

Surgery: operative intervention may be indicated if: pneumoperitoneum, fixed bowel loop, abdominal mass palpable or persistent metabolic acidosis. Peritoneal drainage can be used in patients who are too unstable for surgery or in whom ventilation is difficult due to abdominal fluid. Only resume feeds, preferably breast milk, if abdomen is soft and bowel sounds are present. Feeds may be resumed 5-7 days post-surgery once bowel sounds are present and the stoma is functioning. Intrapartum hypoxia may be suggested by the presence of one or more of the following features: · · · · · · · An acute intrapartum event. If the history and/or clinical signs are not consistent then other causes should be sought. On admission, before history documentation, ensure the following: · Stabilize vital signs, check glucose early and perform a general and neurological examination with particular reference to the presence of congenital anomalies. History documentation Make particular note of the following: Maternal and family history · · · Previous pregnancies: Live/still born or miscarriages or neonatal deaths. Current pregnancy: Gestation, medication, complications results of booking investigations and scans. Labour and delivery: » Augmentation, foetal heart monitoring, medication, sepsis, intrapartum events, length of second stage, presentation, method and indication for caesarean section or vacuum delivery. Initially restrict fluids to 40ml/kg/24hrs with potassium free 10% glucose and 1/5 to Ѕ normal saline. Potassium containing fluid may be used if urine output and serum potassium are normal. Treat hyponatremia <130mmol/l with further fluid restriction consider normal saline. Communication with parents · · · Explain the clinical condition and potential for other causes. Prepare them for a potential poor outcome if signs and investigations are suggestive. Stage 2 (moderate): lethargy, decreased tone and primitive reflexes, often with seizures. Stage 3 (severe): stupor or coma, flaccid tone and seizures often clinically less apparent. Moderately or severely affected infants typically develop increasingly obvious signs during the first 48-72 hours. Contraindications to cooling · · · Major congenital abnormalities likely to affect neurological outcome or moribund and unlikely to benefit from cooling. Severe pulmonary hypertension/systemic hypotension responding poorly to treatment. If heart rate above 110bpm, check for overheating or consider inadequate sedation or consider hypovolaemia. Subtle: eye deviation, eyelid fluttering, buccolingual movement or pedalling of arms and legs. They are usually born with an average haemoglobin count of 17g/dl (15-18) and normal haematocrit is 45-55 for neonates. The levels continue to decline after birth till the third week of life when they hit 11g/dl. Neonatal (cephalohaematoma, subgaleal haemorrhage, intracranial haemorrhage, bleeding into abdominal organs). To calculate volume based on observed and desired haematocrit, estimated blood volume of 80ml/kg. For mild anaemia, nutritional supplementation of iron, folate and vitamin E may be prescribed for a period of time. Prevention: Infants at risk of iron deficiency should receive supplemental oral iron (2-4mg of elemental iron/kg/day) once they are tolerating full enteral feeds. At risk infants include preterms and those with substantial blood loss via bleeding or phlebotomy. In term infants, the haemoglobin level typically reaches an average nadir of 11g/dl at approximately 8 to 12 weeks after birth. In preterm infants who are already born with a lower haematocrit, this decline, referred to as anaemia of prematurity, occurs earlier and is more pronounced in its severity than the anaemia seen in term infants. For gastrointestinal tract bleeding, rule out swallowed maternal blood using an Apt test.
Although there were only two locations, these sites, and especially Miami, were highly cosmopolitan. This is as representative of the national average for the entire age range of adults as has been obtained. The cutting points indicating brain damage were set differently for the two programs. A second study (Tombaugh & Hubley, 1998) developed excellent norms for the 60Item Boston Naming Test. This had correctly classified 88% of normals and 80% of the brain-damaged subjects. In the first study the cutoff points for the indices and the index tests are presented. Studies have continued to support the greater accuracy of a group of tests in distinguishing brain damage from nonbrain damage (Russell & Starkey, 1993). In this table the Source is the battery or computer program for which the indices were created. The Neuropsychological Key (Russell, Neuringer, & Goldstein, 1970) was fairly widely used but is now out of date. At present there are indices for two kinds of neurological conditions, existence of and lateralization of brain damage. There are two general types of indices for the existence of brain damage, presence and average impairment. When a certain number of the tests in the index are in the brain damaged range the index designates the existence of brain damage. A certain score indicates brain damage and the index score also indicates the severity of impairment. A full discussion of these indices including a description of the unused indices and keys is provided in Russell (1995). It is very complicated and difficult to calculate the index without the computer program. The items in each one of these scoring methods are assigned numbers and then summed. Consequently, it appears to be the most sensitive index of brain damage in existence, at least in the age range up to about 60 years. They are scored separately in part because they measure impairment in each hemisphere as well as lateralization. There have been two validation studies of these indices (Reitan, 1991b; Sherer & Adams, 1993). Eighty-seven percent of both right- and left-hemisphere lesions were correctly classified, and there were no errors in the opposite direction. This is the highest lateralization hit rate reported in the literature (Russell, 1995). Correct lateralization classification for head trauma and other categories that do not have clear-cut lateralization were lower. The only cross-validation study completed at this time was done by Sherer and Adams (1993). Findings of possible lateralization significance on a test are marked on the printout by the symbols #L for left-hemisphere impairment and #R for right-hemisphere impairment. These indicate that a certain score, such as lefthand Finger Tapping, is sufficiently different from the equivalent test for the opposite side of the body to indicate a lateralized condition. The brain-damage indices, which are calculated by the program, require that at least 7 of the 10 index tests be administered. Unpublished norming studies indicated that they were not as accurate as the other tests in the index (Russell, 1995; Russell & Starkey, 1993). The Percent Impaired Index is the percent of the 10 component tests that constitute this index that fall within the brain-damage range.
Syndromes
Severe forms progress to hemorrhagic fever with multiorgan failure Droplet, mosquitoborne Supportive. Leading cause of serious illness and death among children in some Asian and Latin American countries. The influenza vaccination is the most effective preventative measure and is recommended for patients who are > age 65 or are immunocompromised. Newer medications such as laninamivir may be used to treat oseltamivir-resistant viruses. For patients presenting with altered mental status or seizures, supportive management of neurologic symptoms such as increased intracranial pressure, cerebral edema, seizure, and fever forms the foundation of therapy. Mechanical ventilation may be necessary for those with hypoxemia or for airway protection from aspiration if mental status is significantly depressed. For most other viruses including those that cause viral hemorrhagic fever, there are no known effective therapeutic interventions besides supportive therapy. In addition to the treatment of the affected patient, immediate isolation is critical for effective infection control and prevention of transmission. Appropriate choice of isolation including differentiating between airborne, droplet and contact precautions should be identified and implemented immediately. In the case of potentially epidemic and pandemic diseases, communication with local and national public health authorities may help prevent a possible outbreak. Bautista E, Chotpitayasunondh T, Gao Z, et al: Clinical aspects of pandemic 2009 influenza A (H1N1) virus infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Updated interim recommendations for the use of antiviral medications in the treatment and prevention of influenza for the 2009-2010 season. Foster C, Mistry N, Peddi P, Shivak S: the Washington Manual of Medical Therapeutics. Tabarsi P, Moradi A, Marjani M, et al: Factors associated with death or intensive care unit admission due to pandemic 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection. Administration of corticosteroids 373 Section 4 the Immunocompromised Patient Key Points: · the management of an immunosuppressed critically ill patient requires a multidisciplinary team. Intraoperative course was notable for long cardiopulmonary bypass time, hypotension requiring pressors, and large blood loss. She then developed a waxing and waning mental status, which was interpreted as delirium by the floor team, along with several episodes of relative hypotension. Recognition of the altered presentation of infection and sepsis, and prompt initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy A multidisciplinary approach is imperative and relevant consults should be obtained early. However, often times the intensivist will need to make decisions quickly and should, therefore, be familiar with immunosuppressive pathophysiology and pharmacology. These patients are prone to life-threatening infections (secondary to surgical/technical complications combined with immunosuppression) and, thus, prevention and prompt treatment of infections are imperative. Detailed guidelines are available from the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons (2,4). Risk factors can also come from the donor: active or latent infections at time of procurement and those secondary to intraoperative events. Lastly, they may be related to post-transplant events: immunosuppression, indwelling cannulas, and nosocomial or community exposure. Immunosuppression is induced just before or during transplantation with high-dose steroids and/or antibody therapy. Polyclonal antibody therapy (antithymocyte globulin) carries the risk of serum sickness as well as broad immunosuppressive effects. For the most part, antithymocyte globulin has been replaced with monoclonal antibodies. High-dose steroids are typically tapered down and maintained at low doses for life. Maintenance therapy should not be interrupted if at all possible unless toxicity is present. Serum levels need to be monitored daily and frequent consultation with the hospital pharmacist, in addition to transplant sub-specialist, is needed to adjust doses in the presence of renal or liver dysfunction. Infection patterns in organ transplant patients are well studied and can guide empiric antibiotics.
This type of memory deficit is reminiscent of a psychiatric dissociative state caused by severe emotional trauma, but it is not what occurs with neurologic injury or disease. Anterograde amnesia is the loss of the ability to encode and learn new information after a defined event (such as head injury, lesion, or disease onset). After the accident, she had difficulty learning new information (anterograde amnesia). Her mild retrograde amnesia is evidenced by her memory for driving out of the grocery store parking lot, which was about five blocks from the accident. Amnesias of this type are common in closed head injury (this condition is described further in Chapter 13). In general, anterograde (or a combination of anterograde-retrograde) amnesia is evident with brain injury. However, there are instances of retrograde amnesia with relatively spared anterograde learning and memory (Levine et al. Amnesia can be caused by a number of different problems and can take several forms. Sensory memory is fleeting, lasting only milliseconds, but its capacity is essentially unlimited in what may be taken in. Neuropsychological conceptualizations of memory generally do not consider sensory memory; rather, it is thought of as a component of sensory processing. Neuropsychology concerns itself with understanding how memory systems work in correspondence with known brain functioning. One way in which researchers can support the idea of separate structures is by showing a double dissociation between behaviors. One day while working on a model airplane, he suffered an accident that would affect him for the rest of his life. His roommate, apparently in a playful mood, took a miniature fencing foil from the wall, tapped N. The foil pierced his third cranial nerve, but more important, it made a small lesion in the left dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus. In addition, this minute injury left him with a devastating impairment in his ability to register new verbal memories (anterograde amnesia). In meeting him, the casual observer may not initially suspect there is anything wrong. But after talking with him for a few minutes, it becomes apparent that he does not remember details of just a few minutes ago. If he is distracted by a passing thought or a passing car, the thread of conversation is lost. If you meet again the next day, he probably will not remember you or what transpired in your previous meeting with him. He becomes upset at his mother if she moves the telephone or one of his model airplanes. For example, he has a vague idea that Watergate was a political scandal in "Washington or Florida" but recalls no other details. Interestingly, when he had to learn a new route from his house to the Veterans Administration hospital for therapy, even after 4 years he was unable to form a spatial map. He found his way much like an adult returning to a childhood neighborhood after years of absence. As pieces of the visual scenery popped up before him, he decided if the landmark looked familiar and turned accordingly. This haphazard approach of seeing things sometimes required him to back up or retrace his steps until something looked familiar. This case demonstrates that even a very small lesion, strategically placed, can cause a devastating problem of memory. Cognitive psychologists, neuropsychologists, neurologists, and the lay public use various, and sometimes conflicting, terms. However, neuropsychologists are referring to the specific ability to register information (encode), organize the information in a meaningful way (storage), and recall or recognize the information when needed (retrieval). Squire (Squire & Cohen, 1984; Squire & Butters, 1992) and other investigators advocate for a structuralfunctional difference between declarative and nondeclarative memory. Nondeclarative memory is usually implicit, and a person demonstrates it via performance. Squire and Butters (1992) maintain that the domain of nondeclarative or procedural memory is that of rules and procedures, rather than information that can be verbalized, although nondeclarative memory has not been clearly operationally defined and often includes a hodgepodge of tasks such as motor skills learning, mirror reading, and verbal priming.
Although executive dysfunction is suggested, the basis of the deficit remains unanswered. As the authors correctly conclude, the inhibitory deficit may relate to a disturbance of the dorsolateral frontal region, parietal region, and/or interconnecting pathways of the two systems. To test this possible confound, Atkinson and colleagues (2003) have investigated the relation of visual sensory deficits to visuospatial and visuoconstructive performance. Approximately 50% of the children and adolescents sampled for study exhibited some form of visual sensory deficit. The children and adolescents were administered a battery of tests sensitive to visuospatial and visuoconstructive abilities. The results demonstrated a negligible relation between the occurrence of visual sensory deficits and severity of spatial deficits. That is, they rely on local processing when task performance involves the manipulation and construction of spatial elements. If the elements of the task are spatially invariant, and mentalmotor manipulation is not required, they are able to use a global processing approach. Dorsal versus Ventral Processing-Because of the significant deficits in visuospatial relative to facial processing, neuroscientists and neuropsychologists have sought to determine whether the disparity represents a dissociation between the ventral and dorsal streams of visual processing. The ventral stream ("what" processing; see Chapter 8) conveys visual object and face recognition to the temporal lobes, whereas the dorsal stream ("where" processing) carries information to the parietal lobes necessary for the processing of spatial relations. Using tasks sensitive to ventral and dorsal processing, investigations (Atkinson et al. Analysis determined that the hypoactivation of the dorsal stream could be attributed to impaired input from this isolated region. A small anomaly (A) of the occipitoparietal region that may disrupt the "downstream" activation of the "where" dorsal stream. The regional activation of the dorsal stream is evident in visuospatial processing of location (B) and construction (C). She later noted, "There are two kinds of Mozart: the kind that hurts and the kind that does not hurt" (Levitin et al. They tend to be overly happy and friendly, yet are also prone to irritability (which appears to abate with age) and moodiness. They are known to approach and speak indiscriminately with others and to be excitable, restless, and inattentive. In addition, they experience high levels of anxiety, worry, fearfulness, and somatic complaints. Although they are proficient at understanding the feelings of others, they find it difficult to recognize their own fears (Lai, 1998). Interestingly, in contrast with healthy children, they do not show an age-related reduction in their fears. The basis of their overfriendliness and sociability is unclear, but it is believed that their extreme focus on the faces of others may play a role in shaping these characteristics (Mervis et al. The amygdala is implicated in the support of a number of emotion-related functions, including the monitoring of environmental events for danger. For healthy control participants, the amygdala showed greater activation when processing threatening faces than threatening scenes. That is, the decreased activation may indicate an attenuation of normal social fear or apprehension. In contrast, the greater activation of the amygdala to threatening scenes may underpin their high rates of nonsocial anxiety, worry, and fears. Hypercalcemia contributes to these gastrointestinal disturbances, requiring medical attention and dietary restrictions. Orthopedic and physical/occupational services are often needed to address these problems. Accordingly, environmental modifications to reduce or alleviate the occurrence of loud and disturbing noises are needed. For example, the child might be removed from the classroom in advance of a fire drill and placed in a room where the sound of the fire alarm is muffled or be allowed to use ear plugs or ear phones. During the preschool and elementary school years, the child often warrants special or remedial educational services because of general cognitive delays.
Pediatric sport-related concussion: a review of the clinical management of an oft-neglected population. Spinal immobilization on a flat backboard: does it result in neutral position of the cervical spine? Guidelines for the acute medical management of severe traumatic brain injury in infants, children, and adolescents-second edition. Update on the 2012 guidelines for the management of pediatric traumatic brain injury-information for the anesthesiologist. Clinical practice parameters for hemodynamic support of pediatric and neonatal septic shock: 2007 update from the American College of Critical Care Medicine. Frontiers in pulmonary hypertension in infants and children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Noninvasive support and ventilation for pediatric Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: proceedings from the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Use of high flow nasal cannula in critically ill infants, children, and adults: a critical review of the literature. From Bright Futures Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children, and Adolescents. Medical History Includesinformationaboutchronicconditions/medications(including illicitandperformance-enhancingagents),hospitalizations/surgeries, allergies(especiallythoseassociatedwithanaphylaxisorrespiratory compromise),congenitalheartdisease,seizuredisorders,and immunizationstatus. Adolescent Physical Examination (Most Pertinent Aspects)3,4,14 Whenever possible, examine the patient in a gown to ensure a complete and thorough examination. Abdomen:Hepatosplenomegaly(contraindicationforcontactsports), abdominalpain/tenderness Chapter 5 Adolescent Medicine 113 11. It is not routinely recommended for healthy asymptomatic women under 21 years of age. Indicationsincludevaginaldischarge(assesscervixfor mucopurulentdischarge,friability,largeectropion,foreignbody), lowerabdominalorpelvicpain,urinarysymptomsinsexually activefemales,menstrualdisorders(amenorrhea,abnormal vaginalbleeding,ordysmenorrhearefractorytomedicaltherapy), considerationofintrauterinedeviceordiaphragm,andsuspected orreportedsexualabuseorrape(refertoaspecializedcenterif notappropriatelytrainedandequippedtodocumentevidenceof traumaandcollectforensicspecimens). A lack of research and evidence for screening examinations in adolescencehasledtovariabilityinguidelinesfortopicssuchas screeningfordyslipidemia,iron-deficiencyanemia,diabetes,and tuberculosis. Sexually transmitted infections, screening guidelines, and treatment recommendations for sexually active adolescents. Repeat testing (3 weeks posttreatment) to document chlamydial eradication is in all pregnant patients. Vaginal swabs are as sensitive and specific as cervical swabs, and both are more accurate than urine samples. For severe recurrent disease, initiate therapy at start of prodrome or within 1 day. Patient-administered therapies include: podofilox gel or imiquimod cream (contraindicated in pregnancy). Clinician-applied therapies include: bichloracetic or trichloroacetic acid, surgical removal, and cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen or cryoprobe. Cervical cancer cytologic analysis[Papanicolaou(Pap)smear]23 Immunocompetent:Regardlessofageofsexualdebut,cervical cancerscreeningwithPapsmearshouldnotbeginuntilawoman is21yearsold. Consider in high-risk patients who did not receive routine vaccination as children. People 13 years of age and older (who have never had chickenpox or received chickenpox vaccine) should get two doses of the varicella vaccine at least 28 days apart. Plan B Plan B One Step Next Choice Swallow the pills within 3 days after having unprotected sex. Yes Begin hormonal contraception method today and advise abstinence/condoms for 1 week Yes Unprotected intercourse 5 days ago? No Give prescription or supplies for chosen method and advise to start with next menses Advise abstinence/condoms from initial visit through one week after starting new method. Riskfactors includemalesex,AmericanIndian/AlaskaNativeracialbackground, bisexualorhomosexualorientation,isolationorlivingalone,historyof acutestressororrecentloss,familyhistoryofsuicide,personalor familyhistoryofsuicideattempt,personalorparentalmentalhealth problems,physicalorsexualabuse,substanceuse,andfirearmsin thehome(evenifproperlystoredandsecured). Screening questions for suicidal ideation are best asked after initial questioning regarding stressors, mood, and depressive symptoms. In addition to risk factors above,assessmentofsuicidalriskshould alsoincludewhethertheadolescenthasaplan,thepotentiallethality oftheplan,accesstomeanstocarryouttheplan,andwhetherthe planhaseverbeenattempted. Any adolescent with risk factors and a suicide plan should be considered an imminent risk and not be allowed to leave the office. Any adolescent with risk factors but no suicide plan or preparation should be considered moderate risk.
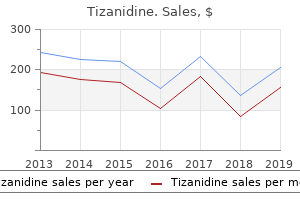
Tetramethylene-1,4-diol (Butanediol (Bd)). Tizanidine.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96071

The Miniflex pump head features a wide occlusion angle that prevents fluid backflow up to the rated pressure of the tubing. Self-lubricating thermoplastic polyester rollers are low friction and long wearing for smooth operation and long life. In addition, the quaternary diaphragm design enables risk-free dry-running, self-priming, and a high turn-down ratio. Both the single-use and multiple-use models safely and reliably pump plasma products, proteins, monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and more. You can quickly turn around equipment from one batch to the next, maximising production operations. Multiple-use pump systems ensure total product containment without abrasion and minimal particle creation. Stainless steel construction handles higher pressure applications including cross-flow filtration and chromatography columns. Special Masterflex Drives were developed to best take advantage of the operating parameters of the Quattroflow pumps. Drives feature an intuitive interface, remote control functionality, and a brushless, maintenance-free motor with ±0. Sealed stainless steel housing and sealed keypad are protected from dust, water, and chemicals in the washdown environment-simply hose down to clean. You review every step of the process to take care of your staff and to benefit your business. Pumps, Masterflex Open-Head Interlock Sensor Technology Available integrated into select L/S and I/P drives or as a retrofit system, the open-head interlock sensors add an extra level of protection for operators who maintain pumps. When paired with an open-head sensor equipped pump head, the drive automatically shuts down when the pump head is opened, eliminating exposure to the moving rollers connected to the drive shaft. Read the article How Masterflex Pumps with Open Head Sensors Enhance Worker Protection on our web site at. The system includes a control box that easily connects to your drive and an open-head sensor equipped pump head. If pump head is opened during operation, the interlock control box instantly shuts down the drive. Controller 77097-00 includes power cables and a single extension cable to connect one sensor-equipped pump head. Includes mounting plate and four screws In France: +33 (0) 1486 37800 or cpcontact@coleparmer. L/S Multichannel pump heads for Precision pump tubing, sizes L/S 13, L/S 14, L/S 16 Four Six 24 Eight B. Solution the manufacturer now uses a Masterflex L/S digital drive with an L/S four-channel pump head 07536-04. Size L/S 15 two-stop silicone tubing (06421-15) met the smaller flow requirement; while size L/S 35 two-stop silicone tubing (06421-35) met the larger flow requirement. Careful calibration of the drive, and the synchronous multichannel flow capability of the pump head enabled the manufacturer to meet the accuracy target. Models 77420-20 and -28 feature a powder-coated steel housing with anodised aluminum base. Use in process, manufacturing, and water-treatment applications where stainless steel is not a critical requirement. Shipped with country-specific plug/ cord set; please specify ultimate destination when ordering. Required for model 77411-00 to operate the remote inputs and outputs 134 ColeParmer. C/L Digital Microflex Pump Icon-driven menu allows quick programming and setup Flow range of 0. Handheld Remote Controllers these handheld controllers are designed to control basic drive operations. Handles accept Masterflex tubing sizes L/S 13, L/S 14, L/S 16, L/S 25, L/S 17, L/S 18, L/S 15, and L/S 24 (up to 11. On/Off Foot Switches Foot switches allow for remote control of specific functions of your Masterflex drive. Remote Control Cable Assemblies Cable assemblies include terminal connector and 7.
Adenocarcinoma is a malignant proliferation of glands; most common type of esophageal carcinoma in the West 1. Arises from preexisting Barrett esophagus; usually involves the lower one-third of the esophagus. Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant proliferation of squamous cells; most common esophageal cancer worldwide l. Usually arises in upper or middle third of the esophagus; major risk factors include i. Symptoms include progressive dysphagia (solids to liquids), weight loss, pain, and hematemesis. Squamous cell carcinoma may additionally present with hoarse voice (recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement) and cough (tracheal involvement). Location of lymph node spread depends on the level of the esophagus that is involved. Congenital malformation of the anterior abdominal wall leading to exposure of abdominal contents. Due to failure of herniated intestines to return to the body cavity during development l. Defenses include mucin layer produced by foveolar cells, bicarbonate secretion by surface epithelium, and normal blood supply (provides nutrients and picks up leaked acid). Increased intracranial pressure (Cushing ulcer}-Increased stimulation of vagus nerve leads to increased acid production. Acid damage results in superficial inflammation, erosion (loss of superficial epithelium), or ulcer (loss of mucosal layer). Divided into two types based on underlying etiology: chronic autoimmune gastritis and chronic H pylori gastritis C. Chronic autoimmune gastritis is due to autoimmune destruction of gastric parietal cells, which are located in the stomach body and fundus. Chronic H pylori gastritis is due to H pylori-induced acute and chronic inflammation; most common form of gastritis (90%} l. H pylori ureases and proteases along with inflammation weaken mucosal defenses; antrum is the most common site. Negative urea breath test and lack of stool antigen confirm eradication of Hpylori. Solitary mucosal ulcer involving proximal duodenum (90%) or distal stomach (10%) B. May rupture leading to bleeding from the gastroduodenal artery (anterior ulcer) or acute pancreatitis (posterior ulcer) C. Duodenal ulcers are almost never malignant (duodenal carcinoma is extremely rare). Benign peptic ulcers are usually small(< 3 em), sharply demarcated ("punched-out"), and surrounded by radiating folds of mucosa. Intestinal type (more common) presents as a large, irregular ulcer with heaped up margins; most commonly involves the lesser curvature of the antrum (similar to gastric ulcer) 1. Diffuse type is characterized by signet ring cells that diffusely infiltrate the gastric wall. Gastric carcinoma presents late with weight loss, abdominal pain, anemia, and early satiety; rarely presents as acanthosis nigricans or Leser-Trelat sign F. Can present during the first 2 years of life with bleeding (due to heterotopic gastric mucosa), volvulus, intussusception, or obstruction (mimics appendicitis); however, most cases are asymptomatic. Telescoped segment is pulled forward by peristalsis, resulting in obstruction and disruption of blood supply with infarction. Transmural infarction occurs with thrombosis/embolism of the superior mesenteric artery or thrombosis of the mesenteric vein. Clinical features include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and decreased bowel sounds. Decreased function of the lactase enzyme found in the brush border of enterocytes 1.
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, Chapter 585, "Congenital Anomalies of the Central Nervous System," Section 585. Management of stroke in infants and children: a scientific statement from a Special Writing Group of the American Heart Association Stroke Council and the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Stroke in Childhood: Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosis, Management and Rehabilitation. Preventing stroke among children with sickle cell anemia: an analysis of strategies that involve transcranial Doppler testing and chronic transfusion. Guidelines for thrombolytic therapy for acute stroke: a supplement to the guidelines for the management of patients with acute ischemic stroke. A statement for healthcare professionals from a Special Writing Group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Infant and Pediatric Formula Company Websites Forcompleteandup-to-dateproductinformationregardingmore specializedandmetabolicformulas,seethesewebsites: · Enfamil,Enfacare,Nutramigen,andPregestimil: Clinical longitudinal standards for height and height velocity in North American Children. A systematic review and meta-analysis to revise the Fenton growth chart for preterm infants. Thushiscatch-upgrowth requirementwouldbeasfollows: 98 kcal/kg/day Ч (9 kg/ 7 kg) = 126 kcal/kg/day *Ideal weight can be 10th85th percentile weight for height, depending on past growth trends; clinical judgment should be used. In view of evidence linking folate intake with neural tube defects in the fetus, it is recommended that all women capable of becoming pregnant consume 400 mcg from supplements or fortified foods in addition to intake of food folate from a varied diet. It is assumed that women will continue consuming 400 mcg from supplements or fortified food until their pregnancy is confirmed and they enter prenatal care, which ordinarily occurs after the end of the periconceptual period-the critical time for formation of the neural tube. Also contains biotin, 15 mcg; pantothenic acid, 3 mg; 87% vitamin A as -carotene; coenzyme Q10, 2 mg; selenium, 10 mcg. Recommended for use in infants with fat malabsorption, such as cystic fibrosis, liver disease. Mixing Instructions for Full-Term Standard and Soy-Based Infant Formulas (Table21. An estimate of the osmolarity of parenteral nutrition can be obtained with the following formula: Estimated osmolarity = (dextrose concentration Ч 50) + (amino acid concentration Ч 100) + (mEq of electrolytes Ч 2). Essential fatty acid deficiency may occur in fat-free parenteral nutrition within 24 weeks in infants and children and as early as 214 days in neonates. The period before nutritional goals are reached or during any period of instability. Expert Committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: summary report. Expert Committee Recommendations on the Assessment, Prevention and Treatment of Child and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity - 2007. Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children 0 through 3 years. Enteral Nutrition Practice Recommendations Task Force, Bankhead R, Boullata J, et al. Commonly used monotherapies include antipseudomonal -lactams and fourth-generation cephalosporins or carbapenems. Identify all components of therapy received:Comprehensivetreatment summaryfromoncologist,summarizing: a. Guideline for the management of fever and neutropenia in children with cancer and/or undergoing hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Clinical practice guideline for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guideline for the prevention of acute nausea and vomiting due to antineoplastic medication in pediatric cancer patients. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective.
In the ma l e, h o w e v e r, a me s e n c h y ma l c o n d e n s a t i o n, the g u b e r n a c u l u m (w h i c h a l s o f o r ms i n f e ma l e s b u t a t t a c h e s t o the uterus), attaches the caudal pole of the testis, first to the inguinal region a n d the n t o the s c r o t a l s w e l l i n g s. G r o w t h a n d r e t r a c t i o n o f the g u b e r n a c u l u m, t o g e the r w i t h i n c r e a s i n g i n t r a - a b d o mi n a l p r e s s u r e, c a u s e the t e s t i s t o descend. Failure of these processes causes undescended testes, known as c r y p t o r c h i s m. Ap p r o xi ma t e l y 2 % t o 3 % o f t e r m ma l e i n f a n t s h a v e a n u n d e s c e n d e d t e s t i c l e, a n d i n 2 5 % o f the s e the c o n d i t i o n i s b i l a t e r a l. In ma n y c a s e s, the u n d e s c e n d e d t e s t i s d e s c e n d s b y a g e 1. If i t d o e s n o t, t e s t o s t e r o n e a d mi n i s t r a t i o n (s i n c e t h i s h o r mo n e i s t h o u g h t t o p l a y a r o l e i n d e s c e n t) o r s u r g e r y ma y b e n e c e s s a r y. F e r t i l i t y ma y b e a f f e c t e d i f the c o n d i t i o n i s b i l a t e r a l 3. M a l e a n d f e ma l e e xt e r n a l g e n i t a l i a p a s s t h r o u g h a n i n d i f f e r e n t s t a g e d u r i n g w h i c h i t i s i mp o s s i b l e t o d i f f e r e n t i a t e b e t w e e n the t w o s e xe s. U n d e r the i n f l u e n c e o f t e s t o s t e r o n e, the s e s t r u c t u r e s a s s u me a ma s c u l i n e a p p e a r a n c e, b u t the d e r i v a t i v e s a r e h o mo l o g o u s b e t w e e n ma l e s a n d f e ma l e s. T h e s e h o mo l o g i e s i n c l u d e t(h e c l i t o r i s a n d p e n i s, d e r i v e d f r o m the g e n i t a l t u b e r c l e; a) (b) the l a b i a ma j o r a a n d s c r o t u m, d e r i v e d f r o m the g e n i t a l s w e l l i n g s t h a t f u s e i n the ma l e; a ncd (h e l a b i a mi n o r a a n d p e n i l e u r e t h r a, d e r i v e d f r o m the) t u r e t h r a l f o l d s t h a t f u s e i n the ma l. D u r i n g e a r l y s t a g e s, the g e n i t a l t u b e r c l e i s l a r g e r i n the f e ma l e t h a n i n the ma l e, a n d t h i s h a s l e d t o mi s i d e n t i f i c a t i o n o f sex by ultrasound. T h e u t e r u s i s f o r me d b y f u s i o n o f the l o w e r p o r t i o n s o f the p a r a me s o n e p h r i c (mь l l e r i a n) d u c t s. N u me r o u s a b n o r ma l i t i e s h a v e b e e n d e s c r i b e d; the mo s t c o mmo n c o n s i s t s o f t w o u t e r i n e h o r n s (b i c o r n u a t e u t e r u s). C o mp l i c a t i o n s o f t h i s d e f e c t i n c l u d e d i f f i c u l t i e s i n b e c o mi n g p r e g n a n t, h i g h i n c i d e n c e o f s p o n t a n e o u s a b o r t i o n, a n d a b n o r ma l f e t a l p r e s e n t a t i o n s. N e u r a l c r e s t c e l l s a r e i mp o r t a n t f o r c r a n i o f a c i a l d e v e l o p me n t b e c a u s e the y c o n t r i b u t e t o s o ma n y s t r u c t u r e s i n t h i s r e g i o n. T h e y f o r m a l l o f the b o n e s o f the face and the anterior part of the cranial vault, and the connective tissue t h a t p r o v i d e s p a t t e r n i n g o f the f a c i a l mu s c l e s. T h e y a l s o c o n t r i b u t e t o c r a n i a l n e r v e g a n g l i a, me n i n g e s, d e r mi s, o d o n t o b l a s t s, a n d s t r o ma f o r g l a n d s d e r i v e d f r o m p h a r y n g e a l p o u c h e s. In a d d i t i o n, c r e s t c e l l s f r o m the h i n d b r a i n r e g i o n o f the n e u r a l f o l d s mi g r a t e v e n t r a l l y t o p a r t i c i p a t e i n s e p t a t i o n o f the c o n o t r u n c a l r e g i o n o f the h e a r t i n t o a o r t i c a n d p u l mo n a r y v e s s e l s. U n f o r t u n a t e l y, c r e s t c e l l s a p p e a r t o b e v u l n e r a b l e t o a n u mb e r o f c o mp o u n d s, i n c l u d i n g a l c o h o l a n d r e t i n o i d s, p e r h a p s b e c a u s e the y l a c k c a t a l a s e a n d s u p e r o xi d e d i s mu t a s e e n zy me s t h a t s c a v e n g e t o xi c f r e e r a d i c a l s. M a n y c r a n i o f a c i a l d e f e c t s a r e d u e t o i n s u l t s o n n e u r a l c r e s t c e l l s a n d ma y b e a s s o c i a t e d w i t h c a r d i a c a b n o r ma l i t i e s b e c a u s e o f the c o n t r i b u t i o n o f the s e c e l l s t o h e a r t mo r p h o g e n e s i s. T h e c h i l d ma y h a v e D i G e o r g e a n o ma l y, w h i c h i s c h a r a c t e r i ze d b y the s e t y p e s o f c r a n i o f a c i a l d e f e c t s a n d p a r t i a l o r c o mp l e t e a b s e n c e o f t h y mi c t i s s u. It i s the l o s s o f t h y mi c t i s s u e t h a t c o mp r o mi s e s the i mmu n e s y s t e m, r e s u l t i n g i n n u me r o u s i n f e c t i o n s. D a ma g e t o n e u r a l c r e s t c e l l s i s the mo s t l i k e l y c a u s e o f the s e q u e n c e, s i n c e the s e c e l l s c o n t r i b u t e t o d e v e l o p me n t o f a l l o f the s e s t r u c t u r e s, i n c l u d i n g the s t r o ma o f the t h y mu s. The r a t o g e n s, s u c h a s a l c o h o l, h a v e b e e n s h o w n t o c a u s e the s e d e f e c t s e xp e r i me n t a l l y. C h i l d r e n w i t h mi d l i n e c l e f t s o f the l i p o f t e n h a v e me n t a l r e t a r d a t i o n. M e d i a n c l e f t s a r e a s s o c i a t e d w i t h l o s s o f o the r mi d l i n e s t r u c t u r e s, i n c l u d i n g t h o s e i n the b r a i n. In i t s e xt r e me f o r m, the e n t i r e c r a n i a l mi d l i n e i s l o s t, a n d the l a t e r a l v e n t r i c l e s o f the c e r e b r a l h e mi s p h e r e s a r e f u s e d i n t o a s i n g l e v e n t r i c l e, a c o n d i t i o n c a l l e d h o l o p r o s e n c e p h a l y. M i d l i n e c l e f t s, i n d u c e d a s the c r a n i a l n e u r a l f o l d s b e g i n t o f o r m (a p p r o xi ma t e l y d a y s 1 9 2 1), r e s u l t f r o m the l o s s o f mi d l i n e t i s s u e i n the p r e c h o r d a l p l a t e r e g i o n. T h e c h i l d mo s t l i k e l y h a s a t h y r o g l o s s a l c y s t t h a t r e s u l t s f r o m i n c o mp l e t e r e g r e s s i o n o f the t h y r o g l o s s a l d u c t. T h e s e c y s t s ma y f o r m a n y w h e r e a l o n g the l i n e o f d e s c e n t o f the t h y r o i d g l a n d a s i t mi g r a t e s f r o m the r e g i o n o f the f o r a me n c e c u m o f the t o n g u e t o i t s p o s i t i o n i n the n e c k. A c y s t mu s t b e d i f f e r e n t i a t e d f r o m e c t o p i c g l a n d u l a r t i s s u e, w h i c h ma y a l s o r e ma i n a l o n g t h i s p a t h w a y.
References: