
With the increase in television viewing and stationary pursuits such as video games, sedentary lifestyles have become the norm. Organic Precursors the organic molecules required for building cellular material and tissues must come from food. Carbohydrates or sugars are the primary source of organic carbons in the animal body. During digestion, digestible carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into glucose and used to provide energy through metabolic pathways. Complex carbohydrates, including polysaccharides, can be broken down into glucose through biochemical modification; however, humans do not produce the enzyme cellulase and lack the ability to derive glucose from the polysaccharide cellulose. In humans, these molecules provide the fiber required for moving waste through the large intestine and a healthy colon. The intestinal flora in the human gut are able to extract some nutrition from these plant fibers. The excess sugars in the body are converted into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles for later use. Glycogen stores are used to fuel prolonged exertions, such as long-distance running, and to provide energy during food shortage. Excess glycogen can be converted to fats, which are stored in the lower layer of the skin of mammals for insulation and energy storage. Excess digestible carbohydrates are stored by mammals in order to survive famine and aid in mobility. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and protein breakdown provides amino acids that are used for cellular function. The carbon and nitrogen derived from these become the building block for nucleotides, nucleic acids, proteins, cells, and tissues. Fatty foods are also significant sources of energy because one gram of fat contains nine calories. Fats are required in the diet to aid the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and the production of fat-soluble hormones. Essential Nutrients While the animal body can synthesize many of the molecules required for function from the organic precursors, there are some nutrients that need to be consumed from food. These nutrients are termed essential nutrients, meaning they must be eaten, and the body cannot produce them. The omega-3 alpha-linolenic acid and the omega-6 linoleic acid are essential fatty acids needed to make some membrane phospholipids. Vitamins are another class of essential organic molecules that are required in small quantities for many enzymes to function and, for this reason, are considered to be co-enzymes. Absence or low levels of vitamins can have a dramatic effect on health, as outlined in Table 25. Among their many functions, minerals help in structure and regulation and are considered co-factors. Certain amino acids also must be procured from food and cannot be synthesized by the body. The human body can synthesize only 11 of the 20 required amino acids; the rest must be obtained from food. Homeostasis is the ability of a system to maintain a stable internal environment even in the face of external changes to the environment. Humans maintain this temperature even when the external temperature is hot or cold. It takes energy to maintain this body temperature, and animals obtain this energy from food. It is used to build the organic molecules that are required for cells and tissues; it provides energy for muscle contraction and for the transmission of electrical signals in the nervous system. Glycogen is a polymeric form of glucose and is stored in the liver and skeletal muscle cells. Fatty foods are calorie-dense, meaning that they have more calories per unit mass than carbohydrates or proteins. One gram of carbohydrates has four calories, one gram of protein has four calories, and one gram of fat has nine calories. The signals of hunger ("time to eat") and satiety ("time to stop eating") are controlled in the hypothalamus region of the brain. Foods that are rich in fatty acids tend to promote satiety more than foods that are rich only in carbohydrates.
One example of this type of enzyme-linked receptor is the tyrosine kinase receptor (Figure 9. The tyrosine kinase receptor transfers phosphate groups to tyrosine molecules (tyrosine residues). First, signaling molecules bind to the extracellular domain of two nearby tyrosine kinase receptors. Phosphates are then added to tyrosine residues on the intracellular domain of the receptors (phosphorylation). The phosphorylated residues can then transmit the signal to the next messenger within the cytoplasm. Binding of a signaling molecule to the extracellular domain causes the receptor to dimerize. Tyrosine residues on the intracellular domain are then autophosphorylated, triggering a downstream cellular response. The signal is terminated by a phosphatase that removes the phosphates from the phosphotyrosine residues. Besides autophosphorylation, which of the following steps would be inhibited by Lapatinib The types of molecules that serve as ligands are incredibly varied and range from small proteins to small ions like calcium (Ca2+). Small Hydrophobic Ligands Small hydrophobic ligands can directly diffuse through the plasma membrane and interact with internal receptors. Steroids are lipids that have a hydrocarbon skeleton with four fused rings; different steroids have different functional groups attached to the carbon skeleton. Steroid hormones include the female sex hormone, estradiol, which is a type of estrogen; the male sex hormone, testosterone; and cholesterol, which is an important structural component of biological membranes and a precursor of steriod hormones (Figure 9. In order to be soluble in blood, hydrophobic ligands must bind to carrier proteins while they are being transported through the bloodstream. Because these molecules are small and hydrophobic, they can diffuse directly across the plasma membrane into the cell, where they interact with internal receptors. Water-Soluble Ligands Water-soluble ligands are polar and therefore cannot pass through the plasma membrane unaided; sometimes, they are too large to pass through the membrane at all. Instead, most water-soluble ligands bind to the extracellular domain of cellsurface receptors. This group of ligands is quite diverse and includes small molecules, peptides, and proteins. It is able to diffuse directly across the plasma membrane, and one of its roles is to interact with receptors in smooth muscle and induce relaxation of the tissue. If a ligand is then added to the solution, observations show that the dye enters the cell. Describe the type of receptor the ligand most likely binds to and explain your reasoning. Besides autophosphorylation, explain another feature of the cell signaling pathway that can be affected by Lapatinib. A significant contributor to cell signaling cascades is the phosphorylation of molecules by enzymes known as kinases. A Learning Objective merges required content with one or more of the seven Science Practices. Conformational changes of the extracellular domain upon ligand binding can propagate through the membrane region of the receptor and lead to activation of the intracellular domain or its associated proteins. In some cases, binding of the ligand causes dimerization of the receptor, which means that two receptors bind to each other to form a stable complex called a dimer. A dimer is a chemical compound formed when two molecules (often identical) join together. The binding of the receptors in this manner enables their intracellular domains to come into close contact and activate each other. The events in the cascade occur in a series, much like a current flows in a river. Interactions that occur before a certain point are defined as upstream events, and events after that point are called downstream events.
Syndromes
These cells absorb material from the lumen of the digestive tract and prepare it for entry into the body through the circulatory and lymphatic systems. However, each cell is attached to the base membrane of the tissue and, therefore, they are simple tissues. The nuclei are arranged at different levels in the layer of cells, making it appear as though there is more than one layer, as seen in Figure 24. The cilia enhance the movement of mucous and trapped particles out of the respiratory tract, helping to protect the system from invasive microorganisms and harmful material that has been breathed into the body. Goblet cells are interspersed in some tissues (such as the lining of the trachea). The goblet cells contain mucous that traps irritants, which in the case of the trachea keep these irritants from getting into the lungs. They exist in one layer, but the arrangement of nuclei at different levels makes it appear that there is more than one layer. Goblet cells interspersed between the columnar epithelial cells secrete mucous into the respiratory tract. Transitional Epithelia Transitional or uroepithelial cells appear only in the urinary system, primarily in the bladder and ureter. These cells are arranged in a stratified layer, but they have the capability of appearing to pile up on top of each other in a relaxed, empty bladder, as illustrated in Figure 24. As the urinary bladder fills, the epithelial layer unfolds and expands to hold the volume of urine introduced into it. An empty bladder is composed of piled up transitional cells with a folded epithelial lining. Connective Tissues Connective tissues are made up of a matrix consisting of living cells and a non-living substance, called the ground substance. The ground substance is made of an organic substance (usually a protein) and an inorganic substance (usually a mineral or water). Fibroblasts are motile, able to carry out mitosis, and can synthesize whichever connective tissue is needed. Macrophages, lymphocytes, and, occasionally, leukocytes can be found in some of the tissues. When a connective tissue has a high concentration of cells or fibers, it has proportionally a less dense matrix. The organic portion or protein fibers found in connective tissues are either collagen, elastic, or reticular fibers. Collagen fibers provide strength to the tissue, preventing it from being torn or separated from the surrounding tissues. Elastic fibers are made of the protein elastin; this fiber can stretch to one and one half of its length and return to its original size and shape. This fiber consists of thin strands of collagen that form a network of fibers to support the tissue and other organs to which it is connected. The various types of connective tissues, the types of cells and fibers they are made of, and sample locations of the tissues is summarized in Table 24. Collagen fibers are relatively wide and stain a light pink, while elastic fibers are thin and stain dark blue to black. The material in the connective tissue gives it a loose consistency similar to a cotton ball that has been pulled apart. Loose connective tissue is found around every blood vessel and helps to keep the vessel in place. The fibers and other components of the connective tissue matrix are secreted by fibroblasts. Fibrous Connective Tissue Fibrous connective tissues contain large amounts of collagen fibers and few cells or matrix material. The fibers can be arranged irregularly or regularly with the strands lined up in parallel.
Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei that are usually partitioned into two new cells. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division are genetically identical to the original nucleus. They have the same number of sets of chromosomes, one set in the case of haploid cells and two sets in the case of diploid cells. In most plants and all animal species, it is typically diploid cells that undergo mitosis to form new diploid cells. In contrast, meiosis consists of two nuclear divisions resulting in four nuclei that are usually partitioned into four new cells. The nuclei resulting from meiosis are not genetically identical and they contain one chromosome set only. This is half the number of chromosome sets in the original cell, which is diploid. In meiosis I, the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other, are bound together with the synaptonemal complex, develop chiasmata and undergo crossover between sister chromatids, and line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with kinetochore fibers from opposite spindle poles attached to each kinetochore of a homolog in a tetrad. When the chiasmata resolve and the tetrad is broken up with the homologs moving to one pole or another, the ploidy level-the number of sets of chromosomes in each future nucleus-has been reduced from two to one. In this case, the duplicated chromosomes (only one set of them) line up on the metaphase plate with divided kinetochores attached to kinetochore fibers from opposite poles. Instead, they are different because there has always been at least one crossover per chromosome. The four daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and genetically distinct. The daughter cells resulting from mitosis are diploid and identical to the parent cell. Meiosis is such an extraordinarily complex series of cellular events that biologists have had trouble hypothesizing and testing how it may have evolved. Although meiosis is inextricably entwined with sexual reproduction and its advantages and disadvantages, it is important to separate the questions of the evolution of meiosis and the evolution of sex, because early meiosis may have been advantageous for different reasons than it is now. Thinking outside the box and imagining what the early benefits from meiosis might have been is one approach to uncovering how it may have evolved. Meiosis and mitosis share obvious cellular processes and it makes sense that meiosis evolved from mitosis. Adam Wilkins and Robin Holliday[1] summarized the unique events that needed to occur for the evolution of meiosis from mitosis. They argue that the first step is the hardest and most important, and that understanding how it evolved would make the evolutionary process clearer. They suggest genetic experiments that might shed light on the evolution of synapsis. Comparing the meiotic divisions of different protists may shed light on the evolution of meiosis. Marilee Ramesh and colleagues[2] compared the genes involved in meiosis in protists to understand when and where meiosis might have evolved. Although research is still ongoing, recent scholarship into meiosis in protists suggests that some aspects of meiosis may have evolved later than others. This kind of genetic comparison can tell us what aspects of meiosis are the oldest and what cellular processes they may have borrowed from in earlier cells. Explain how the genetic makeup of these organisms differs from organisms that undergo meiosis. Organisms reproducing through mitosis produce genetically different daughter cells whereas those producing through meiosis have genetically identical daughter cells.
Chitin is also a major component of the cell walls of fungi, the kingdom that includes molds and mushrooms. Chitin is a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide, with repeating units of N-acetyl- -Dglucosamine, a modified sugar. Chitin is similar to inulin, a polysaccharide with fructose, but with additional glucose monomers. Chitin contains phosphate groups that give it a stiffness not found in other polysaccharides. What categories of amino acids would you expect to find on the surface of a soluble protein and which would you expect to find in the interior Non-polar and charged amino acids will be present on the surface and polar in the interior of the membrane whereas non-polar will be found in the membrane embedded proteins. Non-polar and uncharged proteins will be found on the surface with non-polar in the interior, while only non-polar will be found in the embedded proteins. Polar and charged amino acids will be found on the surface whereas non-polar in the interior. Polar and charged amino acids will be found on the surface of a membrane protein whereas nonpolar in the interior. Arginine is a negatively charged amino acid and could attach to the glutamate at the end of the segment b. Inserting arginine places a positively charged amino acid in a portion that is non-polar, creating the possibility of a hydrogen bond in this area. What would happen if even one amino acid is substituted for another in a polypeptide The change will definitely not be sufficient to have any effect on the function and structure of the protein. The amino acid may not show any significant effect the protein structure and function or it may have a significant effect, as in the case of hemoglobin in individuals with sickle cell trait. These changes would increase the possibility of having extra bends and loops in the proteins as in Leber congenital disease. For many years, scientist believed that proteins were the source of heritable information. The viral protein was tagged with an isotope, and the host cell was infected by it. The genetic code is based on each amino acid being coded for by a distinctive series of three nucleic acid bases called a codon. An addition of C for G, lengthening the strand and changing every codon past the addition c. A deletion of an A, resulting in a shortening and changing every codon past the deletion d. What is the difference between the effects of the changes in the two types of nucleic acids The capture of radiant energy through the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates is the engine that drives life on Earth. Create visual representations to show how when bonds in the glucose molecules are broken between carbon number 1 and the oxygen atom and between carbons 3 and 4, two molecules of pyruvic acid are produced. Use your representation to show that both phosphorylation (the addition of a phosphate ion) at carbon 5 and removal of the hydroxide at carbon 2 produce water molecules in an aqueous solution where hydrogen ions are abundant. A phospholipid consists of a pair of fatty acids that may or may not have carbon-carbon double bonds, fused at the carboxylic acid with a three-carbon glycerol that is terminated by a phosphate, as shown in the figure below. Most cell membranes comprise two phospholipid layers with the hydrophilic phosphate ends of each molecule in the outer and inner surfaces. The hydrophobic chains of carbon atoms extend into the space between these two surfaces. Glycolysis is a sequence of chemical reactions that convert glucose to two three-carbon compounds called pyruvic acid. One type of membrane was obtained from the cells in the eyeball of a calf (lens lipid).
Activation energy is required for a reaction to proceed, and it is lower if the reaction is catalyzed. When we eat sucrose it is converted to carbon dioxide and water, as with other carbohydrates. Based on your identification, explain if cubes of sugar can be stored in a sugar bowl by creating a diagram similar to Figure 6. If table sugar is placed in a spoon held over a high flame, the sugar is charred and becomes a blackened mixture composed primarily of carbon. Create a visual representation that includes a chemical equation to explain the role of the flame in this process. In terms of your answers to questions 1-3, predict if sugar cubes in a bowl placed in a dish of water can be stored on a table, and justify your prediction. The natural logarithm of the reaction rate constant is a linear function of the inverse of the temperature in Kelvin degrees. The negative of the slope of that graph is the energy of activation divided by the universal ideal gas constant, R = 8. For each process, identify if it is endergonic or exergonic, and provide reasoning for your identification that includes your definition of the system. Explain your reasoning in terms of changes in the amount of order within the system. Explain your reasoning in terms of (a) the source of the energy input into the system and (b) the interaction between the system and its environment that provides that input of energy. For each scenario, describe the system and explain how the second law of thermodynamics applies to the system in terms of energy input and change in entropy. Consider a simple process that illustrates the change in entropy when energy is transferred. The time scale required for half of the molecules of initial sucrose to remain can be estimated. For each process, explain an expected outcome and describe an example of a specific exercise that can lead to the expected outcome. Explanations of the behavior of a poorly understood phenomenon can often be constructed by analogy to a phenomenon that is well understood. For each of the following cellular functions that require free energy, describe a parallel human activity and identify a source of free energy for that activity. For example, the synthesis of proteins can be expected to proceed as an assembly of a small set of sub-components, just as the construction of a building is accomplished by gathering and joining materials. It is consistent with our analogy to expect that there must be a free-energy resource that is consumed in the synthesis of proteins, just as hydrocarbon fuels are a source of energy for the construction of a building. Describe changes in the motion and interactions of water molecules before and after melting. Predict the effect of the energy transfer on the entropy on the system, and justify your prediction. Describe changes in the motion and interactions of water molecules before and after boiling. Predict the effect of the energy transfer on the entropy of the system, and justify your prediction. Describe the source of energy transfer to the system of photosynthetic plants and algae. Explain what happens to the entropy of this trophic level when energy transfer occurs. Explain what happens to the entropy of this system composed of photosynthetic organisms and their abiotic environment. Predict the change in entropy of the system when both autotrophs and their abiotic environment are considered. Predict the signs of the entropy changes in both biotic and abiotic components of this system. Predict the relative magnitudes of these entropy changes, and justify your prediction.
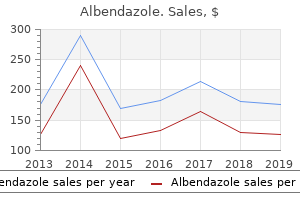
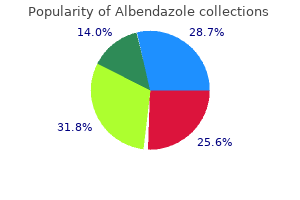
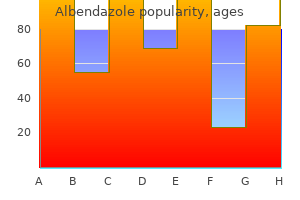
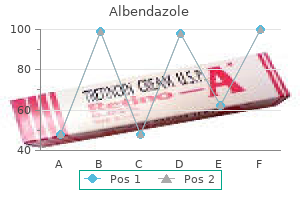
Dade (Date Palm). Albendazole.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96434
This is called wobble; the pairing of the codon and anticodon can "wobble" at this specific nucleotide-to-nucleotide pairing site. Because of wobble, the translation of a codon is least sensitive to a change at the third position. A missense effect will occur when a different amino acid is incorporated at the corresponding site in the protein molecule. This mistaken amino acid-or missense, depending upon its location in the specific protein-might be acceptable, partially acceptable, or unacceptable to the function of that protein molecule. From a careful examination of the genetic code, one can conclude that most single-base changes would result in the replacement of one amino acid by another with rather similar functional groups. This is an effective mechanism to avoid drastic change in the physical properties of a protein molecule. If an acceptable missense effect occurs, the resulting protein molecule may not be distinguishable from the normal one. A partially acceptable missense will result in a protein molecule with partial but abnormal function. If an unacceptable missense effect occurs, then the protein molecule will not be capable of functioning normally. A nonsense codon may appear that would then result in the premature termination of amino acid incorporation into a peptide chain and the production of only a fragment of the intended protein molecule. The probability is high that a prematurely terminated protein molecule or peptide fragment will not function in its assigned role. Some Mutations Occur by Base Substitution Single-base changes (point mutations) may be transitions or transversions. In the former, a given pyrimidine is changed to the other pyrimidine or a given purine is changed to the other purine. There may be no detectable effect because of the degeneracy of the code; such mutations are often referred to as si- Hemoglobin Illustrates the Effects of Single-Base Changes in Protein Encoding Genes Some mutations have no apparent effect. Hemoglobin Milwaukee has at position 67 a glutamic acid; hemoglobin Bristol contains aspartic acid at position 67. The amino acid alterations and possible alterations in the respective codons are indicated. The hemoglobin Hikari -chain mutation has apparently normal physiologic properties but is electrophoretically altered. Hemoglobin S has a -chain mutation and partial function; hemoglobin S binds oxygen but precipitates when deoxygenated. Hemoglobin M Boston, an -chain mutation, permits the oxidation of the heme ferrous iron to the ferric state and so will not bind oxygen at all. This hemoglobin has asparagine substituted for lysine at the 61 position in the chain. The replacement of the specific lysine with asparagine apparently does not alter the normal function of the chain in these individuals. Because the reading frame is a triplet, the reading phase will not be disturbed for those codons distal to the deletion. If, however, deletion of one or two nucleotides occurs just prior to or within the normal termination codon (nonsense codon), the reading of the normal termination signal is disturbed.
Depolarization after peak action potential would be affected because that is the point when K+ begins to leave the cell. Repolarization after peak action potential would be affected because that is the point when K+ begins to leave the cell. Repolarization after peak action potential would be affected because that is the point when K+ begins to enter the cell. Polarization after peak action potential would be affected because that is the point when K+ begins to enter the cell. A nerve impulse opens the Na+ channel, which makes Na+ enter the cell and depolarizes the membrane. A nerve impulse opens the Ca+2 channel, which makes Ca+2 enter the cell and depolarizes the membrane. A nerve impulse opens the Na+ channel, which makes Na+ enter the cell and repolarizes the membrane. A nerve impulse opens the K+ channel, which makes K+ enter the cell and polarizes the membrane. Chemical and electrical synapse are two mechanisms by which signals can be transferred between neurons. Chemical synapse is a multiple-step process in which neurotransmitters undergo transfer and binding to different parts of the cell. However, the left cerebral hemisphere controls the right side of the body, whereas the right cerebral hemisphere controls the left side of the body. The descending neural connections are not switched in the brainstem, which means that the neural connections of the left hemisphere are transmitted to the right side of the body and vice versa. The ascending neural connections are not switched in the brainstem, which means that the neural connections of the left hemisphere are transmitted to the right side of the body and vice versa. The descending neural connections are switched in the brainstem, which means that the neural connections of the left hemisphere are transmitted to the right side of the body and vice versa. The ascending neural connections are switched in the brainstem, which means that the neural connections of the left hemisphere are transmitted to the right side of the body and vice versa. If an increased number of folds in the cortical sheets of the brain is associated with increased social complexity, which of the following animals has the greatest social complexity All myelin sheaths are located in the gray matter, which transmit signals along the brain and spinal cord through the gray matter. All synapses are located in the gray matter, which transmit signals along the brain and spinal cord through the gray matter. All synapses are located in the gray matter, which transmit signals along the spinal cord through the gray matter. All dendrites are located in the gray matter, which transmit signals along the spinal cord through the gray matter. The parietal lobe has been cut, which severs the ability of the left hemisphere from communicating but increases the ability of the right hemisphere. The corpus callosum has been cut, which severs the ability of the left hemisphere from communicating but increases the ability of the right hemisphere. The frontal lobe has been cut, which severs the ability of the left and right hemispheres to communicate. The corpus callosum has been cut, which severs the ability of the left and right hemispheres to communicate. This figure depicts the parts of the body that are controlled by different parts of the motor cortex. What can be inferred about the organization of the motor cortex relative to the organization of muscles in the body Motor cortex neurons are generally located near neurons that control nearby body parts. The thalamus is part of the brain that is involved in various functions in the human body.

Pheromones are sent to the amygdala instead of the main olfactory bulb and are not consciously perceived. Pheromones are sent to the main olfactory bulb instead of the amygdala and are consciously perceived. If an individual was born without the malleus in either ear, explain why they might have problems with hearing. Without the malleus and incus, the vibrations of the tympanum would not be able to reach the stapes and then be sent to the cochlea. Without the malleus and incus, the vibrations of the pinna would not be able to reach the stapes and then be sent to the cochlea. Without the malleus and incus, sound waves would not be collected by the tympanum. Explain how being on the moon, which has less gravity than Earth, might affect vestibular sensation and why. Ultraviolet light includes heat emitted by prey organisms of reptiles which is outside the visual spectrum for humans because the wavelength is less than 380 nm. Infrared light includes heat emitted by prey organisms of reptiles which is outside the visual spectrum for humans because the wavelength is less than 380 nm. Infrared light includes heat emitted by prey organisms of reptiles, which is outside the visual spectrum for humans because the wavelength is more than 400 nm. Ultraviolet light includes heat emitted by prey organisms of reptiles, which is outside the visual spectrum for humans because the wavelength is more than 400 nm. Explain what the color receptors in your eyes are perceiving if you see a white building. All of the color receptors in your eyes are equally stimulated when you see the color white. Both L and M cones are equally stimulated in your eyes when you see the color white. L cones are stimulated strongly and S cones are weakly stimulated when you see the color white. Discuss how the relationship between photoreceptors and bipolar cells is different from other sensory receptors and adjacent cells. Photoreceptors and bipolar cells are depolarized, whereas other sensory receptors typically remain polarized. Photoreceptors and bipolar cells are hyperpolarized, whereas other sensory receptors typically remain polarized. Photoreceptors and bipolar cells are depolarized, whereas other sensory receptors typically become hyperpolarized. Photoreceptors and bipolar cells are hyperpolarized, whereas other sensory receptors typically become depolarized. Some signals go to the temporal lobe, which detects "where" information, and other signals go to the parietal lobe, which detects "where" and "what" signals. Some signals go to the parietal lobe, which detects "where" information, and other signals go to the temporal lobe, which detects "what" signals. Some signals go to the parietal lobe, which detects "where" and "what" information and other signals go to the temporal lobe, which also detects "where" and "what" signals. Some signals go to the parietal lobe, which detects "where" information, and other signals go to the temporal lobe, which detects "where" and "what" signals. The complexity of the human sense of smell can be represented visually as a grid of 100 cells (10 x 10 grid) with each cell associated with a unique molecule-receptor pair. An odorant is detected when the brain integrates the signals generated by each molecule in the mixture. Four olfactory sensors, each innervated by a nerve that transmits information to the brain as an action potential, are shown in the diagram at the right. Three of the sensors each respond to one of the three odor molecules in the geometric representation of the odorant mixture. In the diagram the odorant-receptor pairing is imagined geometrically; a round peg fits in a round hold and a square peg does not. The receptors are located in the epidermal cell surface, shown in the drawing as a light gray line. Create a geometric representation by drawing receptors on the surfaces of the sensors that are activated by one of the molecules in the mixture.
Compare the partial pressure of oxygen between venous blood in an alveolus and air and between arterial blood and body tissues This ratio increases as the lungs become stiff and less pliable, increasing further when there is increased resistance in the lung. This ratio decreases as the lungs become stiff and less pliable, increasing when there is increased resistance in the lung. This ratio increases as the lungs become stiff and less pliable, decreasing when there is increased resistance in the lung. This ratio decreases as the lungs become stiff and less pliable, decreasing further when there is increased resistance in the lung. Amphibians, such as frogs, breathe by collecting air in a pouch below their throat. Inhalation in humans and other mammals involves the openings called spiracles, which connect to the tubular network to allow the oxygen to pass into the body. Inhalation in humans and other mammals involve direct diffusion across the outer membrane to meet oxygen requirements. Inhalation in humans and other mammals involve contracting the thoracic cavity by creating negative pressure in the lungs, which causes air to diffuse into the lungs. Inhalation in humans and other mammals involves expanding the thoracic cavity by creating negative pressure in the lungs, which causes air to diffuse into the lungs. If a patient has increased resistance in his or her lungs, how can this be detected by a doctor By detecting the rate at which air can be taken into the lung, a diagnosis of a restrictive disease can be made. By detecting the rate at which air can be expelled from the lung, a diagnosis of a restrictive disease can be made. When someone is standing, gravity stretches the bottom of the lung down toward the floor to a greater extent than the top of the lung. Pleural pressure gradient leads to increased ventilation further down in the lung. Pleural pressure gradient leads to decreased ventilation further down in the lung. How does the administration of 100 percent oxygen save a patient from carbon monoxide poisoning At that concentration, oxygen will displace the carbon monoxide from the hemoglobin. At that concentration, oxygen will be transported in the body at a high rate by dissolving in blood. The maximum amount of carbon dioxide would be transported in the blood away from the tissues. Only 15 percent of carbon dioxide would be transported in the blood away from the tissues. What is sickle cell anemia and how does it affect the perfusion of oxygen in the blood It is a genetic disease in which red blood cells are sickle-shaped, reducing oxygen perfusion into the blood. It is a genetic disease in which red blood cells are sickle-shaped, increasing oxygen perfusion into the blood. It is a deficiency disease in which red blood cells are sickle-shaped, reducing oxygen perfusion into the blood. It is a deficiency disease in which red blood cells are sickle-shaped, increasing oxygen perfusion into the blood. In the past, the Earth has experienced environmental changes, which have changed the amount of available oxygen and carbon dioxide in the water and air. For example, there is evidence of less oxygen available in the air during the time of the dinosaurs, a result of high volcanic activity creating a large amount of carbon dioxide. How might red blood cells in the dinosaurs have evolved, in terms of size and shape, to adapt to the loweroxygen atmosphere The cell of the unicellular algae Ventricaria ventricosa is one of the largest known, reaching one to five centimeters in diameter. Intubation is a procedure used by ambulance crews that allows a person to breathe if part of the respiratory system is blocked by a foreign object (or otherwise injured). During intubation, a long, plastic tube is placed in the respiratory system so that air can bypass the obstructed area and reach the lungs.
References: