
The age-adjusted incidence rate for prostate cancer was 167/100,000 from 2002 to 2006 (Figure 7. In Massachusetts, prostate cancer deaths decreased between 2002 and 2006, but this decline was not statistically significant. National incidence rates for prostate cancer also decreased non-significantly during this period. Mortality of Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer was the second leading cause of cancer deaths among Massachusetts males between 2002 and 2006, representing approximately 11% of all cancer deaths in this group. From 2002 to 2006, Massachusetts 132 Health of Massachusetts deaths due to prostate cancer decreased annually by 4. Other risk factors include a diet high in fat and animal protein and low in fiber and folic acid. Wellness and Chronic Disease 133 the age-adjusted incidence rates for colorectal cancer were 64/100,000 among males and 46/100,000 among females. Colorectal cancer in males decreased significantly from 2002 to 2006 at approximately 6% per year (Figure 7. National data show that colorectal cancer incidence rates decreased significantly by 2% per year from 1996 to 2005 for males. In Massachusetts the incidence rate of colorectal cancer among females decreased significantly by 5% per year from 2002 through 2006. Nationally, the incidence of colorectal cancer in females decreased significantly by 2% per year from 1996-2005. Mortality of Colorectal Cancer Colorectal cancer was the third leading cause of cancer death in Massachusetts for both males and females between 2002 and 2006. It accounted for approximately 9% of all cancer deaths in males and 10% of all cancer deaths in females. During this period, the age-adjusted mortality rate of colorectal cancer was 22/100,000 for males and 16/100,000 for females (Figure 7. From 2002 to 2006 colorectal cancer mortality decreased by 5% per year among males and 6% per year among females. Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which cancer cells develop in the lung tissue. Other risk factors include exposure to second-hand smoke; radon, a radioactive gas that damages lung cells; asbestos and other substances including arsenic, chromium, nickel, or tar; air pollution; a family history of lung cancer; a personal history of lung cancer; and age over 65. Mortality of Lung Cancer Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death for Massachusetts males and females between 2002 and 2006, accounting for approximately 29% of all cancer deaths in males and 26% of cancer deaths among females. Among Massachusetts males, mortality from lung cancer decreased significantly by 1% per year between 2002 and 2006. Among Massachusetts Wellness and Chronic Disease 135 females, mortality decreased non-significantly by 1% per year between 2002 and 2006. Disparities in Cancer From 2002 to 2006, Black males had the highest incidence rate of all cancer types combined (Figure 7. This rate was significantly higher than the rates for Asians and Hispanics, but not for Whites. Among men, Blacks had the highest age-adjusted mortality rates for all types of cancer combined from 2002 to 2006 (Figure 7. The mortality rate among Black males was significantly higher than the rates for the three other racial/ethnic groups, and these disparities were evident in each of the leading cancer types. From 2002 to 2006, Black males had the highest rates of prostate cancer incidence (247/100,000) (Figure 7. Nationally, prostate cancer incidence rates among Black males are decreasing, but the rates remain higher than among White males (236/100,000 vs. From 2002 to 2006, White males had the highest incidence rate of colorectal cancer (65/100,000), followed by 54/100,000 among Blacks, 46/100,000 among Hispanics, and 43/100,000 among Asians (Figure 7. From 2002 to 2006, lung cancer was the second leading cancer among males in all racial groups, except among Hispanic males, where it was the third leading cancer. Black men had significantly higher lung cancer mortality rates compared with White men (77/ 100,000 vs. From 2002 through 2006, White females had the highest incidence rate of all cancer types combined among all racial/ethnic groups (Figure 7.
Such plans may be generic for particular technologies rather than specific for individual systems. Implementation of surveillance will generally include a mixture of these approaches according to supply type and may involve using rolling programmes whereby systems are addressed progressively. Often it is not possible to undertake extensive surveillance of all community or household supplies. In these cases, well designed surveys should be undertaken in order to understand the situation at the national or regional level. It is increasingly common that analytical services are procured from accredited external laboratories. Some authorities are also experimenting with the use of such arrangements for services such as sanitary inspection, sampling and audit reviews. In response to reports of significant incidents, it is necessary to ensure that: - the event is investigated promptly and appropriately; - the cause of the event is determined and corrected; 86 5. The implementation of an audit-based approach places responsibility on the drinking-water supplier to provide the surveillance agency with information regarding system performance against agreed indicators. In addition, a programme of announced and unannounced visits by auditors to drinking-water suppliers should be implemented to review documentation and records of operational practice in order to ensure that data submitted are reliable. Such an approach does not necessarily imply that water suppliers are likely to falsify records, but it does provide an important means of reassuring consumers that there is true independent verification of the activities of the water supplier. The surveillance agency will normally retain the authority to undertake some analysis of drinking-water quality to verify performance or enter into a third-party arrangement for such analysis. Such an approach often implies that the agency has access to analytical facilities of its own, with staff trained to carry out sampling, analysis and sanitary inspection. Direct assessment also implies that surveillance agencies have the capacity to assess findings and to report to and advise suppliers and communities. A surveillance programme based on direct assessment would normally include: - specified approaches to large municipality / small municipality / community supplies and individual household supplies; - sanitary inspections to be carried out by qualified personnel; - sampling to be carried out by qualified personnel; - tests to be conducted using suitable methods by accredited laboratories or using approved field testing equipment and qualified personnel; and - procedures on reporting findings and follow-up to ensure that they have been acted on. For community-managed drinking-water supplies and where the development of inhouse verification or third-party arrangements is limited, direct assessment may be used as the principal system of surveillance. This may apply to drinking-water supplies in small towns by small-scale private sector operators or local government. Where direct assessment is carried out by the surveillance agency, it complements other verification testing. General guidance on verification testing, which is also applicable to surveillance through direct assessment, is provided in section 4. There will often be a large piped supply with household and public connections and a range of alternative drinking-water supplies, including point sources and vended water. In these situations, the surveillance programme should take account of the different sources of drinking-water and the potential for deterioration in quality during collection, storage and use. Furthermore, the population will vary in terms of socioeconomic status and vulnerability to water-related disease. In many situations, zoning the urban area on the basis of vulnerability and drinking-water supply arrangements is required. The zoning system should include all populations within the urban area, including informal and periurban settlements, regardless of their legal status, in order to direct resources to where greatest improvements (or benefits) to public health will be achieved. This provides a mechanism to ensure that non-piped drinking-water sources are also included within drinking-water supply surveillance activities. Experience has shown that zoning can be developed using qualitative and quantitative methods and is useful in identifying vulnerable groups and priority communities where drinking-water supply improvements are required. The precise definition of a "community drinking-water supply" will vary, but administration and management arrangements are often what set community supplies apart. Community-managed supplies may include simple piped water systems or a range of point sources, such as boreholes with hand pumps, dug wells and protected springs. The control of water safety and implementation of surveillance programmes for such supplies often face significant constraints. These typically include: - limited capacity and skills within the community to undertake process control and verification; this may increase the need both for surveillance to assess the state of drinking-water supplies and for surveillance staff to provide training and support to community members; and - the very large number of widely dispersed supplies, which significantly increases overall costs in undertaking surveillance activities. Furthermore, it is often these supplies that present the greatest water quality problems. Experience from both developing and developed countries has shown that surveillance of community-managed drinking-water supplies can be effective when well designed and when the objectives are geared more towards a supportive role to 88 5. Surveillance of community drinking-water supplies requires a systematic programme of surveys that encompass all aspects of the drinking-water supply to the population as a whole, including sanitary inspection (including catchments) and institutional and community aspects.
Syndromes
The optimal coating concentration of an antigen lot is determined by inspecting optical density values vs. If the old, established lot of antigen is available, wells A1, B1, C1, and D1 are filled with the old qualified antigen, and wells E1, F1, G1 and H1 are coated with the new antigen (see the plate layout figure below). If the old, qualified antigen is not available, all 8 wells are filled with the new antigen. Perform 2-fold serial dilutions from column 1 to column 10 by repeatedly mixing and transferring 100 l to the wells in the next column. After the 10th column, discard 100 l from the 10th column (so that the wells in column 10 have only 100 l). Rows C and D: Buffer ("background wells") Rows E and F: optimum dilution of the reference serum (007sp). Add the diluted reference serum to all wells in rows A, B, E and F and the diluent buffer to all wells in rows C, D, G and H. Plot the signal on the Y-axis and the logarithm of antigen concentration on the X-axis. For outcomes a) and b), pick the antigen concentration yielding the maximum signal because higher concentrations of antigen do not yield a higher signal. For outcome c), pick a coating concentration yielding the maximum possible signal with low background. However, this should not occur since the plates that were tested in the past are being used in this test. Note 2: Antigen titration should yield similar (to the previous) optimal coating concentrations. If marked differences in optimal coating concentrations are found, the new lot of the antigen should be evaluated for differences in purity and for differences in composition with other analytical techniques. Mean absorbance values and their variation from the 92 wells are calculated between wells on a single plate and between each plate. Add the serum dilution to all wells of the plates, excluding 4 blank wells where diluent alone is added. Note any trends in locations of the wells with deviations greater than 20% from the intraplate mean optical density. Plot the concentrations with the new lot (Y-axis) against those with old lot (X-axis). However, properties of polyclonal antisera vary from lot to lot, and each lot of polyclonal antisera must be tested for its binding specificity. The polyclonal antisera for human IgG should bind to all human IgG subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4) equivalently with minimal cross-reactivity to IgA or IgM (less than 5%). Dilute each of the human proteins (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4) to 1 g/ml in carbonate/bicarbonate buffer. D E F G H Old qualified 2є antibody 2 3 4 5 6 IgG IgA IgA IgM IgM New candidate 2є antibody 7 8 9 10 11 12 IgG IgG IgA IgA IgM IgM Diagram 2 1 A 1:250 B 1:500 C 1:1000 D 1:2000 E 1:250 F 1:500 G 1:1000 H 1:2000 IgG1 2 IgG1 3 IgG2 4 IgG2 5 IgG3 6 IgG3 7 IgG4 8 IgG4 Old qualified 2є antibody New candidate 2є antibody 2. Add 100 l of the dilutions of the secondary antibody to the appropriate wells (rows A through G) of the plate, and antibody buffer as a blank (see Diagram 2). To test for IgG specificity, select the dilution that produces an optical density of roughly 1 in the wells coated with IgG. Obtain the optical density of IgG, IgA and IgM isotype coated wells at the dilution of the secondary antibody. A balanced reagent should have a binding ratio close to 1 for all IgG subclass combinations. Also it is assumed that one new secondary antibody is being tested with one old secondary antibody. Dilute the standard serum (007sp) with 4 ml of the "absorption buffer" such that the optical density value at the end of the assay would be about 2. Although the exact dilutions are serotype specific, this dilution is usually about 1:1500 for 007sp (the reference standard). Transfer 200 l of the diluted serum to each well in row A of the "dilution plate". Add 100 l of the antibody buffer to wells in rows B through H in the "dilution plate". Prepare six 2-fold serial dilutions of the standard serum in the "dilution plate" by transferring 100 l from the wells in row A to those in row B etc.
The notification shall include information on the reason for and duration of the use. Additionally, upon activation of such a source, a sample shall be collected and analyzed for perchlorate, and the analytical result shall be reported to the State Board within 48 hours of activation. Unless directed otherwise by the State Board, analyses shall be made in accordance with U. With State Board approval and after completion of one year of monitoring, a water system may alternatively monitor one quarter of all units each calendar quarter. To meet the requirements of section 64418(a)(4), a public water system shall, pursuant to this section, conduct a customer survey and participate in, and provide information for, a public hearing held by the State Board. Notwithstanding the foregoing, where all the water supplied by a public water system for human consumption is treated by the public water system via a single device or facility, regardless of location of the device or facility, the public water system shall be considered to have centralized treatment. To meet the requirements of section 64420(d), a public water system shall, pursuant to this section, conduct a customer survey and participate in, and provide information for, a public hearing held by the State Board. If the water system serves multi-unit residential dwellings including, but not limited to , apartments and residential institutions, whether sub-metered or not, the water system shall provide notice to each resident of such residential dwellings. Samples collected shall represent the water quality in the affected portions of the system. A community water system using groundwater which serves 25-1000 persons may request from the State Board a reduction in monitoring frequency. A nontransient-noncommunity water system using groundwater which serves 25-1000 persons may request from the State Board a reduction in monitoring frequency if it has not violated the requirements in this article during the past twelve months. The minimum reduced frequency shall not be less than one sample in each calendar quarter during which the system provides water to the public. A system using groundwater under the direct influence of surface water shall begin monitoring at this frequency by the end of the sixth month after the State Board has designated the source to be approved surface water. The sample shall be collected within 24 hours of the exceedance and shall be analyzed for total coliforms. The supplier also shall require the laboratory to analyze the same sample for fecal coliforms or Escherichia coli (E. As a minimum, the analytical results shall be reported in terms of the presence or absence of total or fecal coliforms, or E. The water supplier shall also require the laboratory to immediately notify the State Board of any positive bacteriological results if the laboratory cannot make direct contact with the designated contact person within 24 hours. A single service connection system may request that the State Board allow the collection of the repeat sample set over a four-day period. For a water supplier that normally collects one or fewer samples per month, a repeat sample set shall be at least four samples for each total coliform-positive sample. The State Board will then determine how much time the supplier will have to collect the repeat samples. Other repeat samples shall be collected within five service connections upstream or downstream of the original site. At least one sample shall be from upstream and one from downstream unless there is no upstream and/or downstream service connection. If the supplier stops supplying water during the month after the total coliform-positive(s), at least five samples shall be collected during the first month the system resumes operation. A water supplier may request the State Board waive the requirement to collect at least five routine samples the following month, but a waiver will not be granted solely on the basis that all repeat samples are total coliform-negative. To request a waiver, one of the following conditions shall be met: (1) the State Board conducts a site visit before the end of the next month the system provides water to the public to determine whether additional monitoring and/or corrective action is necessary to protect public health. If a waiver is granted, a system shall collect at least one routine sample before the end of the next month it serves water to the public and use it to determine compliance with Section 64426. The water supplier shall require the laboratory to provide the supplier with documentation which shall include, but not be limited to: (A) A letter from the director of the laboratory having generated the data, confirming the invalidation request by reason of laboratory accident or error; (B) Complete sample identification, laboratory sample log number (if used), date and time of collection, date and time of receipt by the laboratory, date and time of analysis for the sample(s) in question; (C) Complete description of the accident or error alleged to have invalidated the result(s); (D) Copies of all analytical, operating, and quality assurance records pertaining to the incident in question; and (E) Any observations noted by laboratory personnel when receiving and analyzing the sample(s) in question. The supplier shall continue to re-sample at the original site within 24 hours and have the samples analyzed until a valid result is obtained. This shall include, but not be limited to: (A) Current operating procedures that are or could potentially be related to the increase in bacterial count; (B) Any interruptions in the treatment process; (C) System pressure loss to less than 5 psi; (D) Vandalism and/or unauthorized access to facilities; (E) Physical evidence indicating bacteriological contamination of facilities; (F) Analytical results of any additional samples collected, including source samples; (G) Community illness suspected of being waterborne; and (H) Records of the investigation and any action taken. A Tier 2 Public Notice shall be given for violations of paragraph (b)(1) or (2), pursuant to section 64463. A Tier 1 Public Notice shall be given for violations of paragraph (b)(3) or (4), pursuant to section 64463.
Chromosomal aberrations are found in a significant percentage of infants who have cystic hygromas, and these lesions are associated frequently with Turner, Noonan, and Down syndromes. Chapters 240, 308, 494, 497, 559, 560, 561, 562, 614, 640, 642, 672 Nelsons Essentials, 6e. Chapter 175 10 Part I u Head,Neck,andEyes 12 Salivary gland enlargement most commonly involves the parotid that obscures the angle of the mandible but may involve the submandibular or minor glands. Endemic goiter due to iodine deficiency is rare in the United States, with iodized salt availability. Salivary calculus formation may be associated with anticholinergic antihistamine drugs. A hard, rapidly growing nodule in the thyroid area should be assessed using a thyroid scan. Histologic examination of specimens obtained by fine needle aspiration or open biopsy are diagnostic indicators of carcinoma of the thyroid, including papillary, follicular, mixed differentiated, and medullary. Thyroid scan demonstrates "hot" or "cold" areas, which indicate increased or decreased activity. If the etiology cannot be determined, fine-needle aspiration or biopsy should be done to exclude malignancy. In addition to the thyroid, there is increase in size of the thymus, spleen, and retroorbital tissue (exophthalmos). Patients exhibit classic signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as heat intolerance, weight loss, palpitations, and tremor. Thyroid scan is not usually needed but shows rapid and diffuse concentration of radioiodine in the thyroid. Hyperthyroidism may rarely be seen with McCune-Albright syndrome and hyperfunctioning thyroid carcinoma. The diagnosis should be considered in patients with enlarging and persistent neck masses and chronic ear or nose drainage that is refractory to therapy. Neuroblastoma should be suspected in patients with a cervical mass and Horner syndrome, which consists of homolateral miosis, mild ptosis, and apparent enophthalmos with slight elevation of the lower lid. If it occurs before age 2, there may be hypopigmentation of the iris on the affected side. Orbital metastases can result in periorbital ecchymoses, resulting in a "raccoon eyes" appearance. Megalencephaly is a disorder of brain growth, usually accompanied by macrocephaly. An increase in growth rate with crossing of percentiles is of more concern than the case of a child with a large head growing at a normal rate. Causes of obstructive (noncommunicating) hydrocephalus include aqueductal stenosis, neonatal meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage in a premature infant, intrauterine viral infections, vein of Galen malformation, and posterior fossa lesions or malformations (tumors, Chiari malformation, Dandy-Walker syndrome). Subarachnoid hemorrhage in a premature infant can also cause nonobstructive (communicating) hydrocephalus. These include lysosomal diseases (Tay-Sachs disease, gangliosidosis, mucopolysaccharidoses), maple syrup urine disease, and leukodystrophies. Plain long bone radiographs may be indicated for evaluation of skeletal dysplasia or trauma. Chapter 187 14 Part I u Head,Neck,andEyes 12 Skull deformational malformations occur as the result of an alteration of the normal forces (in utero, perinatal, or postnatal) acting upon the growing cranium. Positional skull deformity, or plagiocephaly (skull asymmetry), is the most common type of deformational malformation. Its incidence has increased because of the recommendations to place infants on their backs while sleeping. Plagiocephaly is a benign condition that must be distinguished from true cranial suture synostosis. In plagiocephaly, sutures are open, and a frontal and temporal prominence occurs on the same side as the flat occiput.
The societal value of this exclusion is discussed under the Two Islands Approach later in this section. While a greater number of sick people in the pool may put upward pressure on premiums, the increased number of healthy people, who might have been previously priced out of the pool by adverse selection, will likely keep premiums close to their original level, or lower. Furthermore, the cycle of adverse selection where relatively healthy people are priced out by sick people, and then the moderately sick people are priced out by the very sick people, and so on, cannot happen because everyone is required by law to be included in the pool. Essentially, mandatory insurance is tantamount to a one single groupbased insurance pool, which, as we saw above, is a way to combat adverse selection. In any case, uniform subsidies or mandatory insurance do not solve the distributive justice and discrimination concerns raised before. Charging every driver the same premium entails that good drivers subsidize bad drivers, that drivers who drive less subsidize drivers who drive more, and less directly, that the old subsidize the young and that women subsidize men. More generally, there is an inherent question with insurance as to how much the able and lucky should subsidize the unable and unlucky; with car insurance it is the safe drivers against the unsafe, with health insurance it is the healthy against the sick, and with liability insurance it is the nonnegligent-prone against the negligent-prone. These questions are a bit easier to resolve when those subsidizing today will inevitably become those Such mandate was recently held constitutional by the U. In contrast, these questions become starker in situations when the relatively risky classification coincides with other social disadvantages, such as poverty. Doctrinal solutions for the adverse selection problem Insurance law has found ways to facilitate the practice of some of these theoretical solutions in order to alleviate or prevent the effects of adverse selection. Laws establishing a mandatory insurance framework-such as in automobile insurance-are an obvious example. But other legal doctrines, which pertain more closely to disclosure and risk classification, are more intricate and arguably more significant in that they expose private information about insured parties to investigation by insurers. One such doctrine concerns the "warranties" proffered by the insureds prior to the conclusion of the insurance contract. Because of the high cost of a false statement, the warranty doctrine presents a fairly effective means to encourage accurate disclosure. The associated frequent, costly investigations into pre-contractual statements and the potential for a penalty being imposed on the insured for simple pre-contractual carelessness, however, are substantial detriments to the warranty doctrine. Here, an insured party also makes pre-contractual representations to the insurer regarding the risk of the insured. Under this doctrine, instead of being liable for any Mandatory insurance may also increase the risk of moral hazard, to be discussed further below. See Alma Cohen & Rajeev Dehejia, the Effect of Automobile Insurance and Accident Liability Laws on Traffic Fatalities, 47 J. Same holds for state mandates requiring health insurance plans to cover medical treatment. See Jonathan Klick & Thomas Stratmann, Diabetes Treatments and Moral Hazard, 50 J. Thus courts ask whether the insurer would have agreed to cover the risk at all, or whether the premium the insured has paid for the policy covering the event that actually occurred would have been materially higher if an accurate representation had been made. If the penalty is reduction, the amount owed to the insured is usually reduced to the amount that would have been available had no misrepresentation occurred prior to contract formation. The rationale for reduction is that, because it puts the insured in the same position as if her representations were correct, there is no incentive for the insured to be dishonest up front. The problem, however, is that not all misrepresentations will be caught, and if the only penalty is reduction, insureds might gamble that they can get away with the misrepresentation. Voiding the policy outright provides an affirmative penalty, creating a stronger incentive for the insured to be honest at the outset. In some scenarios, like when an insured has been paying premiums for several years, certain statements and representations may not be challenged under the doctrines of warranty or misrepresentation, because after that much time has lapsed there is a high risk of erroneously determining either the validity, or falsity, of pre-contractual statements. In other words while some require that the misrepresentation contributed to the loss actually occurred, others require that it contributed to the risk of loss. Life insurance, health insurance, and disability insurance policies often contain an incontestability clause or are subject to an incontestability statute. Fraud is a common exception where insurers are allowed to challenge the validity of a policy, though what type of fraud avoids an incontestability clause is not always clear.
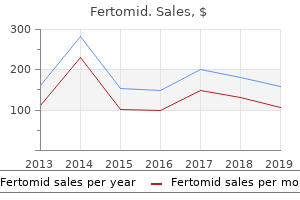
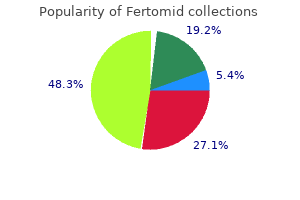
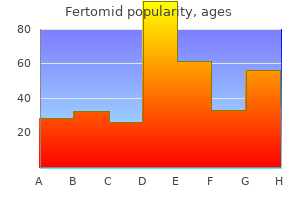
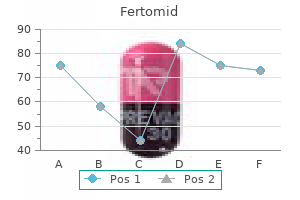
Ispaghula (Blond Psyllium). Fertomid.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96837
Structure and Format of Manuscript the recommended size of an original research paper is under 15,000 words and review papers under 7,000 words. Resources and techniques with sufficient complete experimental details (wherever possible by reference) to permit repetition, sources of information must be given, and numerical methods must be specified by reference. Design has been recognized to be essential to experiments for a considerable time, and the editor has decided that any paper that appears not to have adequate numerical treatments of the data will be returned unrefereed. They will also be published with much fewer delays than those that require much technical and editorial correction. The Editorial Board reserves the right to make literary corrections and suggestions to improve brevity. Author details the full postal address of any related author(s) must be specified. It should be clear and concise and must contain the objective of the paper and inferences drawn. Many researchers searching for information online will use search engines such as Google, Yahoo or others. Global Journals has compiled these guidelines to facilitate you to maximize the webfriendliness of the most public part of your paper. An effective keyword search requires a strategy: planning of a list of possible keywords and phrases to try. One should start brainstorming lists of potential keywords before even beginning searching. It may take the discovery of only one important paper to steer in the right keyword direction because, in most databases, the keywords under which a research paper is abstracted are listed with the paper. Numerical Methods Numerical methods used should be transparent and, where appropriate, supported by references. Abbreviations Authors must list all the abbreviations used in the paper at the end of the paper or in a separate table before using them. Formulas and equations Authors are advised to submit any mathematical equation using either MathJax, KaTeX, or LaTeX, or in a very high-quality image. Preparation of Eletronic Figures for Publication Although low-quality images are sufficient for review purposes, print publication requires high-quality images to prevent the final product being blurred or fuzzy. Please give the data for figures in black and white or submit a Color Work Agreement form. For scanned images, the scanning resolution at final image size ought to be as follows to ensure good reproduction: line art: >650 dpi; halftones (including gel photographs): >350 dpi; figures containing both halftone and line images: >650 dpi. Choosing the topic: In most cases, the topic is selected by the interests of the author, but it can also be suggested by the guides. Also, you might have to do a lot of work to find all the rises and falls of the various data on that subject. Evaluators are human: the first thing to remember is that evaluators are also human beings. Ask your guides: If you are having any difficulty with your research, then do not hesitate to share your difficulty with your guide (if you have one). You may also read some answers for the frequent question of how to write your research paper or find a model research paper. You should always use bookmarks while searching on the internet also, which will make your search easier. Try to mention everything in the introduction-what is the need for a particular research paper. Make backups: When you are going to do any important thing like making a research paper, you should always have backup copies of it either on your computer or on paper. So always try to include diagrams which were made by you to improve the readability of your paper. Use of direct quotes: When you do research relevant to literature, history, or current affairs, then use of quotes becomes essential, but if the study is relevant to science, use of quotes is not preferable. Know what you know: Always try to know what you know by making objectives, otherwise you will be confused and unable to achieve your target.
At 150 mg/kg bw per day, an increased incidence of early, late and total resorptions was seen. In a previously evaluated developmental toxicity study in rabbits, a dose-dependent reduction in feed consumption and increased incidences of soft or scant faeces were seen at 30 and 60 mg/kg bw per day. At the high dose, these effects were marked and occurred early after the start of treatment. At 60 mg/kg bw per day, only 1 out of 19 does produced a viable litter, whereas 10 does had litters that were totally resorbed and 6 does aborted. At this high dose, an increase in the number of early resorptions was observed (mean number 0. The uterus was weighed, and numbers of corpora lutea, implantations, fetuses and early and late resorptions were counted. Subsequently, the fetuses were stained with Alizarin Red S and examined for skeletal alterations. Scant or no faeces were noted in several does at 45 mg/kg bw per day, but generally only after several days of treatment. Daily feed consumption was not affected during this period (feed consumption was 293, 189 and 297 g at 0, 15 and 45 mg/kg bw per day, respectively). No treatment-related effects on gravid uterine weight were noted at any dose level. No treatment-related effects were noted in the number of viable litters, mean numbers of resorptions, live fetuses or dead fetuses or sex ratio per litter at any dose level. A treatment-related decrease (9%) in combined (male and female) fetal body weight was noted in pups at 45 mg/kg bw per day. The difference was not statistically significant when males and females were compared separately. No treatment-related increases were detected in the type or incidence of external, visceral or skeletal variations or malformations at any dose level. The Meeting concluded that the existing database on fenbuconazole was adequate to characterize the potential acute hazard to fetuses, infants and children. The Meeting concluded that the short-term intake of fenbuconazole residues from uses considered by the current Meeting was unlikely to present a public health concern. Published studies primarily evaluating the neurotoxicity of fenpropathrin have also been taken into consideration. Overall, the Meeting considered that the database was adequate for the risk assessment. Biochemical aspects Absorption of fenpropathrin following a single oral administration was rapid, and elimination was almost complete (about 57% in urine, about 40% in faeces) within 48 hours. The major biotransformation reactions of fenpropathrin in rats consisted of oxidation at the methyl groups of the acid moiety and at the 2- and 4-positions of the alcohol moiety, cleavage of the ester linkage and the conjugation of the resultant carboxylic acids, alcohols and phenols with glucuronic acid, sulfuric acid and glycine. Depending on the dose administered, 3050% of the applied radioactivity was excreted in faeces as parent compound. An aryl-hydroxylated ester (-cyano-3-(4hydroxyphenoxy) benzyl ester) was identified in bile. In acute studies with fenpropathrin in mammals, onset of toxic signs is rapid (within a few hours or days), independent of the route of exposure. Toxic signs are those typical for pyrethroids and include hypersensitivity, fibrillation, tremors, clonic convulsions, salivation, lacrimation, urinary incontinence and hindlimb and/or whole-body ataxia. Fenpropathrin is a slight skin irritant and is minimally irritating to the eyes of rabbits. The neurological clinical signs (body tremors, hypersensitivity/hyperreactivity, ataxia and, in dogs only, emesis) and reduced body weight gain are the key and most sensitive toxicological endpoints. In a second study of carcinogenicity in mice, a dose of 1000 ppm caused the death of 38% of the males and 15% of the females within 13 weeks, indicating a steep toxicityresponse curve and permitting the conclusion that the earlier study in which the highest dose tested was 600 ppm (equal to 56 mg/kg bw per day), the maximum achievable dose, was adequate for an assessment of the carcinogenicity of this compound. Fenpropathrin was tested for genotoxicity in an adequate range of assays, both in vitro and in vivo. On the basis of the lack of genotoxicity and the absence of carcinogenicity in mice and rats, the Meeting concluded that fenpropathrin is unlikely to pose a carcinogenic risk to humans. No effects on reproductive parameters were observed at doses up to 360 ppm (equal to 23.
The clinical pharmacist must keep abreast of current medical and therapeutic information. A strong foundational knowledge base must first be monitor patients efficiently and effectively. Similarly, assessing medical problems is an important clinical ability that must be developed and practiced. Hence, clinical pharmacists cannot focus only on medications, but must take into account all patient-specific medical problems as well. Designing and individualizing comprehensive drug therapy regimens also requires clinical experience. Observing patient-specific responses to medications is critical to anticipating potential outcomes of initiating and adjusting drug therapy. Collaborating with patients, caregivers, and other health professionals is another essential ability that deserves attention. They must understand their roles, and the roles of collaborators, in the clinical problem-solving process. Communication and Education the ability to effectively communicate with and educate patients and health care professionals is integral to ensuring optimal patient outcomes. Communicating with patients and other health professionals about a particular issue at the appropriate level of complexity can be challenging, and pharmacists must be aware of barriers to effective communication. Because effective communication and education are so fundamental to the provision of patient care, it is imperative that these abilities be well developed. The clinical pharmacist must identify those issues that are particularly pertinent for patients and physicians to help optimize drug therapy. As with clinical problem solving, experience and judgment are required to advocate for a needed intervention or change in therapy. Students and trainees often lack the clinical experience necessary to recognize new information that should be incorporated into their knowledge base. Skills in interpreting and evaluating biomedical literature assist the clinical pharmacist in effectively integrating new information with prior knowledge. These skills, which are often discounted as unimportant by students and trainees, provide the basis not only for keeping up with the literature but also for making evidence-based decisions. Management of Patient Populations Many clinical pharmacists not only are involved in providing care to individual patients, but work within a health system or other organization to develop protocols and critical pathways that optimize the care of patient populations. These efforts may include analyzing drug utilization evaluations, composing protocols for disease state management, and developing organizational policies and procedures that improve patient care and resource utilization. This may involve the collection and evaluation of information regarding how a particular medication or class of medications is being used such that changes can be implemented to improve care. Drug therapy protocols can be developed to ensure the proper use and monitoring of medications. A clinical pharmacist must possess sufficient experience and clinical judgment in the care of individual patients to effectively contribute to this process. Clinical pharmacists routinely contribute to the development and implementation of critical pathways. Educating others about a critical pathway requires an indepth understanding of the pathway, the evidence on which it is based, and the clinical implications for both health care professionals and patients. These skills are clearly beyond 811 those acquired in a doctor of pharmacy program and require development during postgraduate training and practice. Therapeutic Knowledge Clinical pharmacists must possess a therapeutic knowledge base of sufficient breadth and depth to effectively promote rational medication use. Appendix 1 includes a list of diseases and pharmacotherapeutic principles intended to serve as a guideline for the identification, assessment, and development of clinical pharmacist competencies. In general, to be considered a clinical pharmacist, one must be sufficiently knowledgeable about the diseases and principles in this list to effectively assess and treat these problems in the patient population one serves. It is important to emphasize that a clinical pharmacist must be competent in the therapeutic management of the many disease states that may affect a given patient, not simply those currently identified as active problems. Doctor of pharmacy degree programs provide broad but relatively superficial coverage of disease states, pharmacotherapy, and general therapeutic principles. However, the content and structure of a residency should serve as a model for individuals seeking to become clinical pharmacists but who are unable to pursue formal residency training. Although some clinical pharmacists may distinguish themselves by developing a subspecialty area of expertise.
Antigen M protein-based vaccines Type-specific M peptides Conserved M protein epitopes Mucosal synthetic peptide vaccine. The vaccine was well tolerated and induced Future Vaccines and Vaccine Hesitancy 465 capsular- specific antibody responses, in nonpregnant and pregnant women. It demonstrated an overall survival benefit in men with castrateresistant prostate adenocarcinoma. In the long run, a better target for cancer vaccines may be minimal residual disease rather than eliminating extensive metastatic deposits. Largest-ever outbreak of Ebola virus disease thrusts experimental therapies, vaccines into spotlight. All of these are the same reasons present day antivaxxers or prochoice proponents still use. Worldwide, despite the success of the vaccination programs and the safety of vaccines, there exist a number of vaccine-hesitant parents and vaccine refusers. These should not be confused with antivaccinationists, otherwise colloquially dubbed as antivaxxers. It is incumbent on us as healthcare professionals to listen to their reasons and try to understand their perspective. The analysis should also look into channel availability and audience preferences, including existing community engagement mechanisms that can guide communication interventions. The involvement of community leaders/stakeholders in organizing community dialogs with parents and other target groups for immunization in strengthening the capacity of their healthcare workers to provide inclusive services should be tapped. Other than concerns about vaccine safety, it is also possible that vaccine hesitancy is increasing now because of the "crowded" vaccination schedule along with "greater access to , and more rapid dissemination of, vaccine-critical messages via digital networks"3 Lack. This is demonstrated globally, differing within high-, middle-, or low-income countries as well as within countries based on factors such as socioeconomic and educational status. Within local regions, there may be reasons related to religious beliefs about the contents of vaccines, belief in naturopathy and alternative medicine, conspiracy theories related to "big pharma" etc. This has largely favored antivaccinationists who have leveraged the internet and social media to bypass traditional sources of information and obtain widespread communication and access to the public. The modern communication environment allows any individual with a negative opinion about vaccine safety issues to voice their views online without professional input. There is expected to be a rapid evolution of mobile technologies over the next 5 years with the possible development and widespread use of wearable technologies. Any strategy developed must be highly amendable to change to accommodate new platforms of communication. In the short-and long-term, building partnerships with the media and social media influencers is key to keeping the public regularly informed about and engaged with the benefits of immunization and to timely information sharing on vaccine safety issues. While vaccine hesitancy should be overcome through face-to-face contact by sufficiently trained and knowledgeable healthcare workers with parents and the public, our presence in social media using more and more advanced technology has to go concurrently to counter the influence of the antivaccination lobbies. Vaccine Safety Communication: Guide for Immunization Programme Managers and National Regulatory Authorities. Vaccine Safety Communication: Guide for Immunization Programme Managers and National Regulatory Authorities (1. Increased awareness and health care provider endorsement is required to encourage pregnant women to be vaccinated. Message Framing in Vaccine Communication: A Systematic Review of Published Literature. Utilizing health information technology to improve vaccine communication and coverage. The main outcome measures were menstrual cycle, pregnancy, hirsutism, testosterone concentrations, and premature ovarian failure. Unilateral oophorectomy restored regular menstrual cycles in 12 of the 14 patients. Testosterone blood concentrations decreased significantly within the first year after unilateral oophorectomy in 11 patients. Our results indicate that unilateral oophorectomy restores ovulatory function for many years in the majority of patients and does not result in premature ovarian failure. However, unilateral oophorectomy should not be recommended as a standard treatment for clomiphene citrate-resistant patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Thirdly, in 1984 laparoscopic electrocoagulation of the ovaries and in 1988 laparoscopic laser surgery of the ovaries were introduced as less invasive alternatives to bilateral ovarian wedge resection Ё (Gjonnaess, 1984; Huber, 1988). However, restoration of regular ovulatory cycles in patients who do not conceive seems to be of short duration in the majority of patients (Armar et al.
References: