
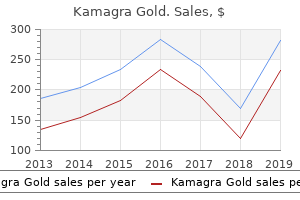
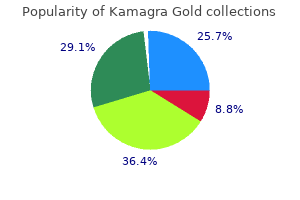
Choledochoduodenal Fistula as the First Sign of Metastatic Ovarian Cancer Muhammad U. Symptomatic Patients Suspected of Eosinophilic Gastritis and/or Enteritis Have Elevated Mucosal Mast Cell Counts Without Eosinophilia: A New Diagnostic Entity Risk Factors for Advanced Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia in a MultiEthnic United States Cohort P2657. Hospitals With Low-Medium Safety-Net Burden Incur the Highest Costs for Hospitalizations of U. Efficacy and Safety of Nitazoxanide-Based Regimen for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis P2659. Tradipitant Complete Responder Analysis in Gastroparesis Patients Presidential Poster Award Jesse L. Patients With Eosinophilic Gastritis and/or Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Endure a Lengthy Path to Diagnosis and Experience Persistent Symptoms After Diagnosis Ira N. Increased Mucosal Innate Immune Activation in Hereditary Alpha Trytpasemia Subjects Is Predictive of Clinical Response to Tofacitanib Therapy Presidential Poster Award Sarah C. Metastatic Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors in Non-Surveillanced Familial Adenomatous Polyposis P2670. An Atypical Case of Metastatic Lung Cancer Presenting as Abdominal Pain and Anemia P2678. Acute Gastric Volvulus - A Rare Complication of a Paraesophageal Hernia Abisola G. Large Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor With Spontaneous Rupture of Necrotic Fluid Collection Eric J. Plexiform Angiomyxoid Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Gastric Cardia: An Uncommon Tumor With an Even Less Common Location P2694. Choleperitoneum Due to Gastric Perforation Masquerading as Acute Pancreatitis in a Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass Patient P2706. Gastric Small Cell Cancer: An Extremely Rare and Lethal Type of Stomach Cancer P2707. Gastritis After Combination Ipilimumab and Nivolumab: A Rare Adverse Event After Immunotherapy P2708. Not for Human Consumption: Caustic Ingestion Causing Delayed Gastric Outlet Obstruction Joy I. Nutritional Deficiencies in a Patient With Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery P2711. A Case Report of Co-Existing Helicobacter pylori and Clostridium difficile Infections: the Need for Treatment Guidelines P2713. Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and a Gastric Mass in a Patient With Acute Epstein-Barr Virus Presidential Poster Award Cesar J. With the variety of exhibitors expected to participate, there are certain to be displays of interest for all attendees. Companies that exhibit include pharmaceutical manufacturers, medical instrument suppliers, research companies, technology companies, publishers, non-profit organizations, recruiters, and many others. This casual social gathering will give all attendees the opportunity to explore the Hall, meet with exhibitors, and network and mingle with fellow professionals. Please do not resubmit abstracts already considered during the regular 2019 abstracts review process. For Becky who helped me all the way through and for Christie and Erica who put up with a lot while it was getting done Contents Preface 1 Introduction 1. Preface xvii Preface this text covers the basic topics in experimental design and analysis and is intended for graduate students and advanced undergraduates. Most of the text soft-pedals theory and mathematics, but Chapter 19 on response surfaces is a little tougher sledding (eigenvectors and eigenvalues creep in through canonical analysis), and Appendix A is an introduction to the theory of linear models. I use the text in a service course for non-statisticians and in a course for first-year Masters students in statistics. The non-statisticians come from departments scattered all around the university including agronomy, ecology, educational psychology, engineering, food science, pharmacy, sociology, and wildlife.
Your fundamental knowledge base draws heavily on the key principles of physiology and pharmacology. To maintain this physiologic homeostasis, anesthesiologists are experts on the latest advances in clinical pharmacology and drug delivery systems. Every day, they use an impressive arsenal of drugs: local and general anesthetics, analgesics, sedatives, cardioactive agents, neuromuscular paralytics, and many more! They are the only physicians who bypass pharmacists and nurses to dose, prepare, and administer the drugs themselves. These intravenous agents cause immediate physiologic outcomes that, for an anesthesiologist, provide instant gratification. In a way, each surgical case offers the opportunity to test a physiologic hypothesis with a pharmacologic intervention. One physician in private practice chose to become an anesthesiologist because of the pace of acute care in the operating room. If you want to become an anesthesiologist, you should feel comfortable manipulating monitors, pumps, ventilators, and other high-tech equipment. These doctors keep a close eye on the patient and the case itself, which is equally as important, and watch for potential problems like acute blood loss or compromised airway. As attentive observers of physiologic parameters, anesthesiologists become adept at multi-tasking. To achieve such crucial goals on a minute-by-minute basis, anesthesiologists make use of a wide array of complex monitoring equipment. Anesthesiology is a great specialty, therefore, for medical students who wish to incorporate the latest advances in biomedical engineering into their careers. From beginning to end, the practice of anesthesiology for each patient is similar to flying an airplane. As captain, the anesthesiologist first conducts a complete preoperative history and physical examination. Induction of anesthesia, using powerful drugs like propofol, represents the "take-off" into the flight of the procedure. This part is more than just pushing medications-anesthesiologists have to set up the appropriate monitoring equipment and then intubate the patient. Once the patient is fully anesthetized, paralyzed, and breathing by a ventilator, maintenance has been achieved. Like a pilot, the anesthesiologist keeps careful watch over the patient, always adjusting physiologic parameters with pharmacologic agents as the case proceeds. Any operating room crises ("wind shear") require rapid interventions and quick thinking. The captain then lands the "anesthesia plane" by reversing neuromuscular paralysis, stopping anesthesia, and safely extubating the patient. The anesthesiologist, not the surgeon, is responsible for making sure that the unconscious patient wakes up at the end of the case alive, well, and breathing spontaneously. For all types of operations, anesthesiologists perform difficult tasks in a life-threatening environment. Always concerned that something may go wrong, anesthesiologists mentally prepare for any potential disasters during every case. Whether the problem involves massive acute hemorrhaging, intra-operative myocardial infarction, or dropping oxygen saturation, anesthesiologists must think fast, act quickly, and draw on their vast medical knowledge to make on-the-spot decisions. Today, many surgical patients are quite sick with multiple medical problems, leading to rather complicated intra-operative courses. Under general anesthesia, even a patient with "only" a history of high blood pressure can create problems for the anesthesiologist. Working with the surgeon, anesthesiologists guard the line between life and death for the unconscious surgical patient. Medical students interested in this field should be aware that anesthesiology requires one to react well to nerve-wracking situations.
Many women in medicine want a specialty that is family friendly-one that lends itself to having greater control over work hours and the possibility of working parttime when they have children. When deciding on her specialty of choice, every female medical student should spend some time honestly weighing these concerns and competing responsibilities. In doing so, you will likely choose the best specialty and have a rewarding professional career in medicine. But surprisingly, a solid number (38%) would choose a new specialty if they could do it all over again. Many variables- work stress, degree of autonomy, work hours, income, and so on-affect how content a doctor is with his or her career. Choosing a medical specialty with the right balance, then, makes a big difference between a happy physician and a dissatisfied one. In fact, the same survey of female physicians revealed that work environment and stress (two factors directly related to their specialty) are the strongest predictors of career satisfaction. Dermatologists, psychiatrists, ophthalmologists, anesthesiologists, and surgeons were among the happiest of all female physicians. Internists and general practitioners, on the other hand, had the strongest desires to change their specialty. With its 8-to-5 workdays and limited call responsibilities, this field should be full of happy doctors. Instead, the same survey found that female radiologists had among the lowest levels of career satisfaction. This was especially surprising in comparison to their colleagues in surgery, who cope with a rigorous lifestyle, long hours, heavy on-call demands, and a male-dominated work environment. Yet despite these perceived lifestyle drawbacks, female surgeons had some of the highest levels of career satisfaction, and 76% even reported that they would definitely not want to enter a different specialty! Perhaps this extraordinary contentment reflects a sense of pride in being a pioneer in surgery, coupled with higher income and more control in their everyday patient care. To ensure the best chance for happiness, female medical students should ask themselves the following questions when thinking about their future career. Some medical students prefer short patient interactions with no continuity, whereas others want to have life-long relationships with all those under their care. In general, women like spending more clinical time than men do with their patients, particularly regarding issues of counseling, preventive medicine, and psychosocial development. If you are more action oriented and like working at a fast pace, then think about emergency medicine, anesthesiology, or surgery. If you seek the latest technical gadgets, then cardiology, radiology, and radiation oncology may be the best specialties for you. The most conspicuous are surgery (and surgical subspecialties), emergency medicine, radiology, and ophthalmology. Keep in mind that high levels of testosterone in the workplace can often lead to inappropriate comments, gender bias, and even sexual harassment. No matter the specialty, it is essential to feel comfortable around the physicians with whom you will be working. It is challenging, but certainly not impossible, for women to maintain a thriving professional career and have children. According to the aforementioned study, the happiest female physicians-no matter the specialty-were the ones who had children. Certain specialties more easily allow for maternity leave and time to raise children, particularly during the peak reproductive years surrounding residency training and initial employment. In a survey of women who entered pediatrics, for example, nearly half based the timing of pregnancy on their career stage, leading to a mean age of conception at 29 years (when most were just out of residency). Take a closer look at whether physicians in your chosen specialty might penalize female physicians for maternity leaves or even actively discourage their pregnancies. For instance, hospital-based specialties such as radiology, anesthesiology, and emergency medicine offer more predictable schedules, ones in which you will rarely take work home with you. Unlike the trauma surgeon, gastroenterologist, or obstetrician, physicians in areas like psychiatry and dermatology seldom get paged for emergencies in the middle of the night. These are all areas of medicine that might be more amenable to flexibility when it comes to timing a pregnancy.
Her family states she has a history of congestive heart failure and hypertension but is usually very active. It is concluded that she has congestive heart failure with possible underlying pneumonia and is placed on supplemental oxygen, diuretics and a course of intravenous antibiotics. However, other organ systems, particularly the gastrointestinal tract, can also be affected, causing hemorrhagic and hypovolemic shock. The incidence of viral infections varies across geographical regions, thus intensivists need to be aware of new and continually emerging diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus, avian influenza, and more recently the Ebola virus. Clinical presentation of a viral infection can be nonspecific and often masquerades as a bacterial infection. Hence, early recognition and diagnosis and close monitoring are key to improved outcomes. Although the majority of viral illnesses in critically ill patients involve the respiratory tract and/or the central nervous system, one needs to be aware of other organ system involvement (such as the gastrointestinal system). Respiratory infections the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia is typically bacterial in nature. Presentation is often nonspecific (fever, tachycardia, hypotension, respiratory distress, altered mental status, and elevated leukocytosis) and can be confused with bacterial infections. Without resolution of the infection with antibiotics, one must explore the possibility of a viral infection. Influenza virus is the most common cause of viral pneumonia in patients with predisposing conditions (diabetes mellitus, chronic lung disease, or immunocompromised) and the elderly. Antivirals with neuraminidase inhibitors (zanamivir, peramivir, oseltamivir, laninamivir) should be considered. Risk factors for worsened morbidity and mortality include delayed initiation of antiviral therapy, history of inhalational substance abuse and symptoms including productive cough, hemoptysis, chest pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness. This may lead to cerebral edema, seizures, and coma, and places these patients at risk for further complications including respiratory failure secondary to aspiration, neuromuscular weakness and atelectasis. Viral causes of shock Shock is an uncommon presentation in viral illnesses but can lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Viral myocarditis, most notably caused by coxsackie viruses, can lead to acute cardiogenic shock. Symptoms resemble that of acute heart failure and may lead to respiratory failure. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hepatitis, encephalitis, neuropathy as well as multi-organ failure can occur depending on the specific virus involved. Management and Treatment Treatment of all viral illnesses remains largely supportive with an emphasis on early diagnosis and recognition. This includes adequate fluid resuscitation and replacement of gastrointestinal and insensible fluid losses as well as respiratory and cardiovascular support. For viral illnesses causing hypoxic respiratory failure, management is supportive care, including lung-protective 370 Table 9. Fever, myalgia, neck pain/ stiffness, photophobia, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, confusion, petechial rash, hepatomegaly/hepatitis, kidney failure Primarily flu-like symptoms. Egypt, Somalia, Tanzania, Saudi Arabia, Yemen Central Africa (first known outbreak, 1976) and West Africa, near tropical rainforests Initial outbreaks in Marburg (1967) and Frankfurt, Germany, and Belgrade, Serbia Mosquitoes. Affects most Asian and Latin American countries, in tropical and sub-tropical climates Primarily flu-like symptoms. Severe forms progress to hemorrhagic fever with multiorgan failure Droplet, mosquitoborne Supportive. Leading cause of serious illness and death among children in some Asian and Latin American countries. The influenza vaccination is the most effective preventative measure and is recommended for patients who are > age 65 or are immunocompromised. Newer medications such as laninamivir may be used to treat oseltamivir-resistant viruses. For patients presenting with altered mental status or seizures, supportive management of neurologic symptoms such as increased intracranial pressure, cerebral edema, seizure, and fever forms the foundation of therapy. Mechanical ventilation may be necessary for those with hypoxemia or for airway protection from aspiration if mental status is significantly depressed. For most other viruses including those that cause viral hemorrhagic fever, there are no known effective therapeutic interventions besides supportive therapy.
The surgeon must communicate effectively with referring physicians, be they from internal medicine, gastroenterology, pulmonology, or other services. The efficient and accurate transfer of information is essential for the care of the surgical patient. Before heading off to a full day in the operating room, surgeons have to round on their pre- and postoperative patients quite early in the morning. There is no argument that surgical training is indeed quite rigorous, perhaps the most time consuming and physically draining of all specialties in medicine. To be a good surgeon and adapt well to the rigorous lifestyle, you need great flexibility. Remember-surgeons have to deal with the unexpected, which may not necessarily come at convenient times. Surgical problems happen at all hours, and many times you will be the physician on call to handle the situation. This is why the lifestyle issue is so important if you are considering becoming a surgeon. It is true that surgery requires intense dedication and that residency is a minimum of 5 years in length, but what happens after that Colon & Rectal Alternatively, you could become one Surgery $277,441 of many surgeons in a group practice. In General Surgery $255,304 this private arrangement, there is a set onPediatric Surgery $270,593 call schedule and a wealth of patients from Transplant Surgery established referral patterns. Although pri(kidney) $217,327 vate practice surgeons may have less conTransplant Surgery trol over when they work, the hours are usu(liver) $325,012 ally predictable and predetermined. Some Trauma Surgery $320,821 of these surgeons also serve as clinical atVascular Surgery $286,286 tendings and have resident coverage. Some Source: American Medical Group Association go into solo private practice where there is maximal control over the work hours, but you are responsible for practice management, reimbursement and referral patterns, which administrators take care of in the academic and mega-medical-group settings. A rare few leave the clinical arena and dedicate their time to industry or research. Whatever practice you choose-and each option has its pros and cons- the bottom line is that the lifestyle of the surgical resident, which admittedly is quite busy, is not the same as that of the attending surgeon. Regardless of work hours, being a surgeon will always require a tremendous amount of dedication. There are many subspecialty areas, however, that build on this experience for advanced operations: cardiothoracic, vascular, transplant, and more. Within the domain of the heart, lungs, and mediastinum, they perform some of the most time consuming, regimented, and physically challenging of all operations. Surgery of the heart is deliSource: National Resident Matching Procate and fascinating. These surgeons treat gram conditions like blocked coronary arteries, thoracic aneurysms, and congenital abnormalities. They also perform esophageal surgery for cancer, achalasia, and other disorders of the esophagus. Colon and Rectal Surgery this area of surgery, which helps bridge the gap between gastroenterology and general surgery, used to be known as proctology. Patients present with a variety of diseases such as colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, motility disorders, diverticulitis, anal fissures and fistulas, fecal incontinence, and constipation. Although it is considered a subspecialty, pediatric surgery stays true to its general surgery roots because you perform operations on entire body regions: abdomen, chest, extremities, and more.
Recent studies have indicated that it may be used safely in patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate $30 mL/min/1. However, it is contraindicated in patients with advanced renal insufficiency and should be used with caution in patients with impaired hepatic function or congestive heart failure due to the increased risk of lactic acidosis. Metformin may be temporarily discontinued before procedures, during hospitalizations, and when acute illness may compromise renal or liver function. Thiazolidinediones Sulfonylureas and other insulin secretagogues are associated with hypoglycemia and should be used with caution. Glyburide is a longer-duration sulfonylurea and contraindicated in older adults (43). Incretin-Based Therapies Thiazolidinediones, if used at all, should be used very cautiously in those with, or at risk for, congestive heart failure and those at risk for falls or fractures. Healthy (few coexisting chronic illnesses, intact cognitive and functional status) A1C,7. Deintensification/deprescribing refers to decreasing the dose or frequency of administration of a treatment or discontinuing a treatment altogether. Consider adjustment of A1C goal if the patient has a condition that may interfere with erythrocyte life span/turnover. Sodium2Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors centers) may rely completely on the care plan and nursing support. Those receiving palliative care (with or without hospice) may require an approach that emphasizes comfort and symptom management, while de-emphasizing strict metabolic and blood pressure control. Hypoglycemia Sodium2glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are administered orally, which may be convenient for older adults with diabetes; however, long-term experience in this population is limited despite the initial efficacy and safety data reported with these agents. In patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, these agents have shown cardiovascular benefits (44). Once-daily basal insulin injection therapy is associated with minimal side effects and may be a reasonable option in many older patients. Multiple daily injections of insulin may be too complex for the older patient with advanced diabetes complications, life-limiting coexisting chronic illnesses, or limited functional status. Resources the needs of older adults with diabetes and their caregivers should be evaluated to construct a tailored care plan. Impaired social functioning may reduce their quality of life and increase the risk of functional dependency (45). Special management considerations include the need to avoid both hypoglycemia and the complications of hyperglycemia (2,47). They have a disproportionately high number of clinical complications and comorbidities that can increase hypoglycemia risk: impaired cognitive and renal function, slowed hormonal regulation and counterregulation, suboptimal hydration, variable appetite and nutritional intake, polypharmacy, and slowed intestinal absorption (49). Although in practice the patients may actually be seen more frequently, the concern is that patients may have uncontrolled glucose levels or wide excursions without the practitioner being notified. Similarly, the intensity of lipid management can be relaxed, and withdrawal of lipid-lowering therapy may be appropriate. E the management of the older adult at the end of life receiving palliative medicine or hospice care is a unique situation. Overall, palliative medicine promotes comfort, symptom control and prevention (pain, hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, and dehydration), and preservation of dignity and quality of life in patients with limited life expectancy (47,51). A patient has the right to refuse testing and treatment, whereas providers may consider withdrawing treatment and limiting diagnostic testing, including a reduction in the frequency of fingerstick testing (52). The decision process may need to involve the patient, family, and caregivers, leading to a care plan that is both convenient and effective for the goals of care (53). If needed, basal insulin can be implemented, accompanied by oral agents and without rapid-acting insulin. Different patient categories have been proposed for diabetes management in those with advanced disease (28). For those with type 2 diabetes, agents that may cause hypoglycemia should be downtitrated. A dying patient: for patients with type 2 diabetes, the discontinuation of all medications may be a reasonable approach, as patients are unlikely to have any oral intake.
Psychotherapy can also aid in alleviating any coexisting mental health concerns. Because changing gender role can have profound personal and social consequences, the decision to do so should include an awareness of what the familial, interpersonal, educational, vocational, economic, and legal challenges are likely to be, so that people can function successfully in their gender role. Many transsexual, transgender, and gender-nonconforming people will present for care without ever having been related to , or accepted in, the gender role that is most congruent with their gender identity. Mental health professionals can help these clients to explore and anticipate the implications of changes in gender role, and to pace the process of implementing these changes. Psychotherapy can provide a space for clients to begin to express themselves in ways that are congruent with their gender identity and, for some clients, overcome fears about changes in gender expression. Calculated risks can be taken outside of therapy to gain experience and build confidence in the new role. Assistance with coming out to family and community (friends, school, workplace) can be provided. Other transsexual, transgender, and gender-nonconforming individuals will present for care already having acquired experience (minimal, moderate, or extensive) living in a gender role that differs from that associated with their birth-assigned sex. Mental health professionals can help these clients to identify and work through potential challenges and foster optimal adjustment as they continue to express changes in their gender role. Family Therapy or Support for Family Members Decisions about changes in gender role and medical interventions for gender dysphoria have implications for, not only clients, but also their families (Emerson & Rosenfeld,; Fraser, a; Lev,). Mental health professionals can assist clients with making thoughtful decisions about communicating with family members and others about their gender identity and treatment decisions. For example, they may want to explore their sexuality and intimacy-related concerns. Follow-Up Care Throughout Life Mental health professionals may work with clients and their families at many stages of their lives. Psychotherapy may be helpful at different times and for various issues throughout the life cycle. E-Therapy, Online Counseling, or Distance Counseling Online or e-therapy has been shown to be particularly useful for people who have difficulty accessing competent in-person psychotherapeutic treatment and who may experience isolation and stigma (Derrig-Palumbo & Zeine,; Fenichel et al. By extrapolation, e-therapy may be a useful modality for psychotherapy with transsexual, transgender, and gendernonconforming people. E-therapy offers opportunities for potentially enhanced, expanded, creative, and tailored delivery of services; however, as a developing modality it may also carry unexpected risk. Telemedicine guidelines are clear in some disciplines in some parts of the United States (Fraser, b; Maheu, Pulier, Wilhelm, McMenamin, & Brown-Connolly,) but not all; the international situation is even less well-defined (Maheu et al. Until sufficient evidencebased data on this use of e-therapy is available, caution in its use is advised. A more thorough description of the potential uses, processes, and ethical concerns related to e-therapy has been published (Fraser, b). Educate and Advocate on Behalf of Clients Within Their Community (Schools, Workplaces, Other Organizations) and Assist Clients with Making Changes in Identity Documents Transsexual, transgender, and gender-nonconforming people may face challenges in their professional, educational, and other types of settings as they actualize their gender identity and expression (Lev,). Mental health professionals can play an important role by educating people in these settings regarding gender nonconformity and by advocating on behalf of their clients (Currah, Juang, & Minter,; Currah & Minter,). Provide Information and Referral for Peer Support For some transsexual, transgender, and gender-nonconforming people, an experience in peer support groups may be more instructive regarding options for gender expression than anything individual psychotherapy could offer (Rachlin,). Both experiences are potentially valuable, and all people exploring gender issues should be encouraged to participate in community activities, if possible. Culture and Its Ramifications for Assessment and Psychotherapy Health professionals work in enormously different environments across the world. Forms of distress that cause people to seek professional assistance in any culture are understood and classified by people in terms that are products of their own cultures (Frank & Frank,). Cultural settings also largely determine how such conditions are understood by mental health professionals. Cultural differences related to gender identity and expression can affect patients, mental health professionals, and accepted psychotherapy practice. Professionals must adhere to the ethical codes of their professional licensing or certifying organizations in all of their work with transsexual, transgender, and gender-nonconforming clients. If no local practitioners are available, consultation may be done via telehealth methods, assuming local requirements for distance consultation are met. Issues of Access to Care Qualified mental health professionals are not universally available; thus, access to quality care might be limited.
The 2k factorial can be confounded into two blocks of size 2k-1 or four blocks of 2k-2, and so on, to 2q blocks of size 2k-q in general. Every factorial effect corresponds to a contrast with 2k-1 plus signs and 2k-1 minus signs. Put all factor-level combinations with a plus sign on the defining contrast in one block and all the factor-level combinations with a minus sign in the other block. This confounds the block difference with the defining contrast effect, so we have zero information on that effect. However, all factorial effects are orthogonal, so block differences are orthogonal to the unconfounded factorial effects, and we have complete information and full efficiency for all unconfounded factorial effects. It makes sense to choose as defining contrast a multifactor interaction, because multifactor interactions are generally of less interest, and we will lose all information about whatever contrast is used as defining contrast. For the 2k factorial in two blocks of size 2k-1, the obvious defining contrast is the k-factor interaction. Confound defining contrast with blocks Use k-factor interaction as defining contrast 23 in two blocks of size four Suppose that we wish to confound a into two blocks of size four. The four factor-level effects with minus signs are (1), ab, ac, and bc; the four factor-level effects with plus signs are a, b, c, and abc. Here are two equivalent procedures that you may find easier, though which method you like best is entirely a personal matter. Divide the factor-level combinations into two groups depending on whether the letters of a factor-level combination contain an even or odd number of letters from the defining contrast. Now we work with the numerical 0/1 designations for the factor-level combinations. What we do is compute for each factorlevel combination the sum of the 0/1 level indicators for the factors that appear in the defining contrast, and then reduce this modulo 2. It is not too hard to see that this 0/1 rule is just the even/odd rule in numerical form. To choose blocks using the even/odd rule, we first find the letters from each factor-level combination that appear in the defining contrast, as shown in Table 15. We then count whether there is an even or odd number of these letters and put the factor-level combinations with an even number of letters matching in one block and those with an odd number matching in a second block. We then reduce the sum modulo 2, and assign the zeroes to one block and the ones to a second block. For 0111 (bcd), this sum is 1 + 1 + 1 = 3, and 3 mod 2 = 1; for 1110 (abc), the sum is 1 + 1 + 0 = 2, and 2 mod 2 = 0. These blocks have some nice mathematical properties that we will find useful in more complicated confounding situations. For any other pair of factor-level combinations, multiply as usual but then reduce exponents modulo 2. There is an analogous operation we can perform with the 0/1 representation of the factor-level combinations. Think of the zeroes and ones as exponents; for example, 1101 corresponds to a1 b1 c0 d1 = abd. Exponents Principal block and alternate block Multiply and reduce exponents mod 2 392 Factorials in Incomplete Blocks-Confounding Get alternate blocks from principal block add when we multiply, so the corresponding operation is to add the zeroes and ones componentwise and then reduce them mod 2. If you multiply any two elements of the principal block together reducing exponents modulo two, you get another element of the principal block. If you multiply all elements of the principal block by an element not in the principal block, you get an alternate block. What this means is that you can find alternate blocks easily once you have the principal block. This is no big deal when there are only two blocks, but can be very useful when we have four, eight, or more blocks. Multiplying every element of the principal block by ac, we get the following (1) ac = ac = ac 2c a ac = a =c bc ac = abc2 = ab abc ac = a2 bc2 = b bd ac = abcd = abcd abd ac = a2 bcd = bcd cd ac = ac2 d = ad acd ac = a2 c2 d = d this is the alternate block, but in a different order than Table 15. The last subsection showed how to confound into two blocks using one defining contrast. We can confound into four blocks using two defining contrasts, and in general we can confound into 2q blocks using q defining contrasts.
References: