
Moderate evidence for lack of efficacy or for adverse outcome supports a recommendation against use. Good evidence for lack of efficacy or for adverse outcome supports a recommendation against use. For most recommendations, prevention strategies are rated by the strength of the recommendation and the quality of the evidence supporting the recommendation (Table 1). The major changes in this document, including changes in recommendation ratings, are summarized here. Following the background section, information on hematopoietic cell product safety is provided. The subsequent sections discuss prevention of infection by specific microorganisms. This will hopefully allow the reader to follow the prevention practices needed from the time a donor is selected until the patient regains immune competence. In recognition of our global society, several organisms are discussed that may be limited to certain regions of the world. Included in that section are also those infections that may be ubiquitous but occur infrequently, such as Pneumocystis jiroveci and Nocardia. Two additional appendices were added to provide information on desensitization to sulfa drugs and visitor screening questionnaires. Finally, the dosing appendix has merged both adult and pediatric dosing, and provides recommendations for several newer antimicrobial agents that were not previously available. In some clinical settings, however, a state of ``mixed chimerism,' wherein elements of both the donor and recipient lymphohematopoietic system survive, may be sufficient to cure the underlying condition [11,12]. First, improvements in the supportive care of patients with severe immunosuppression and myelosuppression have diminished morbidity and mortality because of infection [19,28,29]. For other racial or ethnic groups, however, the chance of finding a suitable donor using existent registries is substantially less. As a result, infectious complications in the immediate posttransplant period usually present as febrile neutropenia, with the severity of risk related to the depth and duration of neutropenia and the degree of mucosal damage induced. In regimens with minimal myelosuppression and minimal mucosal toxicity, the risk for infection in the immediate posttransplant period is reduced. With some regimens, essentially complete eradication of recipient lymphocytes is accomplished by the preparative regimen itself. However, with other regimens, depletion of recipient lymphocytes occurs more gradually via the use of donor leukocyte infusions following transplant. The blue line represents the recovery of relatively radiotherapy/chemotherapy-resistant cells such as plasma cells, tissue dendritic cells (eg, Langerhans cells) and, perhaps, tissue macrophages/microglia. Immunological reconstitution after hematopoietic cell transplantation-its relation to the contents of the graft. Regeneration of lymphocytes in humans is an inefficient process, which primarily involves 2 distinct pathways. B cells are also primarily regenerated from lymphoid progenitor cells, as evidenced by the appearance of primitive B cell subsets as the harbinger of B cell immune reconstitution [51]. Although recent data have demonstrated that mature B cells can also contribute to B cell reconstitution via homeostatic expansion, this pathway appears to be minor compared with the marrow-derived pathway for B cell regeneration. Serum IgG levels provide little insight into B cell reconstitution, because long-lived, radioresistant plasma cells survive many preparative regimens [53] and can produce substantial circulating IgG without providing humoral responses to specific pathogens. The only reliable means by which one can assess humoral immune competence following transplantation is by documenting clinically significant rises in antigen-specific antibodies following vaccination or infection. T cell regeneration is predominantly driven by a thymic-independent pathway, termed homeostatic peripheral expansion. Here, mature T cells contained within the graft dramatically expand in vivo in response to T cell lymphopenia. Memory T cells respond quickly to previously encountered pathogens such as herpesviruses. Second, recipient factors such as age, comorbidities, and infectious exposure prior to transplant contribute substantially to the risk for posttransplant infectious complications. During phase I, prolonged neutropenia and breaks in the mucocutaneous barrier result in substantial risk for bacteremia and fungal infections involving Candida species and, as neutropenia continues, Aspergillus species. Other dominant pathogens during this phase include Pneumocystis jiroveci and Aspergillus species.
Syndromes
Development and validation of a food use checklist for evaluation of community nutrition interventions. Change in the use of traditional foods by the Nuxalk native people of British Columbia. Consideration of and compensation for intra-individual variability in nutrient intakes. Statistical methods to assess and minimize the role of intra-individual variability in obscuring the relationship between dietary lipids and serum cholesterol. Recommended Dietary Allowances: Protein, Calcium, Iron, Vitamin A, Vitamin B (Thiamin), Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid), Riboflavin, Nicotinic Acid, Vitamin D. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, Food and Rural Economics Division. A comparative study of exercise, calcium supplementation, and hormone-replacement therapy. Effects of intraindividual and interindividual variation in repeated dietary records. Simulation extrapolation deconvolution of finite population cumulative distribution function estimators. Differences in reported food frequency by season of questionnaire administration: the 1987 National Health Interview Survey. Statistical estimation of dietary parameters: Implications of patterns in within-subject variation-A case study of sampling strategies. Within- and between-person variations in portion sizes of foods consumed by the Japanese population. Considerations for selecting nutrientcalculation software: Evaluation of the nutrient database. Insights into dietary recall from a longitudinal study: Accuracy over four decades. A study of inter- and intrasubject variability in seven-day weighed dietary intakes with particular emphasis on trace elements. Dietary effects of the National School Lunch Program and the School Breakfast Program. Bone mineral content and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in breast-fed infants with and without supplemental vitamin D: One-year followup. Calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, copper, and manganese balance in adolescent females. Development and validation of dietary assessment methods for culturally diverse populations. Calcium metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis: the influence of dietary calcium and net absorbed calcium. Literacy and body fatness are associated with underreporting of energy intake in U. Dietary nutrient profiles of Canadian Baffin Island Inuit differ by food source, season, and age. Epidemiology Nutrition and Health: Proceedings of the First Berlin Meeting on Nutritional Epidemiology. Within-person variance in biochemical indicators of iron status: Effects on prevalence estimates. Intakes and retentions of nitrogen, calcium and phosphorus by 136 women between 30 and 85 years of age. Dietary fluoride intake of 6-month and 2-year-old children in four dietary regions of the United States. The effects of calcium supplementation (milk powder or tablets) and exercise on bone density in postmenopausal women. Decreasing traditional food use affects diet quality for adult Dene/Metis in 16 communities of the Canadian Northwest Territories. Pantothenic acid nutritional status in the elderly-Institutionalized and noninstitutionalized. Validation of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire: Comparison with a 1-year diet record. Under-reporting in dietary surveys-implications for development of food-based dietary guidelines. Energy under-reporting in Swedish and Irish dietary surveys: Implications for food-based dietary guidelines.
Since solubility of Ca and P is a concern, never reduce the amino acids to less than 2. Sodium phosphate can replace potassium phosphate in the same molar concentrations when potassium intake needs to be limited or potassium phosphate is not available. It is not necessary to decrease prophylactically the Intralipid infusion rate in the absence of any evidence of cholestasis. Guidelines for Acute Care of the Neonate, Edition 26, 201819 Section of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine Section 12-Nutrition Alterations in trace element provision: In Cholestasis - Since copper and manganese are excreted in the bile, in cholestasis, they may accumulate in the liver and cause worsening hepatic dysfunction. Growing infants, however, have a requirement for copper and will ultimately develop copper deficiency in the absence of adequate copper supplementation. In the presence of cholestasis without either jejunostomy or ileostomy, trace minerals (including copper and manganese) should be provided 3 times per week (Monday, Wednesday and Friday), and parenteral zinc should be provided at maintenance levels daily. In the presence of cholestasis with either jejunostomy or ileostomy, apart from the above supplementation, extra zinc should be provided to compensate for gastrointestinal losses. Lab monitoring of copper and zinc levels may indicate the need for further adjustments to supplementation. In those instances, copper and zinc should be supplemented despite cholestasis, but levels should be checked when medically feasible. In infants with cholestasis or renal failure, continue zinc daily per guidelines (Table 12-5c). Use of volume to provide protein is of greater importance in this setting than providing more than 1 g/kg/d of lipids or high concentrations of calcium and phosphorus. It is important to maintain both total blood phosphorous and magnesium within physiological ranges. Recommended goal parenteral nutrition composition for cooling given in Table 12-6b. Generally, the unbalanced addition of carbohydrate is not recommended to increase total calorie intake. Evaluate infant if residuals exceed 50% of the feeding volume or the infant has other symptoms of feeding intolerance. Stable> 2500 Cardiac babies: 20 mL/kg per day 1 Cardiac babies may need 20 mL/kg/for a 25-40 mL/kg per day longer period of time. Feedings for infants < 1500grams are usually best given on a pump for 30-60 minutes. The use of donor milk may be considered for all infants but infant formula is also an appropriate backup for infants > 1500 g birthweight. Low dose pressors, including dopamine (usually 5 mcg/kg/min or less) are compatible with initial trophic feeds. Trophic feeds are typically continued for 3 days for infants 751-1250 g and may continue for 5 days for infants 750 grams birthweight. Trophic feedings may be prolonged if the infant requires high dose pressor support. Consider bolus feeds every 3 hours given on a pump over 30 minutes in presence of feeding intolerance. Due to fat loss in tubing, it is preferred not to give continuous feeds unless severe feeding intolerance. Studies have found that providing oral care with expressed colostrum or breast milk is safe and may impart protection from these factors in an infant that may not be ready to feed. Procedure · · Feeding and Nutrition Goals Human milk is recommended for infants (see exceptions in Human Milk section of this chapter). Unless feeding intolerance necessitates a slower pace, follow the schedules in Tables 127a, 7b, 7c, 7d, 7e and Figure 121. Nutrient components of human milk & fortified human milk are listed in Table 12-10a. Energy intakes of 100 to 130 kcal/kg per day will meet the needs for term and premature infants. Illness or surgery increases protein needs to 2-3 g/kg per day for the term infant. Thus, the caloric distribution and nutrient content of infant formulas are based on that of human milk. Guidelines for Acute Care of the Neonate, Edition 26, 201819 169 Section 12-Nutrition Section of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine Table 12-7c.
Also note that most of the cells undergo normal mitosis resulting in normal cells. Therefore, an individual formed from such an embryo will have 2 populations of cells a trisomic cell population & a normal cell population. And the clinical appearance of such an individual depends on the proportion of trisomic cells. Anyway, the clinical feature is less severe than that of an individual in whom all the cells are trisomic. In general, monosomies & trisomies of the sex chromosomes are compatible with life & usually cause phenotypic abnormalities. And trisomies of all autosomal chromosomes except chromosomes 13, 18, & 21 cause abortion or early death. However, trisomies of the autosomal chromosomes, 13, 18, & 21 permit survival with phenotypic abnormalities. Polyploidy - is a chromosome number that is a multiple greater than 2 of the haploid number. Structural anomalies - result from breakage of chromosomes followed by loss or rearrangement of genetic material - are of the following types (See Fig. Interstitial deletions arise from 2 breaks, loss of the interstitial acentric segment & fusion at the break sites. Ring chromosomes arise from breaks on either side of the centromere & fusion at the breakpoints on the centric segment. Segments distal to the breaks are lost so that individuals with chromosome rings have deletions from both the long arm & short arm of the chromosome involved. Isochromosome formation - results when one arm of a chromosome is lost & the remaining arm is duplicated, resulting in a chromosome consisting of 2 short arms only or 2 long arms only. Inversion is reunion of a chromosome broken at 2 points, in which the internal segment is reinserted in an inverted position. Reciprocal (balanced translocation) - is a break in 2 chromosomes leading to an exchange of chromosomal material between the two chromosomes. Since no genetic material is lost, balanced translocation is often clinically silent. But it can also cause disease as in the t(9,22) which causes chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Robertsonian translocation - is a variant in which the long arms of 2 acrocentric chromosomes are joined with a common centromere, & the short arms are lost. Before going into the discussion of some of the chromosomal disorders, it is good to remember what mosaicism is. Mosaicism is the presence of 2 or more cell lines with different karyotypes in a single individual. In a mosaic individual, a normal diploid cell commonly coexists with an abnormal cell line. A specific cell line may be represented in all tissues or may be confined to single or multiple tissues. The expression of the phenotype depends on the proportion & distribution of the abnormal cell line. Cytogenetic disorders involving autosomes include: o o o o Down syndrome Edward syndrome Patau syndrome Chromosome 22q11 deletion syndrome Down syndrome is the most frequent chromosomal disorder. The fertilized ovum will have 3 chromosomes bearing the chromosome 21 material, the functional equivalent of trisomy 21. Down syndrome has the following clinical features: o o Severe mental retardation Broad (flat) nasal bridge & oblique palpebral fissure. Short broad hands with curvature of the 5th finger, simian crease (a single palmar crease) o o o o o Unusually wide space between the 1st & the 2nd toes Congenital heart disease (in about 40% of the cases). Cytogenetic disorders involving sex chromosomes the following subtopics will be discussed below: 1.
Additionally, renal tubules and glomeruli within the cortex are multifocally expanded and replaced by sharp, radiating, eosinophilic crystalline deposits that range in size from 50-150 microns in diameter and are surrounded by moderate numbers of degenerate heterophils and macrophages (urate tophi). Kidney, tubules: Degeneration, necrosis, and regeneration, multifocal, moderate, with intratubular protein. Conference Comment: the contributor provides an overview of the two most likely etiologic differentials in this case, and conference participants, whom are not privy to the provided clinical history, added avian influenza and Newcastle disease as well. Herpesvirus and polyomavirus may each also cause tubular necrosis in avian species, however, intranuclear inclusions would be prominent in both instances. Urates are actively excreted by renal tubular epithelium, so it stands to reason that loss of tubular epithelium can lead to urate accumulation and subsequent tophi formation. Additionally, a sick bird as described in this case would likely be dehydrated which will further exacerbate urate deposition. The gouty tophi formation was minimal in most sections, thus not likely a significant contributor to the tubular lesions as observed in cases of true renal gout. This virus is unique among coronaviruses in that it replicates, mutates and recombines rapidly resulting in the creation of an extensive number of serotypes. These pose a challenge to poultry producers and veterinarians, as vaccines do not provide cross-protection for different serotypes, necessitating the need to develop specific vaccines to the identified serotype associated with an outbreak. Even the vaccines themselves have been associated with the emergence of new strains capable of causing disease. The most significant protein for virus detection is the club-shaped glycoprotein known as spike. It is composed of two subunits: S1, which makes up the outer portion; and S2, which anchors it to the viral envelope. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry of renal lesions due to infectious bronchitis virus in chicks. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry of renal lesions due to avian infectious bronchitis virus in chicks uninoculated and previously inoculated with highly virulent infectious bursal disease virus. Pathogenesis of renal dysfunction in chicks experimentally induced by avian nephritis virus. Signalment: Tissue from an 8-year-old intact female Miniature Rex rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). The veterinarian reported that all masses that had abruptly appeared regressed and were completely gone by 2-3 months. Haired skin, rabbit: the dermis is expanded by a densely cellular neoplasm which elevates the overlying hyperplastic epithelium. Haired skin, rabbit: the neoplasm within the dermis is composed of densely packed hypertrophic fibroblasts which occasionally contain intracytoplasmic poxviral inclusions. Haired skin, rabbit: the epithelium overlying the neoplasm is markedly hyperplastic with abundant hyperkeratosis. Haired skin, rabbit: the hyperplastic epithelium contains ballooning degeneration and necrosis of individual hepatocytes as well as intracytoplasmic poxviral inclusions. Histopathologic Description: Tissue samples are from haired skin or skin from mucocutaneous junction. The dermis is expanded by a raised, well-demarcated, nonencapsulated neoplastic mass. The mass is comprised of densely-cellular, primarily spindled to polyhedral cells arranged in streams or short, haphazardly-placed bundles or fascicles. The neoplastic cells have large nuclei exhibiting moderate anisokaryosis and prominent, often multiple, nucleoli. The cells have moderate amounts of amphophilic cytoplasm with rare, intracytoplasmic, round, eosinophilic inclusion bodies. The epidermis overlying the mass is variably hyperplastic with regional orthokeratosis and occasional serocellular crusts. Innumerable epidermal cells at nearly all levels (strata) are rounded with either grey-smudged or vacuolated cytoplasm that includes single, conspicuous, roughly round, 5-12 µm in diameter, bright eosinophilic inclusion bodies. Inconsistent lesions across sections include regional edema, acute necrosis of individual neoplastic cells, scattered and variably intense heterophilic infiltrates and surface ulceration. The natural host is the Eastern cottontail (Sylvilagus floridanus) rabbit; however, this is expanded to also include other rabbits, hares and squirrels. Overall, trichoblastomas and collagenous hamartomas were the most common cutaneous tumors reported from this study. Interestingly, this study reported a sex predilection for mesenchymal tumors in rabbits, with mesenchymal proliferations occurring significantly more in male rabbits than females.
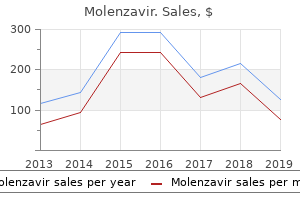
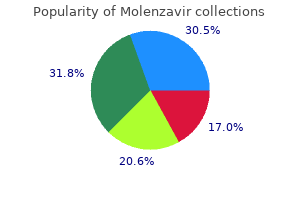
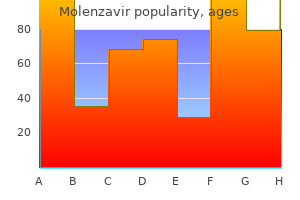
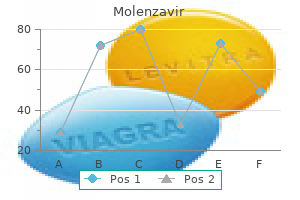
Myristicae Semen (Nutmeg And Mace). Molenzavir.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96767
High dose exercise does not increase hunger or energy intake in free living males. Leisure-time physical activity levels and risk of coronary heart disease and death. Ventilatory threshold and Vo2max changes in children following endurance training. Cardiovascular adaptations in 8- to 12-year-old boys following a 14-week running program. Walking compared with vigorous exercise for the prevention of cardiovascular events in women. Exercise, food intake and body weight in normal rats and genetically obese adult mice. Relation between caloric intake, body weight, and physical work: Studies in an industrial male population in West Bengal. The association of changes in physical-activity level and other lifestyle characteristics with mortality among men. Changes in energy balance and body composition at menopause: A controlled longitudinal study. The effect of aging on the cardiovascular response to dynamic and static exercise. Effects of physical exercise on anxiety, depression, and sensitivity to stress: A unifying theory. Physical fitness as a predictor of mortality among healthy, middle-aged Norwegian men. The effect of intensive endurance exercise training on body fat distribution in young and older men. Luteal and follicular glucose fluxes during rest and exercise in 3-h postabsorptive women. Effects of moderate-intensity endurance and high-intensity intermittent training on anaerobic capacity and Vo2max. Relations of parental obesity status to physical activity and fitness of prepubertal girls. Cardiorespiratory alterations in 9 to 11 year old children following a season of competitive swimming. Effects of addition of exercise to energy restriction on 24-hour energy expenditure, sleeping metabolic rate and daily physical activity. Weight-bearing activity during youth is a more important factor for peak bone mass than calcium intake. Physical activity, physical fitness, and all-cause mortality in women: Do women need to be active? Interaction of dietary sucrose and fiber on serum lipids in healthy young men fed high carbohydrate diets. Insulin resistance of puberty: A defect restricted to peripheral glucose metabolism. Effects of growth hormone releasing hormone on insulin action and insulin secretion in a hypopituitary patient evaluated by the clamp technique. Glucose metabolism during fasting through human pregnancy: Comparison of tracer method with respiratory calorimetry. Ketosis, weight loss, uric acid, and nitrogen balance in obese women fed single nutrients at low caloric levels. Measurement of "true" glucose production rates in infancy and childhood with 6,6-dideuteroglucose. The effects of physiologic amounts of simple sugars on lipoprotein, glucose, and insulin levels in normal subjects. A quantitative assessment of plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease: Probable benefits of increasing folic acid intakes. Thermogenic capacity of brown adipose tissue is reduced in rats fed a high protein, carbohydrate-free diet. Balance of carbohydrate and lipid utilization during exercise: the "crossover" concept. Glycemic index in the diet of European outpatients with type 1 diabetes: Relations to glycated hemoglobin and serum lipids. Prediction of glycemic response to mixed meals in noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects.
First, the variation in nutrient intake may be rather limited in populations selected for study. This feature alone may yield modest relative risk trends across intake categories in the population, even if the nutrient is an important factor in explaining large disease rate variations among populations. Third, many cohort and casecontrol studies have relied on self-reports of diet, typically food records, 24hour recalls, or diet history questionnaires. Repeated application of such instruments to the same individuals shows considerable variation in nutrient consumption estimates from one time period to another with correlations often in the 0. In addition, there may be systematic bias in nutrient consumption estimates from self-reports as the reporting of food intakes and portion sizes may depend on individual characteristics such as body mass, ethnicity, and age. For example, total energy consumption may tend to be substantially underreported (30 to 50 percent) among obese persons, with little or no underreporting among lean persons. Such systematic bias, in conjunction with random measurement error and limited intake range, has the potential to greatly impact analytic epidemiological studies based on self-reported dietary habits. Note that cohort studies using objective (biomarker) measures of nutrient intake may have an important advantage in the avoidance of systematic bias, though important sources of bias. The unique strength of randomized trials is that if the sample is large enough, the study groups will be similar with respect not only to those confounding variables known to the investigators, but also to any unknown factors that might be related to risk of the disease. Thus, randomized trials achieve a degree of control of confounding that is simply not possible with any observational design strategy, and thus they allow for the testing of small effects that are beyond the ability of observational studies to detect reliably. Although randomized controlled trials represent the accepted standard for studies of nutrient consumption in relation to human health, they too possess important limitations. Specifically, persons agreeing to be part of a randomized trial may be a select subset of the population of interest, thus limiting the generalization of trial results. For practical reasons, only a small number of nutri- Copyright © National Academy of Sciences. In addition, the follow-up period will typically be short relative to the preceding time period of nutrient consumption that may be relevant to the health outcomes under study, particularly if chronic disease endpoints are sought. Also, dietary intervention or supplementation trials tend to be costly and logistically difficult, and the maintenance of intervention adherence can be a particular challenge. Because of the many complexities in conducting studies among free-living human populations and the attendant potential for bias and confounding, it is the totality of the evidence from both observational and intervention studies, appropriately weighted, that must form the basis for conclusions about causal relationships between particular exposures and disease outcomes. However, studies published in other scientific journals or readily available reports were considered if they appeared to provide important information not documented elsewhere. On the basis of a thorough review of the scientific literature, clinical, functional, and biochemical indicators of nutritional adequacy and excess were evaluated for each nutrient. The characteristics examined included the study design and the representativeness of the study population; the validity, reliability, and precision of the methods used for measuring intake and indicators of adequacy or excess; the control of biases and confounding factors; and the power of the study to demonstrate a given difference or correlation. The assessment acknowledged the inherent reliability of each type of study design as described above, and it applied standard criteria from Hill concerning the strength, doseresponse, and temporal pattern of estimated nutrientdisease or adverse effect associations, the consistency of associations among studies of various types, and the specificity and biological plausibility of the suggested relationships. For example, biological plausibility would not be sufficient in the presence of a weak association and lack of evidence that exposure preceded the effect. Data were examined to determine whether similar estimates of the requirement resulted from the use of different indicators and different types of studies. Therefore, many of the questions raised about the requirements for and recommended intakes of these nutrients cannot be answered fully. Thus, after careful review and analysis of the evidence, including examination of the extent of congruent findings, scientific judgment was used to determine the basis for establishing the values. The extent to which intake of a nutrient from human milk may exceed the actual requirements of infants is not known, and ethics of experimentation preclude testing the levels known to be potentially inadequate. Using the infant exclusively fed human milk as a model is in keeping with the basis for earlier recommendations for intake. It also supports the recommendation that exclusive intake of human milk is the preferred method of feeding for normal full-term infants for the first 4 to 6 months of life. This recommendation has been made by the Canadian Paediatric Society, the American Academy of Pediatrics, the Institute of Medicine, and many other expert groups, even though most U. In general, this book does not cover possible variations in physiological need during the first month after birth or the variations in intake of nutrients Copyright © National Academy of Sciences. In keeping with the decision made by the Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes, there were not specific recommended intakes to meet the needs of formula-fed infants.
Bacterial identification was carried out using routine biochemical tests, and confirmed with polymerase chain reaction. Susceptibility testing for the bacterial isolates was done using the disk diffusion method. Results: One hundred and seventy (170) bacterial pathogens were isolated, of which 138(81. The statistical analysis showed that there was significant difference in the prevalence rate of the organisms on the surfaces. Conclusion: Lack of a universal procedure for surveillance of nosocomial infection, presence of pathogenic bacteria with multidrug resistant organism, poor hygiene practices and heavy contamination of some important surfaces are the most important problems in our hospitals. Index Terms- Hospital acquired infections; Staphylococcus aureus; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Antibiotic susceptibility patterns; hospital environment. It is a major public health concern these days and a cause of substantial mortality and morbidity for hospitalized patients (Thapa et al. Nosocomial infection caused by the nosocomial pathogens has pose a problem of enormous magnitude globally, hospital localities have proven favourable in transmission of infection due to existing suitable pathogens-host-environment relationship (Samuel et al. The occurrence of multi-drug resistance in hospitalassociated pathogens has resulted in the emergence and reemergence of difficult-to-treat nosocomial infections in patients depicting the pre-antibiotic era. These infections are difficult to eradicate due to resistance to many antibiotics, thus major cause of morbidity and mortality, leading directly and indirectly to an enormous increase in cost of hospital stay for the patients and also emergence of new health hazards for the community. Before samples were collected, information regarding the study was explained to the individual hospital managements and consent for participation in the study was gotten following approval by the ethical committee of Kaduna state Ministry of Health. Sampling design and techniques A total number of one hundred and sixty (160) swabs samples for the studies were collected from floors, door knobs, table tops, bedrails, and sink using sterile swab sticks for the purposes of isolating microorganisms from these sources and These samples were inoculated into two different selective media, to make a total of three hundred and twenty culture plates. Isolation and characterization of isolates Organisms were identified by Gram stain, catalase, coagulase test oxidase test. Eight (8) swab samples from each of the five different surfaces that is, sinks, floor, door knobs, table tops and bed rails in each of the hospitals making a total of forty swab samples per hospital, the swab samples were inoculated each into two(2) different selective media for the purpose of bacterial isolation. The statistical analysis showed that there was significant difference in the prevalence rate of the organisms on the surfaces of the four hospitals P 0. Barau Dikko Specialist hospital has sinks, floor, door knobs, table tops and bed rails with 9. Barau Dikko Specialist hospital has similar pattern with Ampicillin and Amoxillin resistance to S. The resistance rates follow the same pattern in Yusuf Dantsoho hospital with Ampicillin 35(94. Vancomycin also showed 100% susceptibility with good number susceptible to streptomycin 34(91. Isolation of more Gram positive organisms is consistent with previous reports (Neely and Maley, 2000; Chikere et al. Similar study done in selected hospitals in Akoko, Ondo State Southwest Nigeria (Alabi et al. It also correlates with the findings of Atata (2008) among hospitals in Ilorin, North central Nigeria with similar result from Onche and Adeayi, 2004; Oguntibegu and Nwobu, (2004). Also previous studies in this environment confirmed Staphylococcus aureus to be the leading organism on surfaces of hospital environments. The result of this study is similar to the report of Okesola and Oni (2009) which showed that Staphylococcus aureus is the most frequent bacteria isolated in the hospital environments. It is also quite similar to the result of Ijioma et al (2010) which reported that Staphylococcus aureus was the most prevalent bacteria isolated in the environment of labour ward of Umuguma and Umezuruike general hospital, Owerri, while Bouzada et al (2010) reported that coagulase negative Staphylococcus was the most prevalent accounting for 43. Also the result of this study correlates with the report of Chikere et al (2008) which showed that Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus were the most prevalent bacteria isolated in the hospital environments. In contrast, the result of this study did not agree with the work of Orji et al (2005) which showed that Staphylococcus aureus was the least among the isolated bacteria in his study. However, the prevalence rate gotten in this study for Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is still higher than the rate noted by Jalalpoor et al (2009), rates of 30. A study carried out in some selected hospitals in Abeokuta Southwest Nigeria (Okonkwo et al, 2009), recorded prevalence of 20. The high level of recovery of these pathogens could also be as a result of inadequate decontamination of the microbial load from the surfaces (Addy et al.

Most oncologists describe all of the side effects and risks of chemotherapy to their patients as well as the potential benefits in order to help patients make decisions for themselves. Background on Afghani immigrants in the United States* Some history of the immigration from Afghanistan to the United States may also be helpful in thinking about this case and its implications. Prior to the Soviet invasion of 1979 most Afghani immigrants were relatively well educated people from Kabul. The first were a wealthy, educated elite, but later, less affluent and less educated Afghans were able to enter through a family reunification program. After 1989, when the Soviets withdrew from the country, factional fighting led to a more educated, professional wave of emigration, but the numbers were small and ceased altogether in 1994. With the rise to power of the Taliban in 1996 many ethnic minorities were persecuted and fled to Pakistan. Those particularly at risk (especially unaccompanied women and children) were allowed to enter the U. This is mixed, however, with some negative feelings towards the attacking of their homeland and fear of discrimination in this country. Some Afghans feel hesitant to divulge their nationality, though this is beginning to change. Afghans are a diverse group, made up of several different ethnicities-most of which in the U. In fact, the cancer had been there all along, even after the surgery, but the family members serving as interpreters had not translated this to Mr. How does culture influence the way patients and families discuss medical information and make medical decisions? This is generally done with the idea of protecting patients from the bad news and the emotional distress that comes with it. Additionally, the perception that a terminal diagnosis can lead to a loss of will to live and hastening of death is also well documented in the literature on end-of-life care. This goes against the value of patient autonomy and the right to know which most health care professionals in the U. Respecting patient autonomy, however, does not mean that patients must be told their diagnosis and must make their own decisions about care. In fact, patients may waive or relinquish their right to know in favor of allowing a designated individual (a representative of the family, for example) to make decisions on their behalf. This issue will lead to a rich discussion about values with respect to autonomy and disclosure of information to families versus individual patients. Give participants a chance to explain why they feel the way they do and discuss why others may feel differently. After the surgery, when the surgeons stated that they had "gotten it all," the family understood that Mr. Family members acting as interpreters never relayed to Noorzia and others the subsequent discussions with the physicians. We often assume patients are autonomous decision-makers, but in some cultures (and in some families) decisions are made in a more unified, family-oriented way. This is more difficult when the family wants to withhold information from the patient. One way to deal with this situation before it becomes a problem is to ask the patient whether he agrees to have his family make medical decisions for him and to be informed of the results of tests, instead of himself. I should have come with you from the beginning, and you would have started this treatment six months ago. This is an opportunity to discuss how immigration can affect families and their interaction with the health care system. Noorzia speaks English fluently and is more acculturated into the Western, American perspective than her parents and other members of the family. Because of this she becomes the spokesperson for her father to the health care team. Kochi becomes It is important to establish the way a patient and family prefer to receive information and make medical decisions. He is concerned with his quality of life and does not seem to feel that treatments should be tried unless they have a very high likelihood of benefit with little risk. In Afghanistan Noorzia might have a less important role in the family, while in this country the hierarchy is reversed. There is often a tension in immigrant families between the maintenance of the traditional cultural values and customs and the adopting of a new culture and language.
In severely affected animals however, gross examination may reveal enlarged livers that are often described as pale, friable to firm, and waxy; prominent white pulp areas on the cut surfaces of spleens; or thickened gastrointestinal mucosa. Chronically-affected animals may also display emaciation associated with weight loss. Histopathology of tissues obtained as biopsy specimens or from necropsy is the traditional gold standard for diagnosis of secondary/reactive amyloidosis. Amyloid appears as amorphous, acellular, homogenous eosinophilic extracellular material on H&E sections, and occurs most prominently in the space of Disse in the liver, the follicular white pulp areas in the spleen, the lamina propria of the gastrointestinal tract, the medullary interstitium of the kidneys, and the corticomedullary junction of the adrenal glands. We believe that the case of hepatic amyloidosis presented here represents severe localized secondary/reactive amyloidosis in the liver. Observable amyloid deposition was not noted in all other tissues examined histologically. The cause of the amyloidosis was most likely the chronic infection of the subcutaneous tissues under the cranial head-stage implant ("periimplantitis") in this macaque, which is a common cause of secondary/reactive amyloidosis in macaques observed in our institution. Conference Comment: the contributor provides an excellent overview of amyloidosis with emphasis on the variety of manifestations in nonhuman primates. This case is an exceptional example of hepatic amyloidosis, as it nicely illustrates the expansion of the perisinusoidal space with amyloid. This area, known as the space of Disse, is the narrow space between the plates of hepatocytes and sinusoidal lining cells where amyloid is known to accumulate within the liver. Conference participants noted the severity of the lesion in this case and were amazed as to the lack of clinical signs in this animal. Contributing Institution: Veterinary Services Center Department of Comparative Medicine Stanford School of Medicine med. Diagnosis and clinical signs of feline infectious peritonitis in the central nervous system. Performances of different diagnostic tests for feline infectious peritonitis in challenging clinical cases. Clinical, cerebrospinal fluid, and histological data from twenty-seven cats with primary inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. Sharif S, Suri Arshad S, Hair-Bejo M, Rahman Omar A, Allaudin Zeenathul N, Alazawy A. Inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid analysis in cats: Clinical diagnosis and outcome. Clinicopathological findings and disease staging of feline infectious peritonitis: 51 cases from 2003 to 2009 in Taiwan. History: the dog had been bitten on the left femoral skin, and a 12 x 16 mm dermal mass formed at first in the region. He was fitted with an Elizabethan collar to prevent self-trauma and was topically treated with antibiotics and steroids with no clinical improvement. Laboratory Results: None Histopathologic Description: the multiple variably sized masses are present in the dermis and subcutis, with multiple small masses around large masses. Various-sized swollen peripheral nerve fascicles are observed in each mass, with perineurial hyperplasia. Swollen nerve fascicles in each mass consist of thin, unmyelinated nerves with hypertrophic Schwann cells and a thickened perineurium. Each nerve fascicle consisted of thin to unmyelinated nerve fibers, including axons and Schwann cells. Axons in swollen nerve fascicles and hyperplastic perineurium had Schwann cells as well as normal nerve fibers, suggesting a non11 neoplastic lesion. The lack of proliferative activity also indicated that our case was non-neoplastic. The histological features resembled traumatic neuroma except swollen large-sized nerve fascicles and perineurial hyperplasia. With clinical findings and histological features, it was suggested that peripheral nerves of affected area were the result of self-inflicted injury. Traumatic neuroma is a reactive and nonneoplastic proliferative nerve disease to injury or surgery at the proximal end of an injured peripheral nerve. The lesion is commonly seen in the interdigital plantar nerve of third and fourth toes in women. As the lesion progresses, the fibrosis becomes marked and envelops the epineurium and perineurium in a concentric fashion and even extends into the surrounding tissue.
References: