
During a review of systems the patient complains of weight gain, trouble speaking, and vision problems over the past several months. A geneticist tells the mother that her child is genotypically a female, although the child seems to have partially virilized external genitalia. Glucocorticoids are important in the treatment of inflammatory diseases; however, their use is associated with many adverse effects on multiple systems. A 30-year-old woman with no prior medical history is diagnosed with diastolic hypertension. The patient reports symptoms of weakness, fatigue, polyuria, polydipsia, and headache. Laboratory results indicate she is hypokalemic and hypernatremic, has decreased renin levels, and has a metabolic alkalosis. A 42-year-old woman with a history of breast cancer presents to the emergency department with hematuria and costovertebral tenderness. She rates her pain as 8 out of 10 in severity, but says that it seems to "come and go," fluctuating in intensity. She also complains of mild fatigue, along with nausea and constipation for the past few months. Radionuclide imaging demonstrates one area of increased uptake corresponding to her superior left parathyroid gland. A 27-year-old white woman comes to the physician because of a six-month history of progressive weakness and fatigue, and occasional mild abdominal pain. She also has noticed that her skin has become more tan, especially at the elbows, knees, and knuckles, despite the fact that she is not usually in the sun. Laboratory tests show decreased serum levels of sodium, bicarbonate, chloride, and glucose and increased levels of potassium. A 34-year-old woman goes to her primary care physician complaining of visual changes and a recent feeling that "her heart was racing. On physical examination, the physician notes that the patient is tachycardic and has 2+ nonpitting edema in her lower extremities. An 18-year-old woman is referred to a specialist, because she never began menstruating. She is diagnosed with a condition that affects the production of two of the three major adrenal hormones, leaving only one functioning hormone. A 7-year-old girl with a viral upper respiratory infection is brought to the emergency department because of severe confusion, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Infarction of which artery would lead to contralateral deficits of the leg and foot A 6-year-old girl is brought to the clinic by her parents, because they thought she looked like she was "growing breasts. The vasculature of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland is uniquely designed and functionally resembles the design of the gastrointestinal vasculature in that it includes a portal system. Which of the following is the functional significance of this specialized vascular system A 24-year-old nulliparous woman presents to her physician with galactorrhea and bilateral hemianopsia. A 59-year-old man with no prior medical history presents to his physician with marked hyperglycemia, diarrhea, and weight loss. A trial period on an oral hypoglycemic agent has not succeeded in reducing his glucose levels. A particular hormone stimulates the enzyme that converts testosterone to 17b-estradiol in granulosa cells. A 44-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after collapsing at his office. His diabetes has been poorly controlled with glyburide, and his most recent HbA1c level was 8. Her mother says the girl has been very thirsty lately and urinating more frequently; she has also lost 4. Laboratory studies show a markedly elevated blood glucose level and a decreased insulin level; levels of a specific antibody are also elevated. Antibodies against which of the following organs are most likely present in this girl
We live in a dry semi-desert climate getting ever more dry with global warming, and we cannot afford to waste such a huge amount of water. We are living in the driest year since 2004 and we continually ask the citizens to use less water (as we should be doing). We already have 700,000 metric tons of depleted uranium waste from weapons production. After the facility is built, almost all the workers will be transferred from other buildings. Even the Environmental Impact Statement admits that the socioeconomic impact on New Mexico is minimal. The total cost of nuclear weapons complex across the country is estimated to be $180 billion over the next ten years. Rather than cutting domestic services to the poorest and most disadvantaged in our society in order to balance the federal budget, the $6 billion (and growing) could be used to create jobs for education, health care, mass transit, affordable housing, renewable energy, bridge upgrades, and better food distribution. Even though the first phase has been completed it is not too late to stop this facility which is a danger to us all. If we ask other nations to cease development, we should lead the way by ppublically doing the same. I dont want my taxes funding such activities that contradict our commitment to humanity. I have family in Nevada and they do not want the nuclear waste dumped in the Yucca area. Two-the money should be spent on more life-giving expenditures, like clean water for all, solar ovens, etc. Money to make more nuclear triggers should obviously be spent better to help our true treasure, our true security-our children. Tegtmeier: Please accept this as a formal public comment from Conejos County Clean Water, Inc. In particular, to build awareness surrounding the transfer from truck to rail of radioactive, hazardous and Response side of this page intentionally left blank. It has been a farm and ranching community for over 150 years, and many of the residents work in agriculture, following in the footsteps of their parents and grandparents. Conejos County is among the poorest counties in the country, and unemployment levels run above the state and national averages (Conejos County 10. A May 2007, updated seismic hazards analysis showed a potential huge increase in seismic ground motion and activity. Given the instability of its building site, the most recent vastly fortified design for this building is still in flux. The costs of trying to build a plutonium pit production complex in a geologically unstable area are extremely high. However, a Jason study of aging plutonium argues against the need for pit replacement within the next hundred years. The Kleinfelder report accounts for the weight of the building and demonstrates that the bearing capacity of the soil (20,000 pounds per square foot [97,600 kilograms per square kilometer]) is substantially greater than the pressure due to the building (4,850 pounds per square foot [23,700 kilograms per square meter]) for the Shallow Excavation Option (Kleinfelder 2007a). At the current level of design maturity, this approach, known as the Shallow Excavation Option, appears 176-3 176-3 176-4 5 Commentor No. Socio Economics How does money spent on unusable nuclear weapons spur economic growth Money for education, health care, green jobs, renewable energy, public transportation, all would keep circulating and foster sustainable economic growth. Furthermore, a new nuclear facility will detract from cleanup of the existing waste. The Order requires cleanup of certain sites by December 31, 2015; including, the Area G dump site at Technical Area 54.
Diseases
By definition, there is no external bleeding because the blood forms a hematoma that is hidden behind the placenta. This patient does not describe contractions at regular intervals, but rather a constant pain with intermittent cramping. Placenta accreta refers to the abnormally strong adherence of the placenta to the uterine wall. This happens because the placental villi attach directly to the myometrium as a result of a defect in the decidua basalis layer. Placenta accreta manifests as incomplete separation of the placenta after delivery and can result in severe postpartum hemorrhage. Risk factors include placenta previa, prior cesarean delivery, and prior intrauterine manipulation or surgery. The most common setting for accreta involves a placenta previa after a prior cesarean delivery. The distinction between placenta previa and abruptio placentae is classically made based on the presence (abruptio placentae) or absence (placenta previa) of pain. Androgenic steroids are used to treat hypogonadism either due to failure of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (secondary hypogonadism) or due to Leydig cell dysfunction (primary hypogonadism). Patients should be warned that androgens cause premature closing of the epiphyseal plates by promoting calcium deposition in the bones. This adverse affect is another risk factor for premature coronary artery disease and thrombosis. The lipid profile disturbance increases the possibility of atherosclerotic change and raises the risk of early coronary artery disease. These patients demonstrate hypotonia, downslanting of the lateral portion of the palpebral fissures, and microcephaly. More than 90% of these children do not survive past 12 months, and those who do are severely mentally retarded. This choice describes spina bifida occulta, a specific type of neural tube defect. The ureters are muscular ducts with narrow lumina that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. These retroperitoneal structures cross the external iliac artery just beyond the bifurcation of the common iliac artery and pass under the ductus deferens and testicular vessels ("water under the bridge"). Efferent ductules transport sperm from the rete testis to the epididymis, where they are stored. The tail of the epididymis is continuous with the ductus deferens, the next sperm destination during ejacu- lation. The spermatic cord contains the ductus deferens, testicular artery, pampiniform plexus, and lymphatic vessels. Sympathetic nerve fibers are constituents of the spermatic cord that run with the testicular arteries. The testicular artery arises from the aorta and supplies the testis and epididymis. It runs parallel to , but does not cross, the ductus deferens to enter the spermatic cord. This patient most likely suffers from osteoporosis, or weakened bones, as a complication of menopause. At menopause, estrogen production ceases due to a decreased number of ovarian follicles. Menopause, however, is a primary dysfunction of estrogen production in the ovaries, with a normally functioning anterior pituitary gland. Ketoconazole is an antifungal drug used to treat tinea corporis that acts by blocking the formation of fungal membrane sterols. Excessive melanocyte-stimulating hormone can cause increased integumentary pigmentation such as in patients with Addison disease.
A 10-day course of oral acyclovir would be appropriate treatment for genital herpes viral infection. Herpes lesions are also painful, but are commonly multiple, and microscopic examination (Tzanck test) shows multinucleated giant cells with viral inclusion bodies. Nystatin powder is effective treatment for candidal intertrigo in moist areas such as inguinal folds. Although this patient has inguinal lymphadenopathy, he has no reported skin changes in this area consistent with candidal intertrigo. Complications include premature delivery, hyrdrops fetalis, uterine tetany, and hypvolemic shock. In contrast to placenta previa, placental abruption is a clinical diagnosis, because ultrasound is not sensitive for abruption inasmuch as the clot has the same texture as the placenta and is easily missed. In any case, this patient is hemodynamically unstable and there is fetal distress, so an emergency cesarean section is indicated regardless of the underlying diagnosis. Pre-eclampsia usually presents during the third trimester of pregnancy with hypertension, proteinuria, and edema. Spontaneous delivery is preferable to cesarean section, as it has fewer sequelae for future pregnancies. It is a tool used to look for internal bleeding as may be the case in a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. However, ectopic pregnancies usually become symptomatic within the first few weeks of pregnancy and are hence unlikely in this patient. Amniotic fluid embolism is also referred to as anaphylactoid syndrome of pregnancy and is characterized by hypoxia, respiratory distress, cardiogenic shock, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. It occurs with tearing of maternal vessels and can result in maternal respiratory distress. However, genital ulcers in syphilis are typically painless, and Gram stain is unrevealing. Abruptio placentae is premature separation of the placenta, most commonly during the third trimester after week 30 of gestation. It results in painful vaginal bleeding, uterine contractions, and possible fetal death secondary to uteroplacental insufficiency. Treatment is usually supportive, and includes emergent cesarean section to reduce maternal oxygen demand and prevent more amniotic fluid from entering maternal circulation 43. This woman is in the secretory (also called luteal) phase of her menstrual cycle, which occurs after ovulation (approximately day 14 of a typical menstrual cycle) through the end of the cycle. Progesterone increases after ovulation (as it is produced by the corpus luteum) and usually peaks around day 21-22. Progesterone is responsible for the increased glandular production of glycogen and the differentiation and maintenance of the endometrium. After ovulation the estrogen levels begin to rise again, returning to a relative peak during the luteal phase (around day 21). This combination of hormone changes is seen during the end of the menstrual cycle, when the corpus luteum degenerates. During this time, progesterone levels are low and stable due to the lack of a corpus luteum, which is responsible for secretion of the hormone later in the cycle. Progesterone levels remain low and stable, due to the lack of a corpus luteum, which is responsible for the secretion of the hormone later in the cycle. This combination of hormone changes is seen immediately following ovulation, when estrogen levels are decreasing (prior to increasing again during the luteal phase) and progesterone levels are increasing (since the hormone is secreted by the newly formed corpus luteum). In this case, the large prostate encasing the prostatic urethra caused urinary obstruction, leading to a decline in renal function reflected by an increase in creatinine level. However, his creatinine level is not severely elevated, and he is still making urine. Therefore removal of the prostate is not indicated, as it might be for some cases of prostate cancer. Dihydrotestosterone is required for the development of the penis and scrotum during embryogenesis.
Specialized intestinal metaplasia on biopsy is associated with an risk of adenocarcinoma (not squamous). Adenocarcinoma surveillance is necessary only if patients are candidates for esophagectomy. High-grade dysplasia: Management is controversial but includes early esophagectomy or intensive endoscopic surveillance every three months until cancer is diagnosed, followed by esophagectomy. In the United States, the prevalence of dyspepsia is 25%, but only 25% of those affected seek care. In patients < 50 years of age with no alarm features, gastric cancer is a rare etiology of dyspepsia, and direct endoscopy is not a costeffective measure. If no alarm features are present: Assess diet and provide education; discontinue suspect medications. Consider a trial of empiric acid suppression; consider testing for and treating H. Water brash (excess salivation), bitter taste, globus sensation (throat fullness), odynophagia, dysphagia, halitosis, and otalgia are also commonly seen. If the patient is unresponsive to therapy or has alarm symptoms (dysphagia, odynophagia, weight loss, anemia, long-standing symptoms, blood in stool, age > 50), proceed as follows: Barium esophagography: Has a limited role, but can identify strictures. Chronic "maintenance" therapy: Indicated in patients with recurrent ulcers who either are H. Avoid metronidazole regimens in areas of known high resistance or in patients who have failed a course of treatment that included metronidazole. Upper endoscopy with biopsy: the standard exam in the presence of alarm symptoms (dysphagia, odynophagia, weight loss, bleeding, anemia). Indicated for correlating symptoms with pH parameters when endoscopy is normal and (1) symptoms are unresponsive to medical therapy, (2) antireflux surgery is being considered, or (3) there are atypical symptoms. Advise patients to eat smaller meals, reduce fat intake, lose weight, avoid recumbency after eating, and avoid certain foods. Generally safe and effective, but now associated with pneumonia, atrophic gastritis (hypergastrinemia), enteric infections (C. Surgical fundoplication (Nissen or Belsey wrap): Often performed laparoscopically. Indicated for patients who cannot tolerate medical therapy or who have persistent regurgitation. Outcome: More than 50% of patients require continued acid suppressive medication, and > 20% develop new symptoms (dysphagia, bloating, dyspepsia). Atypical symptoms (cough, wheezing, chest pain) often occur without typical heartburn symptoms. Posterior laryngitis: Chronic hoarseness from vocal cord ulceration and granulomas. Asthma: Typically has an adult onset; nonatopic and unresponsive to traditional asthma interventions. Most commonly related to diabetes, viral infection, neuropsychiatric disease, or postsurgical complications. Poor glycemic control, postsurgical (postvagotomy or Roux-en-Y), nonulcer dyspepsia, medications (anticholinergics, opiates). Hypothyroidism, scleroderma, muscular dystrophies, paraneoplastic syndrome (small cell lung cancer), amyloidosis. Solid-phase nuclear medicine gastric emptying scan: Following the administration of a radiolabeled meal, normal gastric retention is < 90%, < 60%, and < 10% at 60, 120, and 240 minutes, respectively. Gastroduodenal manometry: Not widely available, but can often distinguish myopathic from neuropathic patterns. Domperidone: A dopamine antagonist that is not approved for use in the United States. Jejunostomy tube: For intractable, severe gastroparesis without small bowel dysmotility. Usually toxin mediated or infectious, mild, and self-limited; cases are managed on an outpatient basis. Exam may reveal tachycardia, orthostasis, skin turgor with dehydration, abdominal pain, and distention. No alarm features (short duration, nonbloody diarrhea, nontoxic exam): Treat with oral rehydration and symptomatic therapy. Antidiarrheals: Loperamide 4 mg initially and then 2 mg after each stool (maximum 8 mg/day).
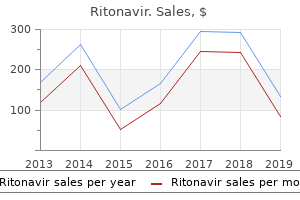
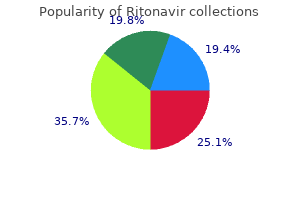
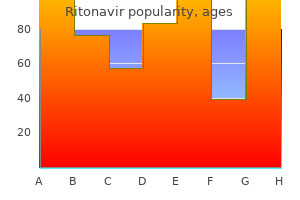
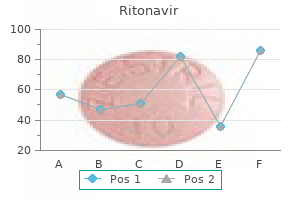
Ipecacuanha (Ipecac). Ritonavir.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96194
As a result, the term "clinical significant" has largely become a useless term, more useful to marketers than to clinicians. The term clinically significant could be made more relevant by recognizing (1) the nature of the benefits (tangible/intangible) and (2) the size of the treatment effect (large/small). Tangible benefits are those treatment outcomes that reflect how a patient feels, functions, or survives. The word "tangible" is defined as "capable of being precisely identified or realized by the mind. Tangible benefits can also be referred to as "clinically relevant" benefits or "clinically meaningful" benefits. Changes in probing attachment level as a result of scaling, changes in enamel mineralization level as a result of fluorides, and changes in the size of a periapical radiolucency as a result of a root canal treatment are examples of changes the mind cannot identify or realize; thus they are intangible treatment benefits. Intangible treatment benefits can often be measured objectively by the clinician or by laboratory methods. A first step in assessing the clinical significance of a treatment is to determine whether the documented treatment benefits are tangible or intangible. This distinction is important because intangible benefits do not necessarily translate into tangible benefits. A medication that lowers elevated blood lipid levels (an intangible benefit) may shorten life span (a tangible patient harm). Factors not often considered in the debate is whether the benefit is tangible and whether the likelihood of obtaining the benefit is large. Results may be statistically significant, yet be of little or no clinical value when small intangible changes such as improvement in pocket depths do not translate into tangible benefits such as tooth retention. A treatment that has been shown to provide tangible benefits has a higher level of clinical significance than a treatment for which only evidence of intangible benefits exists. The finding that an endodontic treatment reliably eliminates tooth pain has a higher level of clinical significance than the finding that chlorhexidine reduces Streptococcus mutans levels. The size of the treatment effect is a comparison of the success rates of the experimental treatment and the control treatment. This comparison of treatments can be a subtraction of the success rates, a division of the success rates, or some other mathematic operation. The size of the treatment effect, regardless of how it is calculated, has long been been recognized as an important part of assessing clinical significance. The larger the likelihood of obtaining an expected benefit of a treatment (relative to a control treatment), the more clinically significant is the treatment. The likelihood of obtaining a treatment benefit (relative to the control) determines to a large extent the methodologic and analytic rigor required to establish treatment effectiveness. For example, no concurrent controlled trials were conducted to assess the effectiveness of general anesthesia. Determining effectiveness for treatments that achieve a dramatic and immediate effect is straightforward, and only essential scientific principles. Reportedly, the words, "Gentleman, this is no humbug," were sufficient to convince an audience that general anesthesia was effective. A large benefit is defined as one that can reliably be identified using epidemiologic methodology. The likelihood of obtaining an treatment benefit is a determinant of clinical significance; the larger the likelihood, the more confident a patient can feel that a treatment will be successful. Although it is possible to have a clear, unequivocal definition of what constitutes a tangible benefit associated with treatment, it is not possible to have similar rigorous definition of what can be considered a large likelihood. ClinicalSignificanceLevel1 Treatments of clinical significance level 1 are the "magical bullets," the "miracle cures" in which the treatment provides a tangible benefit and the size of the treatment effect is large.
It is necessary to remove the tissue distal to the tooth, as well as the flap on the occlusal surface. Incising only the occlusal portion of the flap leaves a deep distal pocket, which invites recurrence of acute pericoronal involvement. A recurrent herpetic episode may be precipitated in individuals with a history of herpesvirus infections by dental treatment, respiratory infections, sunlight exposure, fever, trauma, exposure to chemicals, and emotional stress. Treatment consists of early diagnosis and immediate initiation of antiviral therapy. Until recently, therapy for primary herpetic gingivostomatitis consisted of palliative care. With the development of antiviral therapy, however, the standard of care has changed. Acyclovir reduced symptoms, including fever, from 3 days to 1 day; decreased new extraoral lesions from 5. Furthermore, viral shedding stopped at 1 day for the acyclovir group compared with 5 days for the control group. Overall, oral lesions were present for only 4 days in the acyclovir group but for 10 days in the control group. Although no clear clinical evidence indicates that this regimen will reduce recurrences, research data suggest that a greater number of latent virus copies incorporated into ganglia will increase the severity of recurrences. In summary, if primary herpetic gingivostomatitis is diagnosed within 3 days of onset, acyclovir suspension should be prescribed, 15 mg/kg five times daily for 7 days. If diagnosis occurs after 3 days in an immunocompetent patient, acyclovir therapy may have limited value. All patients, including those presenting more than 3 days after disease onset, may receive palliative care, including removal of plaque and food debris. Periodontal therapy should be postponed until the acute symptoms subside to avoid the possibility of exacerbation (Figure 47-7). Local or systemic application of antibiotics is sometimes advised to prevent opportunistic infection of ulcerations, especially in the immunocompromised patient. If the condition does not resolve with 2 weeks, the patient should be referred to a physician for medical consultation. B, Before treatment, palatal view, showing gingival edema and ruptured vesicle on palate. C, One month after treatment, showing restoration of normal gingival contour and stippling. The symptoms can involve extremely painful gingivae, lymphadenopathy, fever, and general malaise. These conditions clearly demonstrate an exaggerated host response to the periodontal infection. Adding to the enigma of these conditions is that some are confined to the gingiva, whereas others involve periodontal tissues. The affected host mechanisms that permit such a reaction are unknown, but one apparent underlying factor is stress. The stress may result from lack of rest or high anxiety and may be combined with poor oral hygiene and smoking. These mechanisms emphasize the multifactorial nature of these acute conditions and the lack of understanding regarding their pathogenesis. In all cases, however, a bacterial or viral etiology is the basis for stimulating the host response, and mechanical and antimicrobial or antiviral therapies are usually highly effective. Clinicians should be able to diagnose correctly the differences between acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis and acute herpetic gingivostomatitis in the early stages, because each has specific treatment needs. Of particular importance is the possibility of transmission of herpetic lesions to other people and the need to consider immunocompromised conditions as part of the etiologic background for acute gingival disease. The periodontal abscess is an infection located contiguous to the periodontal pocket and may result in destruction of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. The pericoronal abscess is associated with the crown of a partially erupted tooth. Primarily related to incomplete calculus removal, periodontal abscesses have been linked to a number of clinical situations.
Noncartilaginous involvement includes fever, polyarthritis, scleritis, uveitis, middle/inner ear inflammation, hearing loss, and vasculitis. Tx: Treat with corticosteroids, dapsone, colchicine, and immunosuppressants (for refractory disease). Cx: Complications include chronic deformities of the ear (cauliflower ear), nasal septum collapse (saddle nose), laryngotracheal chondritis and stenoses, hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus, and valvular heart disease. Nongonococcal Arthritis Acute-onset, monoarticular joint pain, swelling, warmth, and erythema. Serial arthrocentesis if effusion reaccumulates; surgical drainage if the patient fails medical therapy or the disease involves inaccessible sites. Gonococcal Arthritis (Disseminated Infection) Most common in patients < 40 years of age; women are more frequently affected than men. Tuberculous Arthritis Most common in children, immunosuppressed patients, and the elderly. Lyme Arthritis Early Lyme disease (stages 1 and 2) may have migratory arthralgias and myalgias along with flulike symptoms and an erythema migrans rash. Advanced Lyme disease (stage 3) presents as an acute monoarthritis of the knee; less common is oligo- or polyarthritis. Aerobic exercise: "Start low and go slow" with a focus on adherence to a lifelong program. Complementary therapies: Almost all patients with fibromyalgia use complementary and alternative medicine, at least in part because of distrust of physicians and frustration with the limited efficacy of much traditional care. Acupuncture, hypnotherapy, relaxation techniques (yoga, Tai Chi, and meditation), and osteopathic manipulation appear to have some efficacy. Randomized, controlled clinical trials of dry needling, saline injections, anesthetic injections, botulinum toxin, acupuncture, and sham acupuncture as therapies have not shown significant benefit beyond nonspecific, placebo-related effects. Ultrasound treatment of myofascial "trigger points" is no more effective in reducing pain than sham ultrasound. Sleep disturbances: If good sleep hygiene and sleep medications are ineffective, request a formal sleep study to identify sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome, which are particularly common in fibromyalgia. More than 25% of patients receive some type of disability or other compensation payment. Sx/Exam: Presents with high-spiking fevers, diaphoresis, chills, sore throat, an evanescent salmon-colored rash coincident with fevers, erosive arthritis, serositis, and lymphadenopathy. Dx: Laboratory findings include leukocytosis, anemia, seronegativity, transaminitis, and hyperferritinemia. See the Pulmonary Medicine chapter for nonarticular manifestations of sarcoidosis. Chronic sarcoid arthritis usually involves minimally inflamed joints with synovial swelling/granulomata. Cholesterol Emboli Syndrome Precipitated by invasive arterial procedures in patients with atherosclerotic disease. Features include fever, livedo reticularis, cyanosis/gangrene of the digits, vasculitic/ischemic ulcerations, eosinophilia, renal failure, and other end-organ damage. Diabetic cheiroarthropathy: Diabetic stiff hand syndrome plus prayer sign on exam. Other: Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, Dupuytren contractures, diabetic muscle infarction. Tissue diagnosis, or ultrasound confirming a simple cyst, is required for that purpose. Ask about associations with menstrual cycle, pain (if present, could indicate fibrocystic change), and risk factors for breast cancer. If a dominant mass is present, evaluation should proceed as indicated in Figure 18. Women with benign findings on imaging and biopsy should be followed closely for any progression of a palpable abnormality.
Also, hospitalization rates have decreased by more than half since the start of the programme and a sharp decline in mortality has been observed (73). As Pablos-Mendez stated,"research need not hold back care, we should learn by doing" (74). Because adherence is a complex process, attempts to improve it need to be multifaceted. Factors such as the complexity of the treatment regimen, patient-related factors and the relationship between the patient and the provider of care all affect adherence. Health care providers should work to establish a collaborative treatment relationship with their patients. This can be fostered by involving the patients in selecting regimens with dosing schedules, pill burdens and side-effects that they believe are tolerable and will "fit" into their daily lives. Pharmaceutical companies are currently working diligently to develop once-daily and twice-daily regimens with fewer side-effects and higher tolerability that will better achieve this fit. Providers should openly discuss with patients their readiness to follow treatment, the potential barriers to adherence and possible solutions to problems. While the provider and his or her team can be a source of support, other possible sources (including family, friends and formal support services) should also be discussed with patients. Social and living conditions, fit of regimen to lifestyle, availability and nature of social support and treatment expectations can also affect adherence. No patient should be excluded from consideration for antiretroviral therapy simply because he or she exhibits a behaviour, characteristic or risk factor that might be judged as predictive of nonadherence (62). The health care team should make all possible efforts to ensure that patients adhere to therapies. Poor adherence to a regimen is only one of several possible reasons for its failure. Others that must be assessed include initial resistance to one or more of the therapeutic agents, altered absorption or metabolism, and multi-drug pharmacokinetics that adversely affect levels of therapeutic drugs. It is therefore important to assess patient adherence carefully before changing antiretroviral therapy. Case managers, social workers and other health care providers involved in the care of the patient may assist in this evaluation. Discrepancies in the use of medications: their extent and predictors in an outpatient practice. In: Program and Abstracts of the 8th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. Adherence to oral tamoxifen: a comparison of patient self-report, pill counts, and microelectronic monitoring. Measuring medication adherence: are missed doses reported more accurately then perfect adherence Discordance between physician and adolescent assessments of adherence to treatment: influence of HbA1c level. Correlation between antiretroviral pill burden and durability of virologic response: a systematic overview. Strategies for optimizing adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy: Lessons from research and clinical practice. Reasons for modification and discontinuation of antiretrovirals: results from a single treatment centre. The impact of patient perceptions of body shape changes and metabolic abnormalities on antiretroviral therapy. Sociodemographic and psychological variables influencing adherence to antiretroviral therapy.
Horns of adult goats should be removed under general anesthesia or sedation with postoperative administration of analgesics due to the anatomy and tissues involved and the significant development of horny tissue in older goats, especially bucks. Even though procedures for dehorning ram lambs have been reported, horn growth is not completely eliminated, even after a second procedure approximately 1 mo after the first. Dehorned sites are prone to fly strike, and dehorning does not duplicate the phenotype of genetically polled rams (Dun, 1963). A fine-toothed saw blade may be used to trim and shape the horns so that they are not a danger to the ram, other sheep, or humans. A surgical procedure called "mulesing" was developed to remove wrinkled, wool-bearing skin and reduce fly strike (Primary Industries Standing Committee, 2006; Paull et al. Mulesing has been a common practice in a few countries, but not the United States or other countries where Merino sheep are a minor breed. Even though mulesing seems to reduce the incidence of fly strike, it has been severely criticized because of the apparent discomfort and pain associated with the procedure. A combination of a local anesthetic and a longacting nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug may reduce the discomfort and pain associated with mulesing (Paull et al. In particular, goats are known climbers and benefit from environments that allow for this behavior. Refer to Chapter 4: Environmental Enrichment for information on enrichment of sheep and goat environments. Refer to Chapter 5: Animal Handling and Transport for information on handling and transportation of sheep. However, dairy sheep and goat research and teaching activities are relatively new in North America. Information in Chapter 7: Dairy Cattle of this guide may also be applicable to sheep and goats, although the details are species-specific and management plans should be developed with this in mind. Even though the basic requirements and management of dairy sheep and goats are similar to those for meat animals, machine or hand milking to harvest milk for further processing introduces several conditions that are unique to dairy animals. These include the design, sanitation, and maintenance of milking parlors, milk handling and storage equipment, frequent animal movement and handling, udder care, increased risk of Mulesing Because of their wrinkled skin and heavy fleece, Merino sheep seem to be more susceptible to fly strike, which causes severe discomfort, pain, and often death. Before research and teaching programs with dairy sheep and goats are initiated, each element of dairy production should be evaluated so that the health and well-being of the sheep and goats are ensured. Zoonotic Diseases Zoonotic diseases, the risk of acquiring zoonotic diseases, how to reduce the likelihood of acquiring a zoonotic disease, and the signs, symptoms, and treatment of common zoonotic diseases should be known by people who work with sheep and goats in research and teaching. Predator Control In certain geographic locations and seasons, sheep and goats need to be protected from predators such as dogs, coyotes, bears, wolves, mountain lions, and some species of birds. Contact between unsupervised domestic dogs and sheep and goats should not be allowed. Nonlethal means of predator control such as guard animals, lights, noise, and fencing are preferable but may be inadequate or infeasible. Lethal means of control are appropriate when necessary to reduce injury and loss of sheep and goats. Laboratory Environments Certain laboratory settings do not allow for or utilize any range or pasture. These environments may include traditional outdoor feedlots, indoor/outdoor feedlots, or entirely indoor housing with natural or manufactured surfaces with several bedding possibilities, such as straw, wood shavings, recycled paper products, sand, dirt, and compost. When housed indoors, goats have been noted to select different flooring surfaces for different behaviors; for instance, hard surfaces for lying and wood shavings for defecation and urination (Sutherland et al. Sheep and goats that are used for intensive procedures requiring prolonged restraint, frequent sampling, complete collection of feces and urine, or other procedures may experience less stress if they are pretrained and adapted to these environments (Bowers et al. Sheep and goats may be kept in pens, metabolism stalls, stanchions, respiration chambers, or environmental chambers. If possible, it is recommended that sheep and goats not be housed alone and that they be able to maintain visual contact with other animals (Matteri et al. Only under scientifically justified and approved protocols that dictate isolation such as metabolic, respiratory, or environmental chambers should such housing be considered for sheep and goats. A common and beneficial practice is to shear sheep and fiber-producing goats before they are moved into intensive laboratory conditions. This improves animal and facility hygiene, often prevents reduced feed consumption, and reduces the size of the animals and thus their requirement for usable space. If sheep and goats are managed under intensive laboratory conditions for extended periods, it may be necessary to increase the frequency of hoof trimming. Sheep and goats housed in intensive laboratory environments should be kept clean and dry, and excreta should be removed on an appropriate schedule.
References: