads. For journal submissions, the process is used to ensure a level of confidence in the rigor of the research process utilized to conduct a scientific investigation and the accuracy of the study findings and conclusions presented. Papers published in peer-reviewed journals are assumed to have a higher level of quality than those published elsewhere. For non-scientists, peer-reviewed publications remain the "gold standard" as credible, trusted sources of information. An editorial by William Perrin explored the issues that editors face in finding individuals who will agree to serve as reviewers. The worst case scenario for the editor is having to reach out to reviewers who are not experts in the subject area or not as closely related to the field, increasing the likelihood that the quality of the review will be less than desired. Reviewer Responsibilities the primary responsibilities of a reviewer are to inform the editor about whether a manuscript is acceptable for publication and to provide the author with an understanding about how to improve the submission. Reviewers should not approach a manuscript review thinking about how they would have conducted the study. A request for additional data should not be made lightly, as it places considerable burden on the authors. It is important to remember that submitted manuscripts represent a body of work that has been completed; therefore, if the stated conclusions in the paper are not supported by the work described, then the reviewer should recommend to the editor that the paper be rejected. Second, reviewers may fail to consider whether the paper is appropriate for publication based upon how well the paper aligns with the stated goals and requirements of the journal. A reviewer needs to decide whether a paper that is well-written and novel should be accepted if the paper has not been constructed according to stated guidelines. Reviewers also should consider the amount of work that will be required by the author to revise the paper to meet posted journal standards. The reviewer should clearly communicate these concerns with the editor early in the review process to come to a consensus about how to advise the author about needed revisions. The following is a list of important aspects of reviewing for peer-reviewed journals: 1. Editors may have limited numbers of reviewers with the expertise needed for a particular paper. If reviewers fail to respond, it delays the entire process for the authors and the editorial staff. Many reviewers find ways to reject a paper expecting authors to convince them otherwise. Good reviews help authors improve their work even if their papers are not accepted for publication. Reviews that "tear a paper apart" are not useful to the editor, author or reputation of the journal. The review should provide a balance between positive feedback and critical assessment of what needs to be accomplished to improve the paper. One might wish to approach every review as if it were a graduate student who needs to be mentored. Also, be a role model of good writing by providing reviews that are free of typos and spelling errors. Most reviewer evaluation forms have a section where reviewers can provide confidential comments to the editor.
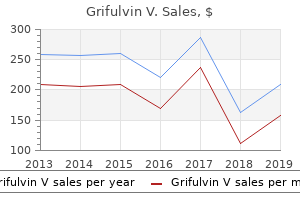
Unfortunately, the information is procedure-related and only indirectly patient-related. On average, two of the eight most common procedures were performed on most patients because the sum of the percentage of patients receiving a procedure is nearly twice that of procedures. In 2011, the number of patients had increased to 741,700, but total procedures for the same eight common procedures jumped even more to 1. This is an increase in the number of procedures by 17%, but only a 12% increase in the number of patients. Because of the increase in spinal fusion and other procedures, as subsequently discussed, hospital diskectomies constitute 28% and 25% of all Copyright © 2014 by the United States Bone and Joint Initiative. Although an absolute larger number of procedures in 2011, diskectomies represent a decreasing share of all procedures in 2011. To what degree this reflects a transfer of procedures to surgicenters is unknown because there is currently no national database. Spinal fusion procedures were listed as the main hospital procedure, being performed on 380,000 patients in 2007 and 457,500 patients in 2011. The majority of insertions of spinal devices, the third most common procedure group, likely occurred in patients with spinal fusions. If we assume that all patients in whom spinal devices were inserted also were fused, only 142,000 patients who were fused did not get a spinal device (18%). Spinal decompression, which may or may not be performed in conjunction with a spinal fusion or in conjunction with a diskectomy, accounted for 14% of all procedures in 2007 and 12. The number of spinal decompression procedures performed, along with other procedures for which inpatient hospitalization is not always required, may not be reflected accurately because an increasing number of these patients are operated on in outpatient surgicenters and facilities. Spinal Fusion: Spine Procedures the rate of spinal fusion procedures has risen rapidly over the past several decades. Spinal fusion is performed either alone or in conjunction with decompression and/or reduction of a spinal deformity. Between the years 1998 and 2011, the number of spinal fusion procedures has more than doubled, from 204,000 in 1998 to 457,000 in 2011. Apart from the period from 2002 to 2004, the increase on a biyearly basis is in the double digits. Relating the number of patients operated on to the estimated population age 18 years and older, the rate has gone from 110 per 100,000 persons in 1998 to 199 per 100,000 in 2011. During the same time period, refusion rates increased by 171%, from 6 to 14 persons per 100,000. Between 1998 and 2011, the average age of patients operated on with a fusion procedure has increased from 49 years to just under 56 years. The mean hospitalization charge in 1998 was $26,000 ($36,000 in 2011 dollars); while in 2011 the charge was $102,000. An increased use of instrumentation and biologicals (mainly bone substitutions) contribute to the higher cost. Spinal refusions are even more expensive, with an average charge of $123,000 in 2011. However, because spinal refusions are a small proportion of all fusion procedures, they account for only 7. This, of course, does not mean that cost or reimbursement was even close to these dollar numbers. These charges are based on what hospitals set as their charges, and do not reflect the contractual agreements they have with the payor community. Likely explanations for the increase in spinal fusions are advances in technology, including the development of new diagnostic techniques and new implant devices that allow for better surgical management. In addition, there has been increased training in spinal surgery and the population has aged, bringing with it the inherent medical problems that aging incurs. Further, quality of life expectations have increased, making patients less accepting of an ongoing back problem and more likely to look for a surgical solution. Lumbar fusion rates and cervical fusion rates are both increasing rapidly, while thoracic fusions continue to be less frequent. Lumbar fusions remain the most common, constituting 52% of all spine fusion procedures in 2011. Spinal refusions occur most often to the lumbar region, accounting for 65% of both refusion procedures and refusion patients. Patients in the 45- to 64-year age group were slightly more likely to have a fusion procedure than those younger or older.
Willner S: Continuous screening and treatment of teenage scoliosis is recommended. Juvenile Idiopathic Scoliosis: Spinal Curvature In 12% to 21% of idiopathic scoliosis cases, the diagnosis is made between 4 and 10 years of age. Between the ages of 4 and 6 years, the female-to-male ratio of juvenile idiopathic scoliosis is 1:1. However, the ratio of female to male cases rises to between 2:1 and 4:1 in children between the ages of 4 and 10 years, and to 8:1 in children who are 10 years of age or older. Bracing can be done either on a part-time or full-time basis, depending on the size of the curve as well as the age of the child. Approximately 70% of patients with juvenile idiopathic scoliosis exhibit curve progression and require some form of treatment. In a study conducted in 1981, 55 of 98 patients (56%) with juvenile idiopathic scoliosis required spinal surgery. Infantile Idiopathic Scoliosis: Spinal Curvature Infantile scoliosis currently accounts for less than 1% of all cases of idiopathic scoliosis in the United States. Boys are affected by infantile idiopathic scoliosis at a higher rate than girls (3:2 ratio). Past studies have indicated this rare type of scoliosis occurs more frequently in Europe than in North America. Several common measurement techniques are used, with angles 20° generally considered at low risk for progression. Surgical treatment should be considered when nonsurgical measures, including both bracing and casting, are not successful. Surgical treatment is utilized when a curve is 45° and progressive in an immature child. Surgical options currently utilized include various types of spinal fusion or hemiepiphysiodesis, a minimally invasive implant procedure to slow progression of curve growth. Mehta M: the rib-vertebra angle in the early diagnosis between resolving and progressive infantile scoliosis. Congenital Scoliosis: Spinal Curvature Congenital scoliosis is believed to affect approximately one child for every 1,000 live births. In cases of congenital scoliosis, additional congenital conditions, such as chest wall malformation or kidney or heart abnormalities, are often present. Treatment options for congenital scoliosis are bracing and/or surgery, and are similar to those discussed for idiopathic scoliosis. Bracing is not as effective for congenital scoliosis as it is for idiopathic scoliosis. Major abnormal spinal deformity presenting during infancy or early childhood poses a clinical problem because of the anticipated long growth period (at least 10 years), variable presentation and treatment methods, and the length of time that must pass before meaningful outcome results can be assessed in the small number of patients for definitive studies. Curves that result from congenital scoliosis are often not treated as easily as idiopathic curves because the deformity is in the bones rather than the soft tissue, causing the curve to be rigid. These include muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, spina bifida, and spinal muscular atrophy. Scoliosis associated with these conditions is referred to as neuromuscular scoliosis. Both the likelihood and the severity of the scoliosis generally increases with the severity of the underlying condition. For example, a child with severe cerebral palsy who is unable to walk is more likely to have severe scoliosis than a child with mild cerebral palsy who can walk. Resource Utilization: Scoliosis in Children, Spinal Curvature Because of the low prevalence of scoliosis in children and adolescents, analysis of the health care impact this condition causes is difficult. However, the impact of scoliosis over a lifetime in terms of pain, inability to work, and cost to the health care system are substantial. In 20102011, 92% of the 663,700 health care visits with a diagnosis of scoliosis for those under the age of 18 years were classified as idiopathic scoliosis. The majority (94%) were outpatient visits to either an outpatient clinic or physician office. Only 3% represented hospital discharges; however, this still accounted for 20,100 discharges for this often painful condition in children and adolescents. Spinal fusion was the most common surgery performed, followed by instrumentation and decompression. Patients who had an instrumentation procedure had the highest average charges of $165,600, although this may have been in conjunction with another procedure.
Diseases
Parenting style and parental healthy eating values in relation to healthfulness of food choices Rachel Lucas-Thompson, Dan J. Ruzek, David Grissmer (Event 2-145) Paper Symposium Meeting Room 412 (Hilton Austin) Friday, 12:15pm-1:45pm 2-145. Greenberg (Event 2-144) Paper Symposium Meeting Room 410 (Hilton Austin) Friday, 12:15pm-1:45pm 2-144. Moore, Rima Salah, James Leckmann Impact Evaluation of the the AeioTu Program in Colombia among Low-Income Children Milagros Nores, Raquel Bernal Building a Culture of Respecting Difference: Lessons from Northern Ireland Siobhan Fitzpatrick, Paul Connolly, Pauline Walmsley (Event 2-146) Paper Session Meeting Room 416A (Hilton Austin) Friday, 12:15pm-1:45pm 2-146. Sleep as a mediator of environmental impact Chair: Rebecca H Berger the association between home chaos and academic achievement: the moderating role of sleep duration Rebecca H Berger, Carlos Valiente, Anjolii Diaz, Tracy Spinrad, Nancy Eisenberg, Sarah VanSchyndel, Jody Southworth Associations between objective sleep and weight-related indicators in middle childhood: Preliminary findings from a twin study Reagan S Breitenstein, Leah D. Doane, Cindy Le, Saulo Corona, Allison Fossella, Kathryn Lemery-Chalfant Longitudinal Associations between Sleep Disturbance and Psychiatric Symptoms in Early Adolescence: Moderation by Sex and Puberty Jack Peltz, Thomas G. Caserta the Influence of Neighborhood, Family, Peer Factors on Adolescent Sleep Quality among Low-Income Families Chao Liu, Michael M. Family Processes, Tornado-Related Trauma Exposure and Child Adjustment: Multi-Method Perspectives of Risk and Resilience Chair: Eric M. Vernberg 7 the Modulation of Infant and Maternal Gaze in Naturalistic Play: A Dual Head-mounted Eye-tracking Study Nadia Neesgaard, Natasa Ganea, Atsushi Senju, Tim J. Culham, Gudrun Schwarzer the Effect of Color Information on Location Memory in Children Megan Louise Whelen, Hanako Yoshida Eye-Tracking Study of Memory for Faces in Children and Adults Erin Bertero, Leslie Rollins, Laurie Hunter, Kelly Bowers 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Friday, 2:00pm-3:15pm (Event 2-148) Poster Session Exhibit Hall 4 (Austin Convention Center) Friday, 2:00pm-3:15pm 2-148. Segalowitz, Karen Milligan Subcomponents of attention as predictors of math and pre-literacy skills among low-income preschoolers Katherine A. Shuan Ho, Katherine Guyon-Harris, Sarah Ahlfs-Dunn, Jessica L Riggs, Brittani Hollern, Beth Jakubowski, James E Swain Amygdalar fear responsivity in disruptive youth: the interaction between trauma exposure and callousunemotional traits. Nadja Richter, Marie Manner, Carolyn Lasch, Kirsten A Dalrymple, Jed T Elison Sociodemographic Indicators of Health Disparities: Parent and Provider Concerns about Toddlers Enrolled in Early Intervention Devon Oosting, Elizabeth Frenette, Abbey Eisenhower, Chris Sheldrick, Alice C. Carter Spontaneous Language During the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule in Young Children With or Without Autism Spectrum Disorder Danielle L. Stevenson No Relationship Between Early Androgen Exposure and Autistic Traits Karson T. Kung, Carlo L Acerini, Wendy V Browne, Mihaela Constantinescu, Vivette Glover, Peter C Hindmarsh, Ieuan A Hughes, Sharon Neufeld, Rebecca M Noorderhaven, Thomas G. Weiss, Kristen Lyall, Martin Kharrazi, Lisa A Croen Persistent and Late-Onset Preschool Language Impairment: the Role of Executive Function Hui-Chin Hsu Internalizing and Externalizing Behaviors of Children with and without a Writing Disability Edmund Peter Fernandez, Rebecca L. Jordan, LaraJeane Costa, Stephen R Hooper 59 Reciprocal Relationships Between Physical Aggression and Fast Food Consumption in U. Gotlib Bidirectional Effects of Callous-Unemotional Traits and Negative Parenting Cortney Simmons, Paul Frick, Laurence Steinberg, Elizabeth Cauffman Friendship Quality and Peer Group Identification Moderate the Association Between Peer Delinquency and Adolescent Substance Use Samuel Noah Meisel, Craig Colder Association Between Perceived Physical Appearance and Anxiety Symptom Trajectories during Adolescence Anna Vannucci, Christine M Ohannessian, Jessica W. Guite A multi-level analysis approach to fear learning across development Einav Gafni, Shani Danon, Rivkah Ginat-Frolich, Tomer Shechner Behavioral Inhibition System Effects on Conditional Response Strength after Latent Inhibition Training in Children Kayla Hunt, Judith Dygdon Social Anxiety and Uncinate Fasciculus Integrity in Adolescents Adopted From International Orphanages Lauren Demers, Amanda S. Shaw, Stephanie Sitnick, Erika E Forbes Puberty and alcohol use: indirect and interactive effects with impulsivity and sensation seeking supporting a dualrisk model Charlie Rioux, Natalie Castellanos Ryan, Sophie Parent, Frank Vitaro, Richard Tremblay, Jean R. Sйguin 86 Evaluating the Moderating Role of Classroom Characteristics on the Relationship between Grit and Math Achievement Catherine M. Whitney Moore Motivation for Competitive Swimming in Adolescents: Ethnic and Gender Differences Jessica R Gladstone, Allan Wigfield Mediating Roles of Emotions and Emotional Awareness between Music Participation and Well-Being among Hong Kong Chinese Adolescents Man Chong Leung, Rebecca Y. Cheung An Examination of Extracurricular Activity Participation in Early Childhood Laura L. Koomen 114 Mother-infant interactions for first-borns versus later children and the factors that influence those interactions Tasha LaNae Olson, Lori A. Dodge, Patrick Malone, Paul Oburu, Concetta Pastorelli, Emma Sorbring, Sombat Tapanya, Liliana Maria Uribe Tirado, Arnaldo Zelli, Liane Peсa Alampay, Suha Al-Hassan, Dario Bacchini, Anna Silvia Bombi, Marc Bornstein, Lei Chang, Kirby Deater-Deckard, Laura Di Giunta 168 Parental Monitoring Alters the Degree to which Adolescents are Similar to their Friends in Terms of Aggression Yea Seul Pyun, Celeste Sangiorgio, Kдtlin Peets, Ernest V. Sullivan, Justin Parent, Rex Forehand, Jennifer Elizabeth Potts Dunbar, Kelly Haker Watson, Alexandra H. Bettis, Bruce Compas 178 Associations between Parental Psychological Control and Adolescent Outcomes: A Multidimensional Approach Katelyn Romm, Lauren Alvis, Aaron Metzger 179 An Analysis of Mind-Mindedness, Parenting Stress, and Parenting Style in Families with Multiple Children Abbi Graves, Ulrich Mueller 180 Parent Training and Skill Utilization Among Spanish- and English-Speaking Families Francisco Giovanni Ramos, Angela M.
They can discourage the sale and promotion of alcohol and other substances to minors and support evidence based programs to prevent and reduce youth substance use. Continue to collaborate with the federal initiative to reduce prescription opioid- and heroin-related overdose, death, and dependence. Department of Health and Human Services to identify and implement evidence-informed solutions to the current opioid crisis. Coordinated federal, state, local, and tribal efforts are needed to promote a public health approach to addressing substance use, misuse, and related disorders. As discussed throughout this Report, widespread cultural and systemic issues need to be addressed to reduce the prevalence of substance misuse and related public health consequences. Government agencies have a major role to play in: $ $ $ $ $ $ $ Improving public education and awareness; Conducting research and evaluations; Monitoring public health trends; Providing incentives, funding, and assistance to promote implementation of effective prevention, treatment, and recovery practices, policies, and programs; Addressing legislative and regulatory barriers; Improving coordination between health care, criminal justice, and social service organizations; and Fostering collaborative initiatives with the private sector. Improve coordination between social service systems and the health care system to address the social and environmental factors that contribute to the risk for substance use disorders. Social service systems serve individuals, families, and communities in a variety of capacities, often in tandem with the health care system. Social workers can play a significant role in helping patients with substance use disorders with the wrap-around services that are vital for successful treatment, including finding stable housing, obtaining job training or employment opportunities, and accessing recovery supports and other resources available in the community. In addition, they can coordinate care across providers, offer support for families, and help implement prevention programs. Child and family welfare systems also should implement trauma-informed, recovery-oriented, and public health approaches for parents who are misusing substances, while maintaining a strong focus on the safety and welfare of children. Implement criminal justice reforms to transition to a less punitive and more health-focused approach. The criminal justice and juvenile justice systems can play pivotal roles in addressing substance userelated health issues across the community. Less punitive, health-focused initiatives can have a critical impact on long-term outcomes. For example, drug courts have been a very successful model for diverting people with substance use disorders away from incarceration and into treatment. Many prisoners have access to regular health care services only when they are incarcerated. Significant research supports the value of integrating prevention and treatment into criminal justice settings. Criminal justice systems can reduce these risks and reduce recidivism by coordinating with community health settings to ensure that patients with substance use disorders have continuing access to care upon release. Facilitate research on Schedule I substances Some researchers indicate that the process for conducting studies on Schedule I substances, such as marijuana, can be burdensome and act as disincentives. It is clear that more research is needed to understand how use of these substances affect the brain and body in order to help inform effective treatments for overdose, withdrawal management, and addiction, as well as explore potential therapeutic uses. To help ease administrative burdens, federal agencies should continue to enhance efforts and partnerships to facilitate research. For example, a recent policy change will foster research by expanding the number of U. Making marijuana available from new sources could both speed the pace of research and afford medication developers and researchers more options for formulating marijuana-derived investigational products. Researchers Conduct research that focuses on implementable, sustainable solutions to address high-priority substance use issues. This includes research on the basic genetic and epigenetic contributors to substance use disorders and the environmental and social factors that influence risk; basic neuroscience research on substance use-related effects and brain recovery; studies adapting existing prevention programs to different populations and audiences; and trials of new and improved treatment approaches. Focused research is also needed to help address the significant research-to-practice gap in the implementation of evidence-based prevention and treatment interventions. Research is needed to better understand the barriers to successful and sustainable implementation of evidence-based interventions and to develop implementation strategies that effectively overcome these barriers. These collaborations should also help researchers prioritize efforts to address critical ongoing barriers to effective prevention and treatment of substance use disorders. Effective communication is critical for ensuring that the policies and programs that are implemented reflect the state of the science and have the greatest chance for improving outcomes. Scientific experts have a significant role to play in ensuring that the science is accurately represented in policies and program. Many programs and policies are often implemented without a sufficient evidence base or with limited fidelity to the evidence base; this may have unintended consequences when they are broadly implemented.
Average incremental expenditures for persons of similar characteristics but without a musculoskeletal disease grew from $1,280 to $2,075, but due to population growth and increased prevalence of the conditions, aggregate incremental expenditures grew from $97. Average per-person earnings losses between 1996 to 1998 and 2009 to 2011 due to musculoskeletal diseases increased from $596 to $1,224, while aggregate total earnings losses grew from $28. Incremental earnings losses increased dramatically, from $949 to $2,063 per person and from $46. Earlier estimates summarize the evidence from the studies conducted by Dorothy Rice and colleagues, the last two of which were from prior editions of the present study. The first, total cost, is an indication of all medical care costs and earnings losses incurred by persons with a musculoskeletal disease, regardless of the condition for which the cost was incurred. The second, incremental cost, is an estimate of the magnitude of cost that would be incurred beyond those experienced by persons of similar demographic and health characteristics but who do not have one or more musculoskeletal disease. Cost estimates are produced as the mean per-person medical care cost and as the aggregate, or sum of mean costs overall, associated with all persons with musculoskeletal diseases. Early editions of this book based estimates of the economic impact of musculoskeletal diseases on the Rice cost of illness methodology. The Rice model defines direct cost as those associated with all components of medical care (ie, inpatient and outpatient care, medications, devices, and costs associated with procuring medical care), and indirect cost such as those associated with wage loss due to morbidity or mortality, plus an estimate of intangible costs. In the Rice model, mortality accounted for 7% of total indirect medical cost for all conditions. Hence, total cost presented here represents an under-count by a similar percentage. Because musculoskeletal diseases have a smaller impact on mortality than most other major categories of illness, the under-count will be an unknown, but smaller, Copyright © 2014 by the United States Bone and Joint Initiative. The difference may be due to allocating a higher proportion of diagnoses to the musculoskeletal classification in the Rice study. A series of papers provide a detailed description of the methods of estimating total and incremental direct and indirect cost of conditions, and outline the regression model used to adjust for differences of persons with and without musculoskeletal diseases due to demographic characteristics and health status. However, the present analysis differs from prior analysis due to the use of a generalized linear model with a gamma distribution and a log-link, as opposed to a log transformation with a smearing estimate applied to back-transformed predicted values, in the stages predicting costs among individuals with any positive expenditures. The impact of sampling variability is partially mitigated by smoothing, or averaging, data across 3-year periods. Yelin E, Cisternas M, Pasta D, et al: Medical care expenditures and earnings losses of persons with arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States in 1997: Total and incremental estimates. Yelin E, Herrndorf A, Trupin L, Sonneborn D: A national study of medical care expenditures for musculoskeletal conditions: the impact of health insurance and managed care. Yelin E, Trupin L, Cisternas M: Direct and Indirect Costs of Musculoskeletal Conditions in 1997: Absolute and Incremental Estimates. Cohen S: Sample Design of the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. Cohen S: Sample Design of the 1997 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. Cohen S, DiGaetano R, Goksel H: Estimation Procedures in the 1996 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Household Component. Yelin E, Katz P: Labor force participation among persons with musculoskeletal conditions, 1970-1987: National estimates derived from a series of cross-sections. Conditions included in the base musculoskeletal disease rubric include spine conditions, arthritis and joint pain, the category that includes osteoporosis (other diseases of bone and cartilage), injuries, and an inclusive "other" category for the remaining conditions. Conditions selected for the cost analysis presented are based on condition topics included in this site. Estimates are also provided for a more expansive list of codes of musculoskeletal-related diseases that include conditions for which musculoskeletal diseases are either the primary and secondary cause of the condition. This more expansive list of conditions yields a vastly larger prevalence estimate than the base case list. However, it is reasonable to assume the cost of musculoskeletal diseases probably exceeds the conservative estimates presented here. For example, a person with bone metastases would incur costs to treat the bone manifestation, even though the cancer, not the bone condition, is the primary etiology. Musculoskeletal Injuries Open Wound of Neck: 874 Open Wound of Other and Unspecified Sites, Except Limbs: 879 Contusion of Trunk: 922 Contusion of Upper Limb: 923 Contusion of Lower Limb and of Other and Unspecified Sites: 924 Crushing Injury of Trunk: 926 Other Musculoskeletal Conditions Copyright © 2014 by the United States Bone and Joint Initiative. Sample N (annual) 6,964 7,004 6,025 6,814 8,252 9,166 9,337 8,874 8,947 8,791 8,812 9,181 9,323 9,522 Under 18 11. Year 1996-1998 1997-1999 1998-2000 1999-2001 2000-2002 2001-2003 2002-2004 2003-2005 2004-2006 2005-2007 2006-2008 2007-2009 2008-2010 2009-2011 Sample N (annual) 2,710 2,759 2,414 2,837 3,514 3,931 3,979 3,702 3,683 3,813 4,379 5,153 5,539 5,725 Under 18 [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] 18-44 25.
Tumors of Muscle Tissue Leiomyosarcomas Smooth muscle cells are found in internal organs such as stomach, intestines, blood vessels, or uterus. They can occur almost anywhere in the body, but most often are found in the uterus. A second common site is the retroperitoneum (back of the abdomen) and in the internal organs and blood vessels where leiomyomas also arise. Since they often arise from arteries, resection of these tumors frequently requires an immediate vascular reconstruction. Rhabdomyosarcomas Skeletal muscles are the voluntary muscles that control and allow movement of arms and legs and other body parts. These tumors commonly grow in the arms or legs, but they can also begin in the head and neck area and in reproductive and urinary organs, such as the vagina or bladder. They are treated with aggressive chemotherapy, as well as surgery and/or radiation in many cases. The aggressive treatments often cause permanent life-altering disability, even in survivors. The currently favored name for these sarcomas is malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. Tumors of Blood Vessels and Lymph Vessels Angiosarcomas Malignant tumors can develop either from blood vessels (hemangiosarcomas) or from lymph vessels (lymphangiosarcomas). These tumors often develop in a part of the body that has been exposed to radiation. They are difficult to cure as they spread through the bloodstream to other parts of the body and often spread extensively through the local tissues. Hemangiopericytoma these are tumors of perivascular tissue (tissue around blood vessels). They most often develop in the legs, pelvis, and retroperitoneum (the back of the abdominal cavity) and are most common in adults. They do not often spread to distant sites, but tend to recur where they started, even after surgery, unless widely excised. Following recent research and further histologic, genetic, and clinical evaluations, these have recently been reclassified as one end of the spectrum of malignant solitary fibrous tumors, or possibly identical to malignant solitary fibrous tumors. It usually invades nearby tissues, and sometimes can metastasize to distant parts of the body. Kaposi Sarcoma these cancers are composed of cells similar to those lining blood or lymph vessels. Tumors of Fibrous Tissue Fibrous tissue forms tendons and ligaments and covers bones, muscles and joint capsules, as well as other organs in the body. They have a characteristic herringbone cloth pattern when viewed under the microscope. They are most common between the ages of 20 years and 60 years, but can occur at any age, even in infancy. Due to their slow, insidious Copyright © 2014 by the United States Bone and Joint Initiative. The local recurrence rate is higher than many sarcomas, and has been reported to be as high as 50% in some studies. While death due to disease is uncommon (<5%), the local recurrences can cause significant local morbidity. Although they do not metastasize, they do form in response to genetic alterations identical to many cancers and can cause great disability and even death. These tumors can invade nearby tissues, causing great havoc and occasionally even death. Some doctors may consider these to be a type of low-grade fibrosarcomas; most, however, regard these as benign but locally aggressive. Certain hormones, particularly estrogen, may increase the growth of some desmoid tumors. Antiestrogen drugs are sometimes useful in treating desmoids that cannot be completely removed by surgery.
References: