
When considering mitigation strategies, managers begin with the ultimate goal of preventing adverse effects, but if that is not practicable, they modify their strategies to minimize impacts on marine mammals by reducing eliminating, or rectifying the effects of anthropogenic sound in the marine environment consistent with existing statutes. Management agencies will continue to develop and evaluate the feasibility, applicability, and effectiveness of mitigation measures to address potential adverse effects from anthropogenic sounds on marine mammals. Based on information received as a result of such a dialogue, the Federal agencies plan to expand these efforts to include working with naval architects and ship operators to review existing practices, develop educational programs for designers of recreational and commercial vessels about the potential impacts of anthropogenic sound, and explore the development of voluntary guidelines on operations, design, and construction of ships. Management agencies and relevant stakeholders should work together, where appropriate, to develop "best practice" guidelines, recognizing that a "one size fits all" approach is not practical. Those guidelines should utilize suites of mitigation tools and identify appropriate and feasible ways to apply them to different activities in order to prevent, reduce, eliminate, or rectify adverse effects from sound on marine mammals. These standardized systems should be rigorous enough to support the collection, aggregation, and analysis of scientific information. In conjunction, the Services will continue to develop and improve training and certification programs to ensure that observers are qualified to conduct effective monitoring, enabling data to be utilized. As feasible, the Services will seek public and private partnerships to undertake an outreach program to educate sound producers and the general public, about the risks of anthropogenic sound to marine mammals and how adverse effects can be reduced or minimized. These partnerships should also encourage and explore means for stakeholder cooperation in compiling and sharing information on marine mammals the Federal agencies will work to increase detection of strandings or mortalities at sea associated with sound-producing activities. The Services will strive to make their stranding investigations and other monitoring activities and assessments transparent and accessible to the public in a timely manner, recognizing that it takes time to collect and analyze full scientific information. Sound producers should work with the management agencies to include a verification process in a self-reporting system, or include a mechanism for unannounced inspections. Improvements to any compliance program can result from developing best practices guidelines, developing and applying effective monitoring systems, implementing environmental management systems, and conducting and strengthening enforcement activities. A compliance program should consist of well-designed requirements with clear objectives, sound implementation, and evaluation methods. International Efforts to Reduce Impacts of Sound on Marine Mammals Based on these actions and U. Summary of the mitigation tools currently in use or available for addressing impacts of anthropogenic sound on marine mammals. The order in which the tool types are presented here is not intended to indicate any preferential order for their use. Operational Procedures (Marine Mammal Detection With Activity Modification, Aversive Alarms, etc. Effectiveness depends on appropriately and accurately defining and maintaining a safety zone around the sound source. Moreover, ramp-ups are not always practical for military sonar as they would lead to loss of tactical advantage, although they may be useful for mitigation during some practice maneuvers or testing. Some operational modifications have been successfully applied, but the use of such measures is not widespread, and their effectiveness has not been thoroughly tested. Some operational modifications have been put in place to protect marine mammals from other anthropogenic impacts. A specific type of operational restriction that merits separate mention because they are often overlooked in the protection of marine mammals. Rocket launches, helicopter flights, aerial surveys and other aircraft activities can be subject to a variety of requirements such as maintaining a minimum altitude and/or a maximum speed, or following geographic, seasonal or temporal restrictions. Issues related to the limitations, effectiveness, and potential applications of flight restrictions are similar to those related to other operational restrictions. Temporal, Seasonal, and Geographic Restrictions (Habitat Avoidance, Routing and Positioning, etc. A safety zone is a specified range from the source (generally based on a received sound pressure level) that must be free of marine mammals before an activity can commence (often referred to as determining an "all-clear") and/or must remain free of marine mammals during an activity. Using these methods, it is unlikely that 100% of all marine mammals will be detected. Typically combined with a safety zone and/or observers, this involves the suspension of an activity until the marine mammal has left the safety zone or normal behavior has been restored. Issues related to shut down and stand down are similar to those discussed on observers, passive and active acoustic monitoring, and Dynamic Management Areas. For example, application of shut down or stand down can have significant operational costs.
Syndromes
The main difference between computer-related and traditional fraud is the target of the fraud; if a person is targeted, then it is traditional fraud, but if a computer or computer system is targeted, it becomes computer-related fraud. Although some criminal law systems do not yet cover the manipulation of computer systems for fraudulent purposes, offenders often still can be prosecuted. Nonetheless, many governments may need to include computer-related offenses in their definitions of various crimes in order to prosecute. Computer-related offenses, such as fraud and forgery, generally fall within the purview of criminal law enforcement 132 Broadband Strategies Handbook authorities, while others like the protection of privacy or unsolicited communications (spam) may be the responsibility of data protection authorities or a consumer protection agency. However, if mandates overlap, it is critical for all relevant authorities to coordinate the exercise of their respective functions (Gercke et al. With regard to content-related offenses, the development of legal instruments to deal with these offenses is heavily influenced by national approaches. Cybersecurity and the Need for International Coordination Cybersecurity is highly globalized because cybercrimes and other attacks can be committed against Internet users, businesses, or governments from anywhere in the world. Cybercrime and cyberwar have very clear and direct negative effects on economic activity, but cyber defense can have similar negative effects, due to its high cost and information inefficiencies caused by the deliberate isolation of networks and databases from one another. One is that different countries take different approaches to cybersecurity, which can lead to a lack of multistakeholder participation in both policy making and legislation. Another problem is that upstream policies promoting an e-agenda conflict with the downstream protections of rights and property. In addition, legal concepts may be outdated in the burgeoning world of cyberspace. The core issues of jurisdiction and sovereignty make it difficult to cross borders to address international cybersecurity events. A fourth issue is simple human error when using the Internet or writing software code. A final barrier to international cybersecurity coordination is that existing cybersecurity tools are often not fully applied. Privacy and Data Protection Threats to privacy and data protection must be addressed to foster demand and promote broadband take-up. Legal and regulatory tools to address these issues can help to build consumer trust and confidence, which are indispensable for a full broadband experience. While consumer privacy and data protection are not novel subjects, broadband diffusion and technology innovation compound the potential risks associated with the collection, use, protection, retention, and disposal of a wide range of personal information. Increased data processing and storage capabilities, advances in online profiling, and the aggregation of online and offline information are allowing a diverse set of entities to gather, maintain, and share a wide array of consumer information and data. Governments are also concerned with protecting their citizens from practices that may violate their privacy. Issues such as cloud computing, online behavioral advertising, web tracking, and location-based services may create additional privacy risks, but may also provide tremendous benefits for consumers in the form of new products and services. However, increased collection of personal data is not limited to businesses and the private sector. Governments also increasingly collect such data from their citizens as they engage in e-government and other initiatives. Thus, to promote broadband, countries must set up frameworks that strike the appropriate balance between the benefits to citizens and consumers of new and innovative technologies and the risks such technologies may create to their privacy and 134 Broadband Strategies Handbook personal data. Also, due to the cross-border nature of Internet data traffic flows, international cooperation and coordination will be critical to enforce online privacy frameworks. Scope of Privacy and Data Protection in a Broadband Environment Privacy and data protection in the broadband environment must continue to focus on assessing risks to consumer information throughout its life cycle-from collection to use to storage to transmission to disposal-and then on adopting safeguards that are reasonable and appropriate to mitigate the identified risks. To date, two broad approaches toward personal data protection have been adopted around the world. Under this system, personal data protection is regulated as a fundamental right that applies to all personal data, irrespective of the type of data. More recent developments seem to be bridging this divide, with the European Commission and the U. Federal Trade Commission proposing many common changes and upgrades to privacy protection in the wake of rapid technological developments associated with broadband services and the Internet (European Commission 2010b). This includes emphasizing informed consent, requiring increased transparency of data collection, raising awareness, and increasing responsibility of data controllers (that is, privacy by design). Broadband-enabled activities, such as online behavioral advertising, raise new questions regarding informed consent and the extent to which, for example, Internet browser settings may be considered to deliver such consent or whether a more uniform, comprehensive mechanism should be adopted for online behavioral advertising, sometimes referred to as "do not track.
Alternative Thinking 2011: A Look at 10 of the Top Issues and Trends in Renewable Energy, Deloi e, 2010380 this report explores some of the most crucial issues and trends related to clean energy activities. The analysis investigates uncertainty-related issues, funding, social impact, customer relationship management, income resource development, infrastructure challenges and supply chain development of renewable energy sectors. Energy subsidies, in particular, are often used to alleviate energy poverty and promote economic development by enabling access to affordable modern energy services. Poorly implemented energy subsidies are Green Infrastructure Finance: Leading Initiatives and Research 111 economically costly to taxpayers and can damage the environment through increased emissions of greenhouse gas and other air pollutants. The report also provides a roadmap to guide policy makers, based on lessons drawn from case studies in developed and developing countries. The means to protect these sectors should be developed and concrete adaptation measures fully incorporated into sector planning. In 2010, eight developing economies also volunteered for assessment against the 2010 Bogor Goals. The agricultural sector and some industrial sectors (such as textiles, clothing and footwear) are still afforded conspicuously high levels of protection, both at the border and through domestic support for producers and manufacturers. In the agricultural sector, the level of protection for producers varies greatly among economies. It also contains information on notable energy developments, including policy updates, upstream development, energy efficiency, low-carbon energy, and environmental issues. Green Infrastructure Finance: Leading Initiatives and Research 113 Barriers to Private Sector Investment in the Clean Energy Sector of Developing Countries, Duncan Ritchie, May 20109 this paper examines the barriers that private sector organizations encounter when investing in the clean energy sector of developing countries. Investment volumes continue to be insufficient as a result of the transaction costs and the higher level of risk. Moreover, being a pioneer in this sector and these countries carries very few advantages as differential costs are, in this case, even higher. Governments and development institutions can help reduce preparation costs, reward pioneers, and secure a future for the sector. This paper considers six projects that are using resources from one or all of these sources in combination with development finance to advance low-carbon development. Moreover, the paper describes objectives, overall approaches, project sizes, and financing-related issues of the above-mentioned financing instruments to support low-carbon growth. Finally, this paper draws lessons for the broader development community on how resources from different climate financing instruments can be combined for expanded impact, increased leverage, and enhanced efficiency. At the same time, Brazil has used the abundant natural resources of its territory to explore and develop low-carbon renewable energy. Building Bridges: State of the Voluntary Carbon Markets 2010, Ecosystem Marketplace & Bloomberg New Energy Finance, 2010249 Throughout 2009, while voluntary carbon market transaction volumes remained relatively small, the marketplace thrived as an incubator of innovative protocols, registries, alliances, and project types. In the context of the regulated markets, the voluntary carbon markets proved they could be "the size of a mouse but have the roar of a lion. In 2009 many entities engaged in the voluntary carbon markets solely as a precursor for ensuing major compliance. However, half the marketplace remains driven by "pure" voluntary buyers seeking to offset emissions. These buyers grew increasingly sophisticated, seeking specific credit types from specific locations. Despite the recession, numerous companies initiated offset programs or continued to commit to offse ing goals. However, the concept of offse ing has not lost its controversial edge and many stakeholders continued to emphasize the importance of reducing internal emissions before purchasing offsets. Accordingly, this paper examines the implications of allowance cancellation, considering lessons from other, related experience. The paper argues that the purchase and cancellation of allowances reduces the available allowances in a cap-and-trade system, "tightening the cap" and, in principle, reducing the emissions that can be produced by covered sources. By this logic, purchasing and cancelling an allowance compels covered sources to achieve additional mitigation. Opportunities for voluntary buyers to purchase and cancel tradable compliance units currently exist in several markets, but in small quantities. If the practice of cancelling allowances remains limited to individuals and voluntary corporate buyers, it is likely to remain small and is unlikely to send a strong price signal. In the medium- and long-term this might change if large numbers of sub-national actors choose to cancel allowances. However, this has created new questions regarding both the sources of that money and the policies it is supposed to pay for.
Any exclusion to liability insurance, bond, cash certificate of deposit, annuity or irrevocable letter of credit coverage shall be listed on a form approved by the Director. Bodily injury - fifty thousand dollars ($50,000) per person/one hundred thousand dollars ($100,000) per occurrence. The applicator must notify the Department in writing immediately after cancellation or reduction of the financial coverage. The recertification period for professional applicators will be concurrent with their two (2) year licensing period. This license category will expire on the 31st of December in the year that it was issued. Licenses belonging to professional applicators with last names beginning with A through L, inclusive, expire on December 31st in every odd-numbered year, and licenses belonging to professional applicators with last names beginning with M through Z, inclusive, expire on December 31st in every even-numbered year. Recertification requirements may be accomplished by complying with either Subsection 100. A person accumulates recertification credits by attending Department-accredited pesticide instruction seminars and meet the following criteria: i. Complete a minimum of fifteen (15) credits, based upon one (1) credit for each one (1) hour of instruction for each recertification period. To request accreditation for a seminar not provided by the Department, an applicant must submit a written request to the Department not less than thirty (30) days prior to the scheduled seminar. Under exceptional circumstances, as described in writing by the person requesting accreditation, the thirty (30) day requirement may be waived. The number of credits to be given will be decided by the Department and may be revised if it is later found that the training does not comply. Credit is given only for those parts of seminars that deal with pesticide subjects as listed in Subsection 100. No credit will be given for training given to persons to prepare them for initial certification. Verification of attendance must be submitted with the license renewal application. Recertification examinations may be taken by a professional applicator beginning the thirteenth month of the recertification period. Any professional applicator with less than thirteen (13) months in the licensing period is not required to obtain recertification credits during the initial licensing period. Excess credits may not be carried over to the next recertification period, if a person accumulates more than fifteen (15) credits during the recertification period. Upon earning the recertification credits as described above, license holder is recertified for the next recertification period corresponding with the next issuance of a license, provided that the license renewal application is submitted within twelve (12) months after the expiration date of the license. Any license holder who fails to accumulate the required recertification credits prior to the expiration date of their license will be required to pass the appropriate recertification examination(s) before being licensed. Issuance of variances will not relieve the recipient from compliance with all other responsibilities under the Pesticide and Chemigation Act and Rules. Examination scores are valid for twelve (12) months after the date of the examination. The examination procedure is the same as for professional applicators (Subsection 100. Licenses belonging to private applicators with last names beginning with A through L, inclusive, expire on the last day of the month listed on the chart in Subsection 150. Any person with less than thirteen (13) months in the initial licensing period is not required to obtain recertification credits for the initial period. Recertification and relicensing may be accomplished by complying with either Subsection 050. Last Name Odd Year A-D E-H I-L Even Year M-P Q-T U-Z March July October Month to License b. A person accumulates recertification credits by attending Department-accredited pesticide instruction seminars. Guidelines for obtaining recertification credits are described in Subsections 100. Any credits accumulated beyond the required six (6) in a recertification period may not be carried over to the next recertification period.
Some of the spectrum was awarded to a new operator, shaking up the existing duopoly and triggering intense competition in the mobile broadband market. As a result, mobile broadband, which launched in 2007, surpassed fixed broadband connections by 2009 and made up almost three-quarters of all broadband connections in 2010. Exchanging videos and music, social networking, and Internet telephony are the main uses driving people to broadband, with a combined increase of 25 percentage points in 2010. Considering that the majority of Internet access is over mobile broadband, growing usage is beginning to impose constraints on networks, affecting quality. Further, only about one-quarter of households in Morocco have a broadband connection. Broadband availability in large enterprises is widespread, and most companies have a website. However, the use of online transactions is limited, with only around one-fifth of the population buying or selling goods and services over the Internet. Broadband use by micro, small, and medium enterprises with fewer than 10 employees is much more limited. Targets include creating employment opportunities within the sector 324 Broadband Strategies Handbook and providing broadband to all schools and one-third of households by 2013. The development of local content is a key strategy, including increasing the availability of e-government to some 90 online applications. In an effort to get more small enterprises to adopt broadband, free training will be provided, including sensitizing businesses about the benefits of high-speed Internet for increasing productivity and competitiveness. At the end of 2010, wireline broadband subscription rates stood at almost 30 percent, the highest rate among all countries in the Latin American and Caribbean region. This achievement in broadband can be attributed in part to the small physical size of St. Among the Caribbean islands, however, "smallness" is certainly not unique, and several other factors have contributed to this achievement. The phrase "strength in depth" is borrowed from the world of soccer, the most popular sport on the island. Promoting basic education and digital literacy, building technology awareness, facilitating access to basic technologies, and encouraging a competitive telecommunications environment are but a few examples of where the country has developed its core strengths. Global Footprints: Stories from and for the Developing World 325 the deployment of a second submarine fiber network in 2006 has introduced competition in international backbone capacity that should further enhance the broadband sector. However, as in any ecosystem, sustainability and growth can be threatened by internal weaknesses. Some of these weaknesses have served as lessons learned and were adjusted at the national level; others continue to pose a challenge to the islands. Costly services, an unstable power supply, quality of service issues, lack of high-speed mobile networks, and deficiencies in the availability of local content and applications that create network value for citizens are some of the challenges for future growth of the broadband sector in St. In general, the country has been successful in promoting uptake of broadband Internet by taking measured approaches, which may be of relevance to discussions on broadband strategies pertaining to other small island developing states. Sri Lanka Sri Lanka, an island nation located in the Indian Ocean just south of India, has recently experienced rapid growth in the availability and use of mobile broadband services (Galpaya 2011). Early access to spectrum enabled operators to gain experience and constantly innovate to stay competitive. As a result, Sri Lanka has the fastest mobile broadband technologies in South Asia. A series of comprehensive supply- and demandside projects has helped to create awareness about broadband in the country. For example, one project set up a network of nearly 500 rural telecenters, while a least-cost subsidy scheme has been planned to build and operate a fiber backbone in rural areas as well as to establish a comprehensive e-government program. Additionally, operators have been motivated to invest in network infrastructure in light of projected demand. Beginning in the early 1980s, Sri Lanka was plagued by a violent ethnic conflict, which forced a large portion of the minority Tamil population to leave Sri Lanka and seek refuge in other countries.
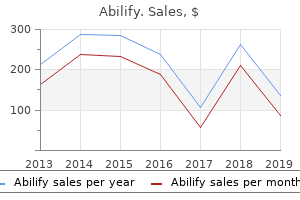
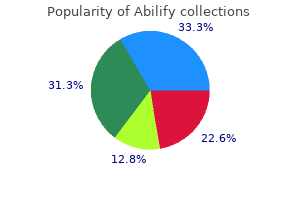
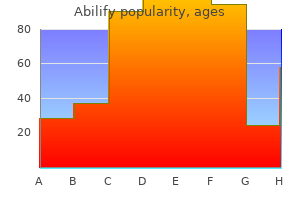
Ruda (Quassia). Abilify.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96313

The full range of options available to marine mammals to overcome masking is not known. There is uncertainty about the potential of general, non-directional ambient noise to cause masking, which results from a lack of information about ambient noise levels. There have been no studies to date specifically investigating these stresses in marine mammals. There is uncertainty about the possible role of acoustic resonance in beaked whale strandings associated with sound exposure. Disagreement currently exists over the possible role of gas bubble growth in beaked whale strandings. It is unclear what, if any, specialized adaptations deep diving marine mammals may have evolved to avoid decompression-type effects during their routine diving behaviors. The long-term, cumulative impacts of sound exposure on behavior are also unknown, making it more difficult to determine the significance of observed behavioral changes over time. Little is known about the extent to which marine mammals can or do adapt their behavior to changes in anthropogenic sound. It is also uncertain how most marine mammal species may respond behaviorally to long-term increases in background noise levels. The characteristics of sound that trigger a behavioral reaction are often unknown. There are few direct data concerning the behavioral effects of sound on marine mammals. Uncertainties about the effects of sound on marine mammals are driven by several fundamental problems. First, the lack of baseline behavioral data for most marine mammals makes it difficult to measure and interpret behavioral responses to sound. Fourth, sample sizes in studies where behavioral changes are documented are often small, and the results are often specific to a particular location and scenario, making general conclusions difficult. In addition, even where behavioral changes are documented, interpreting the effects that are detected is extremely difficult, at best. While the above is not meant to imply that we do not know anything about these issues, it highlights the significant gaps in our current understanding. We do not even know what the hearing range is for most cetaceans (only 11 out of the 83 known species), and we have no measurements on mysticetes at all. Most of what is known about the hearing range of these species comes from studies with one or a few individuals belonging to these 11 species. Extrapolation of these few data points is then used to determine the hearing range of the entire species. We know that there are great variations in the hearing ability and range of individuals within a species, and thus any extrapolation within the same species should include the probability of error and set possible bounds. To then use the extrapolated data to extrapolate again between species where there are no direct observations or experimental data is scientifically inaccurate and can only lead to erroneous conclusions. While extrapolation is a valid scientific tool, extrapolations must be used with great care and underlying assumptions must be clearly stated. More confidence is placed in extrapolations where comparisons are made between more closely related species or where sample size is larger. Use of extrapolations in this field at this early stage of our knowledge is justifiably controversial. Extrapolation increases in validity as the body of knowledge and extent of data increase in robustness. The degree of uncertainty that exists in this newly emerging field of science should not be used as a justification for postponing action to prevent environmental degradation. The potential for harm to occur before it is detected necessitates the use of a precautionary approach to the review and permitting of activities that involve the intentional production of anthropogenic sound.
Other presentations include breast swelling, asymmetry, pain, tumor mass around the implant, and local hyperemia7,8. In the diagnostic assessment before surgery, it is suggested to perform, whenever possible, the immunophenotyping of the periprosthetic fluid by flow cytometry. In the presence of longer periods, the fluid must be discarded18, a fact that emphasizes the need to forward the material in the shortest possible time. It is suggested that no less than 50 mL of seroma be collected for cytopathological assessment and cell block preparation. At the same time, for flow cytometry immunophenotyping, it is recommended that at least 10 mL of aspirated fluid be collected in separate syringes. The collected fluid can be viscous, serous, or hemorrhagic, when anticoagulant can be added, such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or heparin. There are several advantages in performing the cell block since the cytocentrifugation of the collected fluid makes it possible to obtain low-volume, high-cellularity, and paraffin-embedded material, which makes it possible to perform additional cuts and immunohistochemical reactions. The material can be sent without preservatives (in natura), or 70% alcohol, methyl alcohol, or 10% buffered formalin can be added, depending on the preference of the laboratory18,19. The presence of a previous infectious and/or inflammatory process is related to the development of seromas, which may be secondary to infections, trauma, or rupture of the prosthesis. In the presence of a tumor mass, the concomitant resection of the tumor is suggested, with free margins20, since patients with complete resection present better outcome14. However, when there is only diagnostic suspicion, the indication of bilaterality becomes questionable, and the surgeon must previously discuss this fact with the patient. Adjuvant treatment is conducted with the team of clinical oncology or hematology, and the follow-up must be carried out, jointly, every three to six months in the first two years6. Diagnosis of anaplastic large cell lymphoma on late periimplant breast seroma: Management of cytological sample by an integrated approach. Cytological diagnostic features of late breast implant seromas: From reactive to anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma, a systematic review and indepth evaluation of the current understanding. How to Diagnose and Treat Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Achieving Reliable Diagnosis in Late Breast Implant Seromas: From Reactive to Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma - From diagnosis to treatment. In them, space is opened for the presentation of clinical studies, translational studies, experience reports and videos, with the best-designed studies being selected and awarded. The lack of clear criteria allows for differences in assessments, making it difficult to place value on situations associated with research. In order to improve quality, it is necessary to evaluate ethics, the hierarchy of scientific evidence (methodology), the study design, the originality, the relevance, and the linearity of the material presented. The journals present their editorial board, but there are a large number of articles to be evaluated. The editors evaluate the received article and verifies if it fits the scope of the journal. There is a tendency to select new data, which will potentially be the basis for the bibliography of other studies and, consequently, will increase impact. It is then up to authors to create or present material that has been previously rarely addressed. There are major world events, American or European events, national events, state events and local events. It is possible to present a study orally, in a main auditorium, in parallel auditoriums, with posters, and with e-Posters etc. It should be noted that scientific events have greater flexibility than scientific journals. This is because they are spaces reserved for discussion and the dissemination of knowledge, and are associated with the need to group professionals, creating spaces for the presentation of studies and new technologies and allowing for the improvement of interpersonal relationships, and the strengthening of specialties and services. In the selective selection process, there is a relationship between quality and quantity, a fact that is influenced by the availability of space and time for presentations; in addition to the need to include services and young researchers. To enhance the quality of studies, the best studies are given awards according to selection and classification rules and scores.

Range and level of skills One of the reasons that knowledge and skills transfer in the tourism industry is so highly valued is that personal skills are critical at all levels of the tourism chain. This reflects the fact that tourism is an "experience good", in which final consumers are closely linked with the service providers at all stages of the process of production and consumption. Moreover, in countries with a long history of tourism, it is likely that the differences in skill levels within hotels are related more to the nature of the tourism or the type of hotel than to the nationality of its owners. However, some tentative evidence supporting the expectations above emerged during the interviews. However, beach hotels, which are for the most part of a lower standard, reported a smaller proportion of staff with managerial responsibilities, the average being around 3 per cent. The foreign beach hotels reported having a lower proportion of managerial staff compared to the local hotels, but the sample was very small and may not be representative. These hotels are more likely to be linked with foreign ownership and/or management. In Mauritius and the Dominican Republic, on the other hand, there was no discernable difference between the responses given by foreign as compared to local hotels. Training One of the most apparent differences between foreign and local hotels concerns training. They have the benefit of economies of scale and scope, as well as experience in running a systematic training programme directed at international markets. The main channels of knowledge transfer are staff training programmes such as on-the-job training, films, lectures, courses at headquarters and instruction manuals. Another indication of the importance of training in foreign and local hotels can be gleaned from the priority given to this activity. Not all interviewees answered this question in a way that allows direct comparison, but a general impression seems to be that foreign hotels spend more. In some foreign hotels, a regular proportion of annual sales is earmarked in advance for training. One respondent (a foreign hotel in Kenya) cited expenditures of up to $60,000 on training in one year, although others did not give a financial breakdown. In the Dominican Republic, managers of both national and foreign hotels accorded high importance to training, and their employees assist in running external training courses regularly and frequently. The Government levies a specific training tax on the tourism sector, and hoteliers can opt to spend the money directly on training and deduct expenditure from the training tax, so that training is the norm in all hotels. There may also be differences in training related to the particular choice of skills that are emphasized. The gain to the host country is not only that the hotel is run efficiently but also that these skills may spread to the local segments of the tourism industry through the mobility of managers and labour. Many appear to be employed in the United Republic of Tanzania and Dubai, for example. This is particularly marked in some of the countries that are newer to international tourism, and which currently lack a tourism training school. For example in the United Republic of Tanzania, training must be provided in-house. In part, this was to make the best of an unanticipated delay in opening, but it also indicates the resources that are available to global hotel /. In comparison, in a new locally owned hotel that most closely targets the same high-end market, the owners rented a building near the hotel under construction, and used it as a classroom. Using a makeshift kitchen, the first-time employees were trained in cooking, waiting and other elements of customer relations, taught by consultants employed on contract from India. This hotel aims to have the same standards as its foreign competitors and has clearly made a significant investment to this end. In most other local hotels, new entrants were trained in-house, learning more informally from older staff or from the hotel managers.

Digital mammograms use the same X-ray science as older mammograms, but using a digital receiver in lieu of film yields a number of benefits, including less radiation exposure for the patient, immediate lab results, and most importantly, more accurate readings. In addition, electronic storage and transmission of mammograms allows doctors to easily compare mammograms from multiple years or patients to provide more accurate diagnosis. Another advantage of digital images is that they can be analyzed and manipulated by computers after processing. Projects such as the Visible Human Project, for example, have created detailed, threedimensional representations of the human body. Researchers also can model diseases in these virtual environments and help improve research on better treatments. Advances in the fields of medical imaging and robotics have even enabled computer-assisted surgery. The da Vinci Surgical System, for example, allows surgeons to use a robotic eye and robotic arms to conduct minimally invasive surgeries such as removing the gall-bladder, removing the prostate, and conducting other various surgical procedures on the chest. Surgeons control the da Vinci Surgical System through a special console that gives them an enhanced view of the operating table and precise control of the electronically controlled medical instruments. Using high-speed networks to transmit real-time audio, video, and health data, surgeons can remotely operate robotic arms in an operating room thousands of miles away. The first transatlantic surgery occurred in 2001, with the surgeon in New York City and the patient in Strasbourg, France. Telesurgery has the potential to improve care for residents in rural locations by providing them access to the best medical experts. Telesurgery can also be used by patients too sick to travel or in locations without a doctor, such as a war zone or the International Space Station. The use of a head-mounted display that enhances the sense of sight by combining virtual objects with real-world objects is the most common example of this technique. By providing surgeons with virtual X-ray vision, for example, Augmented Reality can allow minimally invasive or noninvasive surgery. Minimally invasive surgery is more difficult than traditional surgery (because small incisions reduce the ability of a surgeon to see inside), but it reduces trauma to the patient and shortens recovery times. A surgeon could create a three-dimensional model of a tumor from ultrasound images, for example, and then superimpose in silico studies, or medical studies conducted by computer simulations. Using grid computing, a researcher may conduct a simulation to evaluate which drug or combination of drugs will likely be most effective on a patient given a set of genetic markers. These simulations require vast amounts of computing power to analyze not only large data sets but also drug interactions, drug resistance, immune responses, and mutations. National Cancer Institute, is the result of a collaborative effort by health care researchers to build an flexible, online platform for cancer research. Applications include a clinical trial case management system, an in vivo imaging system, tissue banks and pathology tools, and numerous Using high-speed networks to transmit real-time audio, video, and health data, surgeons can remotely operate robotic arms in an operating room thousands of miles away. In particular, researchers have looked to grid computing as health care research becomes more data and processor intensive. By distributing storage, data analysis, and data processing across a grid, grid computing enables participants to build better, more advanced, system together than they would have been able to build alone. Traditionally, health researchers conduct in vivo or in vitro studies-medical studies using either living organisms or test tubes. But grid computing has opened up the possibility of biomedical data analysis tools. The process of sequencing each strand in order proved to be too slow for sequencing the entire human genome. Right now, if you do not live near such a facility, Telemedicine systems can also be used to provide access to health care for individuals in remote locations who would otherwise not receive care. Currently, one of the biggest challenges for researchers is to better understand proteins, the organic compounds responsible for many of the essential functions in cells. It is important to understand the three-dimensional structure of a protein because the shape of a protein determines how it interacts with other molecules. Although scientists can find the sequence of amino acids that constitute a particular protein, predicting the shape of the protein requires testing an enormous number of possibilities to discover which structure is most stable. Yet solving the problem by computer still presents an enormous opportunity over the more costly alternative of discovering protein structures in the lab.
Auctions are also more economically efficient, since those willing to pay the highest price place the most value on spectrum, while the winning bids provide additional revenues to governments. Law and Regulation for a Broadband World 99 Spectrum trading (also known as "secondary markets") is another method that facilitates aggregation of spectrum to meet future data traffic demand requirements by permitting existing licensees to transfer all or a part of their spectrum assignments to third parties with little or no government involvement in the process. Implemented in Australia, New Zealand, and the United States, spectrum trading has allowed late entrants to the mobile market to obtain spectrum rights, which can reduce constraints on new entrants with regard to the timing of their market entry. In the absence of spectrum trading, potential entrants and existing operators seeking to build out their networks further must wait for the government to award new spectrum assignments. Ultimately, spectrum trading provides the opportunity for secondary markets to emerge that can improve the rollout of new services, increase the potential for competitive service provision, and encourage investments in the sector (for an in-depth study of spectrum management and reform in developing countries, see Wellenius and Neto 2008). Although placing greater emphasis on market forces and spectrum trading offers many advantages over the traditional models of spectrum management, ineffective regulatory environments may allow incumbent or dominant operators to control key, high-value spectrum bands. This could result in spectrum hoarding and concentration of the wireless broadband market. As such, there is a trade-off between operators having sufficient spectrum and monopolizing the available spectrum. Many countries seek to mitigate this through build-out obligations, while others impose spectrum caps or set aside spectrum blocks for new entrants. However, at least one study argues that spectrum caps in Latin America may hinder the development of mobile broadband. Spectrum License Renewal As spectrum licenses granted in the 1990s and early 2000s reach the end of their initial terms, license renewal policies will become an increasingly relevant regulatory issue to fostering investment in wireless broadband. Legal certainty is of utmost importance to create an environment conducive to 100 Broadband Strategies Handbook investment and the technological upgrades required to deploy wireless broadband services. Principle and Procedure for Renewal While legal regimes vary, most frameworks have adopted a system based on the "presumption of renewal" or "renewal expectancy. In general, renewal expectancy provisions seek to provide regulators with the flexibility to review and adjust license conditions in response to technological developments and market conditions, while providing the regulatory certainty necessary for licensees to continue investments. In Canada, for example, the licensing framework provides a high expectation of renewal unless a breach of license condition has occurred, a fundamental reallocation of spectrum to a new service is required, or an overriding policy need arises. Some countries, such as Australia, provide less long-term certainty to incumbents, opting instead for a legal presumption that, when a spectrum license expires, the license will be reassigned via a price-based method (for example, auction), unless it is in the public interest to do otherwise. If an appropriate balance is not struck, proposed changes to licenses and the review of associated fees in particular can become highly controversial. A similar controversy surrounded the renewal process for mobile licenses in Bangladesh, where a proposal to extract large renewal fees from existing licensees and the imposition of additional obligations created significant opposition from service providers, apparently causing the government to abandon the idea. Many commonly used wireless devices, such as cordless phones, garage door openers, and smart meters for water and gas metering, depend on unlicensed spectrum. In addition, municipal wireless networks also use unlicensed spectrum to create mesh networks that cover downtown areas or even entire cities. An important emerging use for Wi-Fi is as a complement to commercial wireless networks. As wireless broadband services spread, the demand placed on mobile network capacity is increasing exponentially, putting 102 Broadband Strategies Handbook significant strain on available resources. Technical and service rules for unlicensed spectrum typically specify that unlicensed devices must operate at low power and may not cause harmful interference to a licensed user. In addition, unlicensed devices must generally accept interference from licensed users and other unlicensed devices. Although interference and economic issues may make it difficult or impossible to replace all spectrum licenses with unlicensed use, opening bands to unlicensed devices can support broadband development through the growth of new technologies, efficient use of spectrum, and the entry of new network, service, and applications providers. Spectrum Refarming and the Digital Dividend In order to maximize the ability to offer wireless broadband, particularly where spectrum is intensively used, many countries are engaging in spectrum refarming, whereby existing spectrum users are moved out of a band to allow for new broadband uses. The refarming process is often lengthy and costly, since it typically involves negotiations with existing private and public spectrum holders and potential licensees and may also include compensation for the existing licensees to change spectrum bands. As such, it is important to conduct a thorough spectrum inventory to identify unused or underutilized spectrum as well as heavily used bands before implementing a refarming process. In many developing countries, refarming may be less necessary in the near future since available spectrum may be sufficient and more easily allocated for wireless broadband services.
References: