
This information avoids time consuming complications and ensures smooth transition during a time sensitive process. Reductions in medical school curricular time have resulted in evaluation of modes of anatomy teaching. One issue has been the relative value of student dissection versus demonstration on prosected specimens. Since students had dissected in the 1st year, dissection time was decreased and a major component of the laboratory material was taught through demonstration. This was a unique opportunity to compare educational outcomes of learning by active dissection versus more passive demonstration of prepared dissections. Medical students (207) performed 5 (2-hour) dissections of the upper limb, followed by 4 demonstrations of lower limb on specimens dissected by staff. Demonstrations consisted of rotation through 3 stations, 20 minutes each, that included chalk talks of concepts, presentation of dissected specimens, presentation on bones and plastinated specimens, and self-study. The practical exam included 54 cadaver tags, 6 bone tags, and 12 image tags (1 minute/station). The performance was marginally better on material learned through dissection versus demonstration. Student comments on the relative experiences of dissection versus demonstration were solicited. On the basis of performance in this exam setting, learning through dissection is approximately equal to (although marginally better than) that through demonstration. Uncertain is the relative retention of learned material, ability to apply it to the clinical setting, and the perceived quality of the student experience. These data are useful as anatomy programs assess their mode of delivery of content. It arises from the transverse process of the cervical vertebrae and is inserted into the upper surface of the first rib. This study investigated the configuration of the scalenus medius to verify its precise functions. After the removal of the impeditive structures, the spatial relationships between the muscle fibers of the scalenus medius were examined under a binocular continued on next page page 113 microscope in 15 Japanese cadavers. The dorsal part attached to the anterior and posterior tubercles of the third to seventh cervical transverse process. The bundle from the third vertebra descended parallel to the vertebral column and was inserted into the tubercle of the first rib. The bundles from the lower vertebrae passed anteromedially to those from the upper vertebrae and sequentially joined the anterior side of the insertion. The bundles from the first and second cervical vertebrae attached above to the anterior region of the transverse process. Below they were linked by a tendinous connection to the bundle from the third cervical vertebra. The ventral part attached by tendinous slips to the anterior tubercle of the fourth to seventh cervical transverse processes. The bundle from the fourth vertebra passed downward and laterally to be inserted into the shaft of the first rib anterolateral to the tubercle. The bundles from the lower vertebrae passed posteromedially to those from the upper vertebrae and sequentially joined the medial side of the insertion. The attachments and directions of the muscle fibers imply the difference in the functions of the two parts of the scalenus medius. It was suggested that the dorsal vertical part mainly bends the cervical portion of the vertebral column and the ventral oblique part can raise the first rib. In addition to material that is covered in lecture and laboratory, practical aspects of anatomy must be addressed. One promising modality is the use of video, in which individual anatomical structures can be labeled and demonstrated. The treatment participants were undergraduate students enrolled in a cadaver-based human anatomy course in the fall of 2010 (n=144).
In the case of boiling fowl, ducks, turkeys, and geese, a few feathers may also be present on other parts. Some damage, bruising and discolouration is allowed, provided that it is small and unobtrusive, and not present on the breast or legs. For frozen or quick-frozen poultry there should be no traces of freezer burn (freezer burn is the local or area-type irreversible drying up of skin and/or flesh which may produce changes: in the original colour (usually paler); or in smell (rancid); or in flavour (flavourless); or in texture (dry, spongy) on the breast or legs. Small unobtrusive traces of freezer burn are allowed on other parts of the carcass. Such a system is of interest to further processors who are looking for meat that will hold added moisture (high quality protein) and not fall apart during cooking (good texture) regardless of skin tears or missing parts (Barbut, 1998). Note: for labeling purposes, the designation of sex within the class name is optional, and the two classes of young turkeys may be grouped and designated as "young turkeys. Overview on current practices of poultry slaughtering and poultry meat inspection. Overall, welfare considerations are becoming more important and today various agencies evaluate/monitor compliance with animal welfare standards. A notable change from the previous regulations is the requirement that a certain level of current should be applied to each individual bird when electrical stunning is applied. In other regions conditions for poultry stunning are not always specifically legislated. Nevertheless, all plants use stunning (electrical, gas, or mechanical) with help from national guidelines/regulations. Stunning and immobilizing poultry also assists in operating an efficient automated line. Initially, electrical stunning for poultry was introduced to immobilize the animals to allow application of bleeding through a high speed automated process. Later, gas stunning was introduced (Fletcher, 1999) and today both methods are widely used around the world.
The treatment room, emergency department, case room and operating room are obvious examples of such areas. Have a regular plan of maintenance for equipment and plan in advance for the repair and replacement of equipment. Create a list (inventory) of the equipment you have, then work out when the various items will need to be serviced and ultimately replaced. There are broad groupings within this range: Forceps and instruments for holding tissue Needle holders Scissors Retractors. When you have a choice between instruments: Choose the shortest instrument that will comfortably reach the operative site If cutting suture or other non-tissue material, avoid using fine scissors that are designed to cut tissue or dissect tissue planes; use larger and blunter scissors for non-tissue materials Choose instruments in good repair; forceps that cross at the tip, scissors that do not cut easily and needle drivers that do not grip the needle securely can be frustrating and dangerous. When holding instruments: Use three-point control: have three points of contact between your hand and the instrument to stabilize the instruments and increase the precision of use (Figure 2. In this way, rotation of the instrument can come from your wrist and forearm and provide a greater arc of control. Scalpel the way in which the scalpel is held depends on its size and the procedure being performed. Use a #10 blade for large incisions, #11 for stab incision and #15 for fine precision work (Figure 2. Hold the knife parallel to the surface with your third to fifth finger, thumb and index finger; this provides the three-point control. Your index finger will guide the blade and determine the degree of pressure applied. Toothed forceps are also referred to as "atraumatic" as they are less likely to crush tissue. Place your thumb and fingers through the handles just enough to sufficiently control the instrument. Place your index finger on the shaft of the instrument to provide three-point control. Using your left hand Scissors are designed so that the blades come together when used in the right hand. When right handed scissors are used in the left hand, the motion of cutting actually separates the tips of the scissors and widens the space between the blades; this makes cutting difficult, if not impossible. In order to use them with your left hand, it is necessary to hold them and apply pressure in a way that brings the blades closer together. A treatment room has equipment similar to an operating theatre, but on a smaller scale. Both rooms require: Good lighting and ventilation Dedicated equipment for procedures Equipment to monitor patients, as required for the procedure Drugs and other consumables, such as sutures, for routine and emergency use. It is standard practice to count supplies (instruments, needles and sponges): Before beginning a case Before final closure On completing the procedure. Create and make copies of a standard list of equipment for use as a checklist to check equipment as it is set up for the case and then as counts are completed during the case. When trays are created with the instruments for a specific case, such as a Caesarean section, also make a checklist of the instruments included in that tray for future reference. Scrubbing cannot completely sterilize the skin, but will decrease the bacterial load and risk of wound contamination from the hands. Every hospital should develop a written procedure for scrubbing that specifies the length and type of scrub to be undertaken. It is usual that the first scrub of the day is longer (minimum 5 minutes) than any subsequent scrubs between consecutive clean operations (minimum 3 minutes). Promptly change a glove punctured during an operation and rinse your hand with antiseptic or re-scrub if the glove has leaked during the puncture.
Distal tibial nerve injuries at the ankle, including "tarsal tunnel syndrome," often resemble carpal tunnel-like syndrome in their symtomatology. Iatrogenic injury following surgery can also produce injury to the tibial nerve in the lower leg and foot. It bifurcates below the knee into the deep peroneal and superficial peroneal nerves. The level of this bifurcation can vary somewhat, having a potentially large impact on selective fascicular involvement in peroneal nerve injuries at the fibular head. Normal variations of bifurcation of the common peroneal nerve can affect which muscles are clinically weak in a peroneal palsy. Recording from various deep and superficial peroneal-innervated muscles may be helpful in such cases. The superficial peroneal nerve innervates muscles of ankle eversion, including the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis. It provides cutantneous sensation to the dorsum of the foot and to the lateral lower leg. Injuries to the common peroneal nerve and its branches include many of the same types of injuries affecting the posterior tibial nerve, such as direct trauma. Because of its position it often has a predilection to compression injuries and often is more clinically involved in lesions affecting both the tibial and peroneal nerves. The common peroneal nerve is also subject to compression at the fibular head, where it becomes quite superficial, and may be damaged in stretch injuries involving the knee and in compartment syndromes. Distal superficial peroneal nerve injuries sometimes referred to as anterior tarsal tunnel syndrome and iatrogenic injury are all seen. Stimulation is performed at the ankle at a preset distance and below and above the fibular head (see. Conduction velocities are measured between the ankle and a site below the fibular head, and from below to above the fibular head. The distance between the below and above fibular head segment ideally should be around 10 cm but often a shorter distance is required to ensure no volume conduction to the posterior tibial nerve. Careful observance of the clinical movement of the foot to stimulation is critical to avoid volume conduction response. In such instances, higher amplitude is noted with proximal rather than with distal stimulation. Motor studies also can be acquired recording from the tibialis anterior and the peroneus longus while stimulating at the fibular head. Such studies can be very helpful in acquiring additional information about selective fascicular involvement to individual muscles innervated by both the deep and superficial peroneal nerve. Such information may be very helpful in confirming localization of a peroneal palsy. Oftentimes conduction block (abnormal amplitude drop over a short segment) or focal slowing of conduction velocity may be noted. The antidromic method is performed by placing the active (G1) electrode over the dorsum of the foot slightly lateral to midline. Stimulation is performed at a preset distance in the groove just posterior to the insertion of the peroneus longus (see. This sensory study can be invaluable in evaluating demyelination in peroneal nerve injury at the fibular head. In a purely demyelinating lesion, everything below the lesion will be completely normal. If a patient presented with a completely flaccid foot unable to dorsiflex the foot at all, a normal superficial peroneal sensory study would strongly suggest a demyelinating injury at the fibular head. This is because there is a conduction block-type injury and the axons themselves remain intact. When performing motor studies on this type of injury no response would be obtained at the stimulation site above the site of the injury. Usually, at least a 50% drop in amplitude is needed to diagnose partial conduction block. If only the largest myelinated axons were affected, a slowing in conduction velocity may be the only abnormality noted. Because certain fascicles can be affected differently, performing studies from multiple muscles may be helpful. It is not unusual to note partial conduction block to some fascicles and only conduction slowing to others.
The event or exposure occurred in the work environment and caused or contributed to the resultant injury. Therefore, the case is work-related, regardless of the fact that he had not actually checked in, and must be reported as a case involving a Railroad Employee Not On Duty (Class B). Several hours later, the employee goes outside for a "smoke break and to get a pair of sunglasses from his truck. In order for this exception to apply, the case must meet both of the stated conditions. The exception does not apply here because the injury or illness occurred within normal working hours as "breaks" during normal working hours are considered within assigned working hours. A second employee, also on the way to work, approached the first employee, and the two individuals got into a physical altercation in the parking lot. The company deemed this a non-work-related incident, and therefore non-reportable, since the employees had not yet reported to work and a work task was not being performed at the time of the altercation. Response 5: the reporting requirements contain no general exception for purposes of determining workrelatedness for cases involving acts of violence in the work environment. Whether the employee had not clocked in to work does not affect the outcome for determining work-relatedness. Scenario 6: An employee injured a knee performing work-related activities in 2005. The employee had arthroscopic knee surgery 11 months later and was released to full duty a month and a half after the arthroscopic surgery. The employee had a second knee injury 3 months after the return to work release (after the first surgery). After the second surgery, the doctor prescribed Vioxx as an anti-inflammatory drug. However, the doctor told the employee to continue to take Vioxx as prescribed (as needed) and to return to the doctor as needed. The doctor stated that the employee had an inflamed tendon (Grade 1 lateral collateral ligament sprain) that was not part of the initial surgery (patellar tendonitis). The doctor stated in the diagnosis that the original injury that required knee surgery was resolved. Since the employee was already taking the medication prescribed (Vioxx), the railroad does not believe this is reportable as a second incident. Response 6: In the accident/incident regulation and reporting guidelines, the employer is required to follow any determination a physician or other licensed healthcare professional has made about the status of a new case. The inflamed tendon is a new case because the employee had completely recovered from the previous injury and illness and a new event or exposure had occurred in the work environment. Response 7: this case must be reported because it does not meet the exception to work-relatedness for injuries that occur in the work environment but are solely due to personal tasks. The exception does not apply to injuries and illnesses that occur during breaks in the normal work schedule. Scenario 8: Does an employee become a part of the general public once they have timed out? Or, are they considered part of the workforce from the time they get out of their car coming in to work to the time they step into their car to go home at the end of their work day? Punching in and out with a time clock (or signing in and out) does not affect the outcome for determining work-relatedness. The only distinction is whether to report it as a Railroad Employee On Duty (Class A) or Railroad Employee Not On Duty (Class B). Again, an employee does not become a member of the general public solely by being present in the work environment outside of assigned work hours. For example, an employee of a passenger railroad maybe considered a member of the general public in the work environment when they are a passenger on the train for personal reason unconnected to work. Response 9: Since the resultant injury occurred in the work environment, it is work-related, unless a specific exception applies. Are there situations in which an injury or illness occurs to an employee while in the work environment, but would not be reported as an injury to , or illness of, an employee on duty? What activities are considered "personal grooming" for purposes of the exception to the geographic presumption of work-relatedness for employees on duty?

December 2012 2-49 Practitioner Services Coverage and Limitations Handbook Laboratory Services. Organ or Disease Panels There are test combinations for specific organ or disease oriented panels. When all or the majority of the individual component tests that make up a particular panel are performed, the provider must bill for the panel, if the reimbursement for the panel is less than the reimbursement for the tests billed individually. When the components of one panel are duplicated in another panel, only one panel code may be billed. Fetal Fibronectin Medicaid reimburses for fetal fibronectin, procedure code 82731, for diagnoses related to pregnancy risk factors. Genetic carrier screening laboratory testing services are performed to identify recipients who are themselves unaffected but are at risk for passing the condition to their off-spring. December 2012 2-50 Practitioner Services Coverage and Limitations Handbook Laboratory Services. The laboratory testing method must be considered to be a proven method for the identification of a genetically-linked inheritable disease. December 2012 2-51 Practitioner Services Coverage and Limitations Handbook Laboratory Services. Services for specimens sent to an independent laboratory are only reimbursed directly to the independent laboratory. Neonatal critical care is the care and monitoring of an unstable, critically ill, or injured neonate in a variety of medical emergencies that requires constant attention. The care of such infants involves decision-making of high complexity to assess, manipulate, and support central nervous system failure, circulatory failure, shock-like conditions, renal, hepatic, metabolic, or respiratory failure, unpredictable postoperative complications, overwhelming infection, or other vital system functions to treat single or multiple vital system organ system failure or to prevent further deterioration. Critical care may be provided on multiple days when the condition requires the attention as described above. Included Procedures In addition to those procedures listed for the critical care codes, the following procedures are also included in the reimbursement for the neonatal critical care services and cannot be reported separately by the professional. When due to a transfer situation, critical care services are provided to a neonate patient at two separate institutions by practitioner from different groups on the same date of service, the practitioner from the referring institution should report their critical care services with the critical care codes 99291 and 99292. Additional Consultation for Separately Identifiable Medical Conditions An additional initial consultation may be reimbursed to the same provider or provider group during the same hospitalization if, after 30 consecutive days, a separately identifiable medical condition warrants a new consultation from the specialist. Medical documentation of the consultation must be maintained in the medical record. This code cannot be billed in conjunction with other neonatal intensive care service codes. Neurology Services Description Neurology services provide for diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the nervous system. The following criteria and documentation for medical necessity applies to all practitioners, regardless of their accreditation or certification level. Vagus Nerve Stimulator Procedure codes for placement, removal, or revision of vagus nerve stimulators are covered for intractable epilepsy diagnoses for recipients age 3 years and older. File the claim with modifier 22 appended to the procedure code, for medical review. The recipient must be notified in advance that he may be responsible for payment of the service if it is performed for diagnoses other than intractable epilepsy. Newborn Hearing Screenings Description the newborn hearing screening is for the purpose of testing all Medicaideligible newborns for hearing impairment to alleviate the adverse effects of hearing loss on speech and language development, academic performance, and cognitive development. The screening is a test or battery of limited tests administered to determine the need for an in-depth hearing diagnostic evaluation by a hearing services specialist. Note: For additional information regarding new born hearing services and appropriate procedure codes, please see the Florida Medicaid Hearing Services Coverage and Limitations Handbook. Note: See Pricing Modifiers in Chapter 3 of this handbook for instructions on identifying the professional component. The provider must maintain a record that the hearing screening was not performed and attach a written objection that is signed by the parent or guardian.
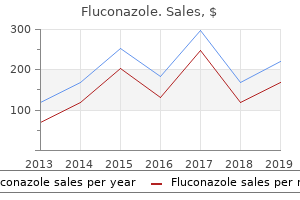
Diseases
The time the material is exposed to heat depends on the size and retention volume of the cooker. The discharged material is dumped into a percolator that consists of a tank with a strainer at the bottom. The free fat is drained and the remaining material is pressed to remove the trapped fat. A continuous, low temperature rendering system, sometimes called a mechanical dewatering system, employs a mechanical means to remove the water and fat. The material is then pressed using a continuous screw-type press and the fat and water are extracted. This process results in a lower heat treatment and reduced energy costs compared to the other processes. Overall, this is a tremendous increase from 1993 ($16 billion) and 2003 ($32 billion). Ockerman and Hansen (2000) noted that the first commercially prepared dog biscuit was introduced in England in 1860. New expanded pet food products were introduced in the 1950s and semi-moist pet food in the 1960s. The demand for pet food (estimated to be over 1 million tons/year of poultry, meat and seafood by-products) has provided the meat industry with a good and stable source of income and pet owners with high quality and nutritious pet food. An annual growth of 4% in pet food retail sales in Japan is also expected due to changing social trends rather than an increase in the number of total pets. Some of the increases are the result of new pet superstores, premium pet foods, and increased awareness/knowledge of feeding pets a nutritionally balanced diet. The meat industry ships fresh and/or frozen materials to the pet food industry. The pet food industry cooks the meat at high temperature and mixes it with other ingredients to produce a balanced diet for different pet food categories. Dry dog food Ingredients: ground corn, wheat shorts, poultry by-product meal, corn gluten, soybean meal, poultry fat preserved with mixed tocopherols (to preserve flavour), rice, molasses, tripolyphosphate, dry whey, calcium carbonate, salt and vitamins. The poultry fat is supplemented with tocopherol (an antioxidant) to protect it from oxidation during heating and storage. The second formula, canned dog food, adds a cereal component to improve the texture, add bulk, and add crude fiber (plant material) to the formula. The formulation also contains different gums (pectin, guar) to assist in texturizing the product. The third formula, canned cat food, illustrates a formula based on meat (listed as chicken) and meat by-products that has been fortified with vitamins and minerals. As with other foods, ingredients are listed in descending order by weight but the nutritional labeling requirements for pet food are not as stringent as they are for human food. For example, the pet food manufacturer can declare a minimum protein content and does not have to provide a list indicating the amount of vitamins and minerals whereas fortified human food must have a precise declaration of all ingredients). Pet food is sold in different ways (wet, semi dry, dry) and protein content can range from 10 to 50%. Recently, there has been substantial product development activity in the high end pet food industry as margins in that sector are high. Pet food companies have also invested in products that adjust for the nutritional needs and flavour and texture preferences of different pets. Feathers are a rich source of protein with approximately 90% protein, 8% water, and 1% fat. Once processed into a regular feather meal, it contains about 70-80% crude protein. However, before using feathers as an animal feed, the protein complex has to be broken down as explained below. Feathers are also used for bedding, ornaments, sporting equipment, and as filler in chemical fertilizer (Ockerman and Hansen, 2000). According to Hardy and Hardy (1949) and Pacific Coast (1997), feathers can be classified as: a.
Several companies recommend removing feed, but not water, 3-4 hrs prior to loading. If the birds are off feed for only 4-6 hrs prior to processing, the chances of intestinal content leaking onto the carcass during a process such as electrical stunning/stimulation. They also reported a sex difference (female broiler intestinal strength was 15% lower than male broilers) and a seasonal effect (strength was 15% higher in winter). Overall, when feed withdrawal is too long, the microstructure of the intestines changes. The amount of time off feed also affects the yield/live shrink weight of the processed birds. Minimizing stress during transport is an important issue from both an animal welfare and meat quality perspective. Considering the large number of birds grown and transported to processing plants. Poultry raised on large farms, scattered around the country, are transported to processing plants 1-5 hrs away (some reports indicate < 2 hrs is ideal). As previously indicated, feed withdrawal and harvesting the birds results in physiological stress. Bayliss and Hinton (1990) reported that up about 40% of deaths of birds arriving to the plant (usually ranges from 0. The same is true in North America where a so-called long journey can extend to 5 hrs and time on the truck to 10-12 hrs. Duncan (1989) used behavioural and physiological responses (heart rate, plasma corticosterone concentration, tonic immobility) to characterize the stress(es) imposed on the birds during transport. This was consistent with observations of an increasing heterophil:lymphoctye ratio. Transport stress was also reported to induce tissue damage, which was reflected by an increased plasma activity of intracellular muscle enzymes such as creatine kinase and others. Over the years, several studies have examined and modelled the effects of heat on metabolic rates in birds during transport (Mitchell and Kettlewell, 1998; Yahav et al. They proposed that stress could be minimized by appropriate control of air flow within the truck, both in motion and at rest. Later, Mitchell and Kettlewell (1998) completed a very comprehensive temperature modelling study that has been used to generate guidelines for poultry transportation. The result of their work is used here to illustrate ways of monitoring the so-called thermal microenvironment zones within the truck. As relative humidity increases, at a constant temperature, it will be more difficult for the bird to lose heat via panting and the bird will perceive a higher body temperature (birds do not have sweat glands). The value is related to the wet bulb temperature and describes the total heat exchange between a wetted surface and the environment. It should be mentioned that the influence of heat loss might be more pronounced inside a crate than on an individual bird under similar conditions in an open space. By installing a monitoring system in the truck it is possible to minimize heat stress and improve the welfare of the birds. It is important to emphasize that the calculations presented here are modelled off of a stocking density of about 53-58 kg/m2 and a transit time of about 3 hrs. Stocking density was 53 kg/m2 in each crate, which was loaded with 21-22 birds in the summer and up to 23 birds in the winter. The study resulted in a 3-dimensional thermal mapping of the transport truck in the summer (curtains left open) and winter (curtains closed). This indicates that when the curtains are closed, a "paradoxical heat stress" may occur within the "thermal core" even when the outside temperature is very low. Dissipation of temperature and humidity gradients and proper distribution of the thermal load within the truck should therefore be a primary objective when designing a new truck or improving the ventilation system of an existing one. This "thermal core" could be seen towards the upper front of the truck where ventilation was minimal and the risk of heat stress was proportionally greater. This is an extremely important point because many trucks rely on "natural ventilation" when the truck is not in motion. It should be noted that the data were derived from what they called a "typical journey"; however, under other commercial conditions, values may exceed those reported here, especially during a warmer period in spring and autumn when trucks may still run with closed curtains. Internal body temperature was measured and blood samples were collected at 0 and 3 hrs after simulated transport conditions (Table 4. Confinement of the birds in the crates tended to induce hyperthermia at all heat loads.
Incidence of reactivation of latent infections (seen in geriatric patients) implies that immune system is incapable of dealing with complex M. First infection of mycobacterium tuberculosis is called primary tuberculosis and is usually a subclinical infection a. Symptomatic primary tuberculosis is rare and more commonly occurs in elderly, children, and immunocompromised 2. Related to public education and routine evaluation of health care workers consisting of a. Colonize the lining of the throat and spread easily through respiratory secretions 2. Conversion from carrier to clinical disease is rare in developed countries (3 in 100,000 in the U. Onset is rapid and typical symptoms include fever, chills, joint pain, neck stiffness or nuchal rigidity (pronounced on flexion), petechial rash, projectile vomiting, and headache 2. Roughly 10% of patients may develop septic shock (Waterhouse-Friderichsen Syndrome) a. Pediatric patients - infants 6 months to 2 years are especially susceptible; maternal antibodies protect neonates to 6 months a. Infants display nonspecific signs such as fever, vomiting, irritability, and lethargy b. Vaccines are effective, especially for older children and adults, and have been instrumental in preventing outbreaks among military recruits in the U. Spread by droplets, prolonged personal contact, or contact with linen soiled with respiratory discharges. Prior to introduction of vaccination for children in 1981, it was the leading cause of meningitis in children aged 6 months to 3 years d. Although treatment with antibiotics is very effective, over 50% of all infected children will have long-term neurologic sequelae. Also implicated in pediatric epiglottitis, septic arthritis, and generalized sepsis Viruses (causes syndromes sometimes referred to as aseptic meningitis) a. There are a variety of viruses known to cause meningeal signs and symptoms (1) Most associated with other specific diseases (2) Seasonal variations may occur b. Bacterial (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, H. Susceptibility is increased by processes that adversely affect the status of respiratory tissues, i. Pediatric patients with low birth weight and malnourishment are very susceptible 4. Onset of pneumonia may be sudden with chills, high-grade fevers, chest pain with respirations, and dyspnea 2. Patient may cough up yellow-green phlegm Patient management and protective measures 1. Patient isolation generally not warranted except in clinical facilities where patient with a resistant strain may be in contact with other patients who have increased susceptibility to infection 4. Tetanus spores introduced into the body through wounds, bums, or other disruptions in the integument 2. Infection has often developed in wounds considered too trivial for medical consultation D. Susceptibility is general, which is why tetanus immunization is recommended for the general population 2. Painful contractions, particularly of the masseter (trismus or lockjaw) and neck muscles, secondarily of trunk muscles 3. Painful spasms often occur, with a characteristic facial contortion known as risus sardonicus, a grotesque grinning expression 5. Temporary passive immunity is provided by post-exposure administration of tetanus immune globulin or tetanus antitoxin (equine origin) 2. Ask patient about immunization status United States Department of Transportation National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Paramedic: National Standard Curriculum 20 Medical: 5 Infectious and Communicable Diseases: 11 G. Causative organism - rabies virus of the genus Lyssavirus System affected - nervous system Route of transmission 1. Transmission from person-to-person is theoretically possible, but has never been documented 3.
While everyone has a different way of using the stethoscope as a monitoring tool in anaesthesia, it is suggested that it should stay round your neck for occasional use all over the chest, rather than be fixed on the chest and fixed in your ears. The weighted stethoscope plus earpiece is a better continuous monitoring tool than the ordinary stethoscope. This device has a heavy metal cylinder that sits on the chest and is connected via a long, lightweight tube to a comfortable single foam earpiece. It allows more freedom of movement, although the sounds are very faint compared to those from the usual stethoscope. Monitoring after a spinal anaesthetic Since the patient who has received spinal anaesthesia is awake, there is often an erroneous assumption that no monitoring is necessary. In fact, spinal anaesthesia may be associated with just as many complications as general anaesthesia, as the figures below show. Monitoring of blood pressure and respiration is, if anything, more important after spinal than after general anaesthesia. Check that cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment is available and working and monitor cerebral perfusion by regularly talking to the patient and observing facial expression. In many district hospitals, there is a high rate of complications of spinal anaesthesia, including severe hypotension (10%) and respiratory arrest (3%) these can easily occur when spinal anaesthesia is treated as an action to be performed rather than a process to be monitored. One of the best ways to monitor such a patient is to talk to them throughout anaesthesia. In most emergencies, you have sufficient control of the cardiovascular system to enable an adequate, non-aware state of anaesthesia to be maintained. The complication of awareness is generally confined to the paralysed patient who cannot show that anaesthesia is too light by moving. When you give an intravenous hypnotic drug, ask yourself: are you sure you gave it? Depth of anaesthesia can be monitored by looking at: Cardiovascular signs: few patients with normal heart rate and blood pressure will be aware, although beta blockers may prevent a tachycardia Pupils: they should be small and non-reactive, although ether may give a large pupil due to its sympathomimetic effects; a reactive pupil probably means the patient can hear you and may feel pain Sweating and tears: these signs mean the patient is too "light". In all the above, you must also consider carbon dioxide retention due to hypoventilation. Urine output A catheterized patient should have a bag connected so that you can check the urine output during the operation. Its greatest value is in diagnosing hypoxia during induction of anaesthesia in healthy patients. Unfortunately, in emergency cases with circulatory collapse, when oxygenation information is most needed, the oximeter often cannot read the capillary pulse. In such cases, when the oximeter suddenly fails to read, it is a sign that deterioration is taking place. On the other hand, when the reading returns, it means the blood pressure has come up and your resuscitation efforts are perhaps being successful. Never believe the oximeter if the indicated pulse rate does not agree with the real one felt at the wrist. Readings from a pulse oximeter are often unreliable in infants and neonates with poor circulation. If an adult probe is used, there may be a 10% saturation difference between readings on the toe and the finger in babies. Every case under anaesthesia should have the pulse oximeter in place, especially: For induction At the end of anaesthesia In recovery. Remember, however, that when things go wrong, except in hypoxia, the pulse oximeter is almost useless. Capnograph Measures carbon dioxide in expired air Can be used to confirm correct position of tracheal tube Can indicate changes in ventilation and cardiac output Can indicate disconnections and respiratory arrest Monitoring events Make regular checks of the volume in the sucker. During caesarean section, it is important to differentiate between aspirated liquor and blood. Change of plan or operation In places where diagnostic facilities are limited, there is more uncertainty about what will be found during surgery. Pay attention to what is going on and adapt your anaesthesia to the changed circumstances.
References: