
These results suggest that it is important to focus on the flexion phase in the relative coordinates of the knee with respect to the hip in evaluating the spatial smoothness of the knee motion of stroke patients. Posture and Gait Title: Developmental changes in postural movement patterns during bilateral arm flexion in children Authors: *T. A total of 174 subjects participated in this study from 4 to 12 years old (number of subjects (n): 4 years: n = 30; 5 years: n = 36; 6 years: n = 41; 7-8 years: n = 21; 9-10 years: n = 15; 11-12 years: n = 31). In response to a visual stimulus presented at 2-4 s after a warning signal, the subjects initiated the bilateral arm flexion as quickly as possible and then stopped their arms voluntarily at a horizontal position. Movement angles of the trunk and leg joints during the arm flexion were analyzed, based on the small reflective markers placed over the following positions: head of the fifth metatarsal, external malleolus, knee, trochanter major, and vertebra prominence. Young children mainly extended the trunk rather than the ankle during the arm movement, while older children leaned the whole body backward. The percentage distribution of each type at aged 11-12 years differed with younger children. These results suggested that the postural movement pattern during bilateral arm flexion would change with age. Runway modeling is a specialized walking style for fashion commercialism, which transmits the information regarding motion attractiveness. In this study, we aimed to investigate the biomechanical features of walking motion generated by the one who are conscious of self-attractiveness and the information transmitted by attractiveness-oriented biological motions. Extracted biomechanical parameters were also analyzed for seeking the meaning of the motion based on Laban movement analysis. During attractive walking condition, participants tried to walk as attractive as possible. Joint motion time series were segmented into each gait cycle started from right foot contact, which was calculated by using heel marker position data. Non-models extended their knees during attractive conditions much more than that during normal condition but not so much as models. Hip adduction was larger for models during stance phase, which reflects "catwalk", and became much larger when the models were conscious of beauty of the movement. Such features of the trunk shape was much more significant for models compared with non-models. Such walking motion could make the whole body shape look "extended", which can be translated as "self-confidence" based on Laban movement analysis. Walking motion of runway models was an exaggeration of such features of non-models during attractive-conscious condition, suggesting that runway walking motion could be based on biologically affective human body movement. In contrast, it is known that neural population involved in generation of its locomotive pattern was not fully identical depended on the locomotion speed. Polarity of the stimulus and reference electrodes were cathodal and anodal respectively. The stimulus intensity was 3 mA and the duration were 15min with 15-s ramp-up and -down periods, while the current was immediately ramped-down after reaching the maximum current in sham stimulus condition. During first 60s of the task, subjects were presented auditory click sound with 1Hz to secure correct cycling rhythm. Following the feedback period, the sound was converted into white noise for last 120s. There were also significant differences of the cycling cadences between cathodal and sham stimulus condition. Movement disorders are directly linked to the impairment of daily activities, such as sit-to-stand. Sit-to-stand often fails due to sit-back at the seat-off, and the support surface cannot be transferred to the foot located in front of the trunk. We examined how the trunk movements of chronic stroke patients are adaptively controlled; thereby contributing to the basic knowledge that helps predict the adaptive process of the nervous system from the resulting movement. We obtained kinematic data using a three-dimensional motion analysis system and calculated three sagittal plane parameters, as shown in the results.
In broad terms, thermodynamics deals with the transfer of energy from one place to another and from one form to another. The key concept is that heat is a form of energy corresponding to a definite amount Species richness the number of species within a given sample, community, or area. Species/ecological community An assemblage or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area and in a particular time. Stakeholder(s) Any individuals, groups or organizations who affect, or could be affected (whether positively or negatively) by a particular issue and its associated policies, decisions and action. Summary for policymakers Is a component of any report, providing a policy-relevant but not policy prescriptive summary of that report. Surface mining Includes strip mining, open-pit mining and mountaintop removal mining, is a broad category of mining in which soil and rock overlying the mineral deposit (the overburden) are removed. By isolating samples of material whose states and properties can be controlled and manipulated, properties and their interrelations can be studied as the system changes from state to state. Tillage In agriculture, the preparation of soil for planting and the cultivation of soil after planting. Tipping point A set of conditions of an ecological or social system where further perturbation will cause rapid change and prevent the system from returning to its former state. Topsoil the upper part of a natural soil that is generally dark coloured and has a higher content of organic matter and nutrients when compared to the (mineral) horizons below. Trade-off A situation where an improvement in the status of one aspect of the environment or of human well-being is necessarily associated with a decline in or loss of a different aspect. Trade-offs characterize most complex systems, and are important to consider when making decisions that aim to improve environmental and/or socioeconomic outcomes. Trade-offs are distinct from synergies (the latter are also referred to as "win-win" scenarios): synergies arise when the enhancement of one desirable outcome leads to enhancement of another. Tragedy of the Commons Title of an influential 1968 essay by biologist Garrett Hardin, which argued that overuse of common resources is a leading cause of environmental degradation. This was interpreted by some, especially economists and free-market libertarians, to mean that private ownership is preferable to the commons for the stewardship of land, water, minerals, etc. Yet in recent years many have challenged this view on both empirical and philosophical grounds. Professor Elinor Ostrom of Indiana University has been a leading figure in demonstrating the practical utility and sustainability of commons governance regimes, particularly in developing countries. This suggests that the vision of human behaviour implicit in the tragedy of the commons metaphor is not as immutable as many economists assert, and that collective management is an eminently practical governance strategy in many circumstances. The tragedy of the "anti-commons" is now frequently invoked to describe the problems associated with excessive privatization and fragmentation of property rights, such that collective action for the common good is thwarted. Transboundary pollution Pollution that originates in one country but, by crossing the border through pathways of water or air, can cause damage to the environment in another country. Transhumance Form of pastoralism or nomadism organized around the migration of livestock between mountain pastures in warm seasons and lower altitudes the rest of the year. Tree-covered area A land cover class that includes any geographic area dominated by natural tree plants with a cover of 10 percent or more. Areas planted with trees for afforestation purposes and forest plantations are included in this class. Trends A general development or change in a situation or in the way that people are behaving. Trophic level the level in the food chain in which one group of organisms serves as a source of nutrition for another group of organisms. Uncertainty Any situation in which the current state of knowledge is such that: (i) the order or nature of things is unknown; (ii) the consequences, extent, or magnitude of circumstances, conditions, or events is unpredictable; and (iii) credible probabilities to possible outcomes cannot be assigned. Uncertainty can result from lack of information or from disagreement about what is known or even knowable. Upscaling the process of scaling information from local, fine-grained resolution to global, coarse-grained resolution. Urban heat island effect the term "heat island" describes built up areas that are hotter than nearby rural areas.
Such events may occur mainly in carp farms where there is an intensive feeding with a high-nitrogen diet, if the fish are also exposed to other stresses caused by. The clinical signs of toxic gill necrosis in carp included the congregation of the fish in the deeper and shaded part of the pond and subsequently, in the advanced stage of disease the body surface darkened and there was a reduced or total absence of the escape response. Pronounced hyperaemia, oedematic swelling and increased accumulation of mucus in the gills are typical features of the patho-anatomic picture. These are followed by a gill necrosis and separation of the epithelium from the gill lamellae. The pillar cells of the gill lamellae are completely exposed over the whole lamellar surface. In the later stages of the disease, necrotic gill lamellae become detached and the margins of the gills are distorted. Histological and pathological examination reveals venostasis, swelling, vacuolization and separation of the respiratory epithelial cells from basal membrane in the gills. Associated with these effects is an increase in the activity of chloride cells in the lamellar epithelium. Dystrophic and necrobiotic cells from the respiratory epithelium (including chloride cells) create a compact mass of debris in the interlamellar space of gills. Extensive effects are characterized by a total lysis and necrotic changes in the cell nucleus. A significant increase in the ammonia level of blood serum in fish is a specific feature of these effects. The main specific effect in carp is the elevated ammonia level in the blood serum. However, because such toxic gill necrosis can be caused by other unfavourable conditions in the pond environment. Preventive measures to control frequent outbreaks of gill necrosis in carp in highly eutrophic ponds are centred on optimizing of the hydrobiological and hydrochemical conditions and ensuring the healthy state of fish stock. Stocking the ponds with fish at the correct time in the spring, and preventing or oxygen deficiency, are among the most important preventive measures. In this context a simple biological test has been developed to determine the optimum timing for the spring stocking of two-year-old carp into ponds with a history of toxic gill necrosis. This test is based on the ability of carp to eliminate ammonia (under the existing physical and chemical conditions of the pond water) given as an oral dose of 350 mg. If the ammonia level in the blood serum decreases to the original value within 6 hours of the dose being given, the fish can be stocked in pond. On the other hand, if the ammonia level in the blood serum remains at a threefold higher level than the original value, the stocking of fish must be postponed until the physical and chemical conditions of pond water allow the fish to eliminate the toxic ammonia. Application of the pesticide Soldep at a rate 200 ml ha-1 (depth of pond l m on average) can ensure the survival of the fish stock when an overproduction of zooplankton, followed by an oxygen deficiency, is expected. Soldep is effective in controlling the daphnid zooplankton and should be applied when there is still a reasonable phytoplankton community in the pond. They are readily oxidized to nitrate or reduced to ammonia, both chemically and biochemically by bacteria. Nitrates are the final product of the aerobic decomposition of organic nitrogen compounds. There is almost no nitrate retention in soil, so it is readily leached to watercourses, ponds and lakes. The main sources of nitrate pollution of surface waters is the use of nitrogenous fertilizers and manures on arable land leading to diffuse inputs, and the discharge of sewage effluents from treatment works. In normal aerobic conditions, ammonia is oxidized to nitrite and then to nitrate by two separate bacterial actions. If the second stage of oxidation is inhibited by bactericidal chemicals in the water, nitrite concentrations will increase. This may be important in small ponds or aquaria where water is recirculated through a purification filter; the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria need to become established for the filter to function, and they may be affected by the use of antibiotics to control fish diseases.
The earliest fossil salmonid, Eosalmo driftwoodensis, dates from roughly 50 million years ago and was described in 1977 from Eocene beds in British Columbia (Wilson and Li 1999). Within the family, the genera Salmo and Oncorhynchus diverged from a common ancestor during the Miocene 15 to 20 million years ago (mya), with Oncorhynchus in the North Pacific Ocean and Salmo in the North Atlantic Ocean. Fossils from the ice ages and interglacial periods of the later Pliocene through the Pleistocene (2. Of more immediate interest, however, and indicative of the incredible ecological flexibility of fishes in the rainbow trout lineage, are the recent discovery and rediscovery of several poorly known trout taxa in mountain drainages Table 1. When authorities are given in parentheses, it indicates that the species was previously described by that author but with a different name. The genus Oncorhynchus includes 10 or 11 species and about 30 subspecies worldwide (Nelson 2006). The name was first applied by Suckley in 1860 to the males (only) of pink salmon (O. Oncorhynchus was, therefore, the earliest applicable genus when biologists recognized the distinct nature of Pacific salmon. With rare exception, this means that the earliest available name becomes the accepted name. Salmo, erected by Linnaeus in 1758 for the Atlantic salmon, was the first valid name in the Family Salmonidae. In 1855, Gibbons described juvenile steelhead from a tributary of San Francisco Bay as S. Subspecies represent geographic variants that exhibit somewhat distinct characteristics from other members of a species elsewhere, yet do not warrant elevation to full species status. Similarly, recognition that the Kamchatka trout and western North American rainbow trout, now more correctly included within the genus Oncorhynchus, did not warrant separate species status led to the reapplication of the law of priority and return to the earliest available species name (mykiss) and the emergence of the new combination, Oncorhynchus mykiss, as the valid name for rainbow trout. Species description Salmonids can generally be distinguished by the presence of a fusiform body, forked tail, adipose fin (a fleshy fin without internal supports along the midline of the back between dorsal fin and tail), and an enlarged fleshy or scaly process (axillary scale or process) at the base of each pelvic fin (Moyle 2002, Nelson 2006). The closely related smelts (Osmeridae) also possess an adipose fin but lack the axillary process, while North American catfishes (Ictaluridae) possess an adipose fin but lack scales and have distinct barbels on the chin. The body of a rainbow trout is usually elongate, becoming somewhat deeper and compressed in larger fish (Moyle 2002, Nelson 2006). The mouth is large and terminal, with the upper jaw usually extending to or beyond the rear margin of the eye. Adult rainbow trout tend to be silvery in background color, with black spots on the back as well as on the 18 dorsal, adipose, and caudal (tail) fins, and a band of pink to red along the sides. The back is often dark blue to brown, the lower sides and belly silvery white to light yellow. Stream residents and spawners tend to be darker, with more intense colors, while lake residents tend to be lighter, brighter, and more silvery. Juveniles often exhibit 5 to 13 dark, oval "parr marks" along the side and light tips to dorsal and anal fins. The fins (except the adipose) are supported by segmented, branched soft rays (no true spines); specific fin ray counts include: dorsal 10 to 12, caudal (tail) 19, anal 8 to 12, pelvic 9 to 10, and pectoral 11 to 17. Scales are small and easily removed, with 110 to 160 pored scales along the lateral line, 18 to 35 scale rows above the lateral line, and 14 to 29 rows below it. Salmonid life history characteristics Conservation and management practices for salmonids must consider the complexity of life histories characteristic of these fishes, particularly when maintenance of self-sustaining populations is desired. The reason for such concern is simply that distinct life history stages must be considered as distinct ecological entities, each with its own habitat requirements, capabilities, tolerances, and ecological pressures. Failure to ensure availability of stage-specific habitats reduces the likelihood that self-sustaining populations may be established or maintained.
PyTral was developed on Python programming language with a graphical user interface programming in pyqtgraph, which allow portability of the tool. At nanoscale resolution, single synapse connectivity maps may radically improve our understanding of neuronal microcircuitry. Coarser resolution datasets provide complimentary approaches and aim to reveal whole-brain connectomes. Insights from these data, and fusion between them, promise to elucidate the function of healthy brains and reveal the neural basis of disease. Computational pipelines for working with these datasets are limited in scale, scope, and accessibility. For many pipelines developed to process neuroscience data, the approach does not scale to terabyte-sized datasets. Many tools are developed for specific datasets, and the results do not generalize to new datasets without extensive development. Finally, research groups often lack the computational expertise to deploy these pipelines for their datasets. Our framework abstracts many of the computer science challenges that are commonly associated with testing neuroscience hypotheses on modern datasets. The framework consists of: 1) canonical tools and pipelines for processing data and benchmarking performance, 2) workflow execution engines for deployment on datasets of varying sizes, and 3) optimization routines to facilitate the application of pipelines to new datasets. We have incorporated ideas and code from open source solutions such as Common Workflow Language, the Galaxy Project, and Apache Airflow. We have developed a robust, reproducible framework for science, specifically for large neuroimaging datasets. We apply this framework to extract connectivity graphs from Electron Microscopy data and cellular densities from 3D volumes of X-ray Microtomography data. We demonstrate how this framework can be easily configured, how a pipeline can be optimized on a small training dataset, and how the resulting pipeline can be deployed at the scale of hundreds of gigabytes or terabytes. To improve the optimization process, we also present results on parameter optimization and reusing methods for new datasets. Overall, this framework aims to provide accessible, reproducible computational neuroscience for a wide range of problems, with an initial focus on large, neuroanatomical datasets. Our goal was to implement a software that is oriented for basic electrophysiology, with a user-friendly graphical interface that allows a user experience that interacts as little as possible with "what is under the hood" unless it is explicitly needed. We introduce a free, open-source software application for integrated and advanced data analytics and visualization in basic e-phys. This tool responds to an unmet need of the large neuroscience community relying on diverse recording techniques, ranging from in vitro slices to free-behaving models. While this ability has resulted in many advances in understanding fundamental mechanisms of brain function in health and disease, it generates staggering amounts of data as a single patient can be implanted with hundreds of electrodes, each sampled thousands of times a second for hours or even days. The difficulty of exploring these vast datasets is the rate-limiting step in using them to improve human health. The first is to keep users "close to the data" so that users may make discoveries about the brain without being misled by artifacts. The second imperative is rigorous statistical methodology, with a focus on transparency and reproducibility of analyses. The final imperative is "play well with others", allowing easy integration of new or pre-existing code written in languages other than R. We describe the data pre-processing and analysis pipeline we have developed and emphasize how our platform enables both confirmatory and exploratory data analysis. However, the question how much extent the optogetical stimulation can be equivalent to electrical stimulation in regulating neuronal encoding has never been thoroughly addressed. Moreover, we found same intensity of optical stimulation induced different ChR2 channel currents at different extracellular Ca2+ concentration. The results suggest that light-evoked action potentials at nerve terminal induce additional calcium influx which may cause the significant change in synaptic transmission and short term plasticity. Our study reveals that direct optical stimulation upon the optogenetically manipulated nerve terminal causes non-physiological change in synaptic transmission and thus calls for further evaluating the scope of application and limitation of optogenetic approach in the study of synaptic transmission as well as neuronal signaling Disclosures: X.
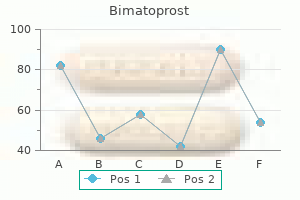
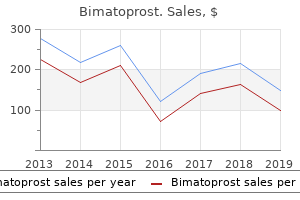
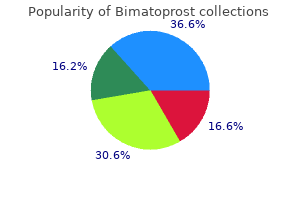
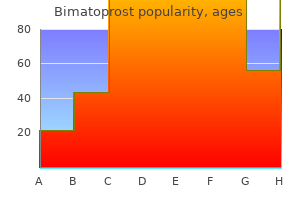
Indian Snakeroot. Bimatoprost.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96766
A tale of two villages: assessing the dynamics of fuelwood supply in communal landscapes in South Africa. Global biomass production potentials exceed expected future demand without the need for cropland expansion. Extreme Weather and Civil War: Does Drought Fuel Conflict in Somalia through Livestock Price Shocks Does increasing energy or electricity consumption improve quality of life in industrial nations Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(15), 6312-6317. International Assessment of Agricultural Knowledge, Science and Technology for Development, Global Report. Forest Product Sale as Natural Insurance: the Effects of Household Characteristics and the Nature of Shock in Eastern Honduras. Deforestation trends in the Congo Basin: reconciling economic growth and forest protection. Sustainability, efficiency and equitability of water consumption and pollution in Latin America and the Caribbean. Integrating indigenous and scientific knowledge bases for disaster risk reduction in Papua New Guinea. Framework for integrating indigenous and scientific knowledge for disaster risk reduction. Gridded population projections for the coastal zone under the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Global analysis of river systems: from Earth system controls to Anthropocene syndromes. Globalization of land use: Distant drivers of land change and geographic displacement of land use. Record-setting algal bloom in Lake Erie caused by agricultural and meteorological trends consistent with expected future conditions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(16), 6448-6452. Reducing nitrogen loading to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River basin: Strategies to counter a persistent ecological problem. Ecosystem services of the tropical seascape: Interactions, substitutions and restoration. New opportunities for combating desertification in Botswana: Women in action for sustainable land and natural resources management. Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(33), 13268-13272. Assessing the distribution of disease-bearing rodents in human-modified tropical landscapes. Co-benefits of biodiversity and carbon from regenerating secondary forests in the Philippines uplands: Implications for forest landscape restoration. Reconciling theory and practice: An alternative conceptual framework for understanding payments for environmental services. Urban charcoal consumption in Tanzania and its implications to present and future forest availability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(47), 18753-18760. Slowing Amazon deforestation through public policy and interventions in beef and soy supply chains. Globalization of the Amazon Soy and Beef Industries: Opportunities for Conservation.
Additional evidence for reproduction is the broad range of adult and juvenile sizes present and report by locals that the species has become increasingly common. The local water bodies are large and the complex area has multiple interconnections with surrounding pond and canal habitats. Extensive dispersal of this fish has probably already occurred because the site is situated in the lowland deltaic tidal plain. The first specimens were netted from a small ditch at the point where it enters into a large reservoir. In contrast, the fisherman stated that the first Oreochromis mossambicus were taken in about 2003, approximately one year before the first "C. This species has been in the ornamental fish trade many decades (Staeck and Linke 1995) and Mr. Welcomme and Vidthayanon (2003:14) reported that Thailand is an important regional center for the aquarium fish trade and that 206 hatcheries breeding and rearing aquarium fishes exist near Bangkok. They also commented that the trade in Thailand (and in other parts of Southeast Asia) is uncontrolled and that some ornamental species had already appeared in the natural environment. A number of cichlid varieties are available in pet markets and shops in Bangkok. However, we have no information indicating the species has been cultured for food in Asia. Our observation in early 2006 that live "Cichlasoma" were being sold at a Bangkok restaurant (Figure 7) is evidence that New World cichlids are being exploited, at least in a minor way, as a food fish in Thailand. We do not know the source for these market specimens and we have not yet observed live or dead "C. Other Southeast Asia Records In addition to our Thailand collections, the only other confirmed population of "C. These fish were taken by cast net from the estuarine area of Punggol River, along the northern coast of Singapore, the first in June and the other in July 2006. The Punggol River is a relatively short, narrow and shallow estuary that flows into the Straits of Johor near the Singapore community of Punggol (approx. Ecological Threat to Southeast Asia To our knowledge the records from Thailand and Singapore represent the first documented cases of "C. Considering its life-history attributes (see Introduction) and given the successful establishment and rapid dispersal of "C. In Florida introduced populations have invaded and become established and are relatively abundant in freshand brackish water habitats, including coastal mangroves and estuaries as well as in a variety of artificial and some natural inland habitats. Results of these past introductions provide perspective on possible outcomes for Southeast Asia. The fish were found at two sites, an estuarine creek system and some freshwater ponds. Since that first discovery, the range of this cichlid in Florida has greatly expanded and it now occupies nearly the entire southern half of the peninsula from mangrove systems of Florida Bay north to the upper Kissimmee River basin and the Indian River lagoon system (Faunce and Lorenz 2000, Matamoros et al. As of 2006, the straightline distance between the site in Everglades National Park, where the species was first encountered, and the approxi-mate northern edge of its expanding front. This equals a rate of invasion dispersal of nearly 15 km per year over the 23year period (1983-2006). Based on unpublished data on the pattern of geographic distribution and the chronology of occurrence, it is likely that "C. Consequently, although not confirmed, the rapid dispersal northward by this species has possibly been facilitated by humans. However, their conclusion was an erroneous representation of the general situation, relying mostly on data presented by Trexler et al. In reality, there is little evidence of a general decline of this species in Florida, and if anything, their continued range expansion and occurrence in samples argues against a general population crash in the state (W. Similar to the situation in Florida, the mere presence and relative abundance of "C. In south Florida, the situation is somewhat unique and may not apply to other parts of the world. Most south Florida fish communities include multiple non-native fish species, including many other New World cichlids.
Initially, the expression of learning depends on the cerebellar cortex, but over time becomes cerebellum-independent, presumably reflecting a transfer of the synaptic changes supporting the memory to a site downstream. In the cerebellar cortex, we used an error-driven rule consistent with the Marr-Albus-Ito theory. In the brainstem, the hypothesized target of consolidation, we used two candidate learning rules based on previous studies: a heterosynaptic rule, and a Hebbian rule with a sliding threshold. In both cases, the dynamics of the brainstem synapse integrate changes in the cortical synapse, and therefore require fine-tuning for stability. Our results suggest that the storage of an analog connection weight for long-term memory is analogous to the maintenance of persistent analog activity in working memory networks; hence, continuous attractor dynamics may also be important for memory consolidation. These techniques included the use of Ca2+ indicators of different affinities and the pharmacological inhibition of specific molecular targets. At longer delays (~100 ms), the supralinear Ca2+ signal is mGluR1-dependent and correlated with an increase in mGluR1-dependent Ca2+ influx via cation channels. In this case, the supralinear Ca2+ signal is not associated with larger depolarisation since the additional Vm transient produced by the cation current is compensated by a slow dendritic hyperpolarisation preventing activation of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. These results shed new light on one of the most important phenomenon in cerebellar physiology. Experimental evidence indicates that climbing fiber-evoked responses in Purkinje cells encode a range of behaviorally relevant information. Excitation from parallel fibers and inhibition from molecular layer interneurons have the potential to modulate climbing fiber-mediated Ca2+ signaling in Purkinje cells contributing to the dynamics of the integrated, dendritic response. It also remains possible that the level of presynaptic climbing fiber activity itself conveys information pertinent for determining the amplitude of the postsynaptic Ca2+ signal. We sought to examine these possibilities by directly monitoring the activity of Purkinje cells, climbing fibers, and molecular layer interneurons in cerebellar Crus I of awake mice to a range of unexpected sensory stimuli. Graded Ca2+ signals were produced in Purkinje cell dendrites; the amplitude of the response changing with the type and intensity of the stimulus. Interestingly, the presynaptic activity level of climbing fibers was altered in a likewise manner. In contrast, molecular layer interneurons responded opposite to what would be expected for these neurons if suppressive inhibition was directly responsible for determining Ca2+ signal amplitude. These results demonstrate that the amplitude of climbing fiber-evoked Ca2+ signals in Purkinje cell dendrites is a largely determined by the firing level of climbing fibers. Blue light was illuminated at 20 Hz (5 ms pulses) for the ChR2 animals, and green light was constant for Arch animals. Animals trained with Arch stimulation showed impaired learning relative to controls, whereas animals trained with ChR2 stimulation showed a slightly enhanced learning curve. The rate of conditioned responses for ChR2 animals was only slightly enhanced compared to controls. Similar to our previous findings (Farley 2016, 2018), no metrics pertaining to the unconditioned response (peak, latency, area, etc) revealed group differences or interactions across opsin groups. Thus, the CeA may have a modulatory role for gating sensory information in precerebellar areas. To test whether sensory prediction error provides a generalizable model to explain the behavior of climbing fibers in other regimes and across other cerebellar regions, we have measured complex spiking in head-fixed mice during two rewarddriven behavioral paradigms. First, we trained mice to associate a visual cue with an upcoming reward and measured complex spiking both at the population level and within individual Purkinje cell dendrites before and after learning. These data suggest that individual climbing fibers can signal distinct task features before and after learning in a manner that is consistent with reward expectation. We also trained mice on a second task that requires a properly timed forelimb movement to receive reward. Population and single dendrite Purkinje cell calcium imaging revealed similar climbing fiber driven responses as observed in the classical conditioning paradigm. Instead, we observed elevated complex spiking when reward expectation was high but no reward was delivered, consistent with climbing fibers signaling an unsigned prediction error related to violated expectation.
References: